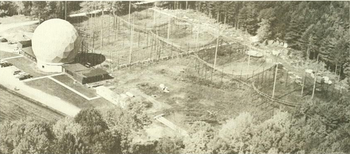
 FCRAO Radome-enclosed 14-m Telescope, on the Prescott Peninsula in the Quabbin Reservoir. Circa 1977. | |
| Organization | |
|---|---|
| Location | Massachusetts |
| Coordinates | 42°23′31″N72°20′39″W / 42.391925°N 72.344097°W |
| Altitude | 306 m (1,004 ft) |
| Established | 1969 |
| Closed | 2011 |
| Website | www |
 | |
The Five College Radio Astronomical Observatory (FCRAO) was a radio astronomy observatory located on a peninsula in the Quabbin Reservoir. It was sited in the town of New Salem, Massachusetts on land that was originally part of Prescott, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1969 by the Five College Astronomy Department (University of Massachusetts Amherst (UMass), Amherst College, Hampshire College, Mount Holyoke College and Smith College). [1] From its inception, the observatory has emphasized research, the development of technology and the training of students—both graduate and undergraduate.
Contents
The initial FCRAO telescope was a customized low-frequency antenna to search for pulsars in the galaxy. The development of instrumentation within the FCRAO labs contributed to the discovery of the binary pulsar system PSR B1913+16 by Joseph Taylor and Russell Hulse, for which they received the 1993 Nobel Prize in Physics. It was replaced by a 14-meter radome-enclosed millimeter-wave telescope in 1976. [2]





