| Fontanelle | |
|---|---|
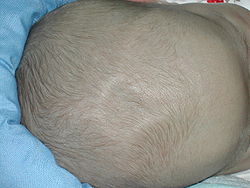
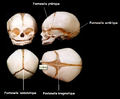
 The skull at birth, showing the anterior and posterior fontanelles | |
 The skull at birth, showing the lateral fontanelles | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fonticuli cranii |
| MeSH | D055762 |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.027 |
| TA2 | 431 |
| FMA | 75437 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A fontanelle (or fontanel) (colloquially, soft spot) is an anatomical feature of the infant human skull comprising soft membranous gaps (sutures) between the cranial bones that make up the calvaria of a fetus or an infant. [1] Fontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. [2] Premature complete ossification of the sutures is called craniosynostosis.
Contents
- Structure
- Closure
- Clinical significance
- Disorders
- Bulging
- Sunken
- Enlarged
- Third
- Other animals
- Primates
- Dogs
- Additional images
- References
After infancy, the anterior fontanelle is known as the bregma.