| Lambdoid suture | |
|---|---|
 Lambdoid suture, posterior view | |
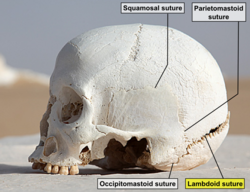 Lambdoid suture (labeled at bottom right) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Skull |
| Nerve | Supraorbital nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sutura lambdoidea |
| TA98 | A03.1.02.004 |
| TA2 | 1577 |
| FMA | 52933 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The lambdoid suture, or lambdoidal suture, is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture.





