The scalp is the area of the head where head hair grows. It is made up of skin, layers of connective and fibrous tissues, and the membrane of the skull. Anatomically, the scalp is part of the epicranium, a collection of structures covering the cranium. The scalp is bordered by the face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. The scientific study of hair and scalp is called trichology.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.

The ophthalmic artery (OA) is an artery of the head. It is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply all the structures in the orbit around the eye, as well as some structures in the nose, face, and meninges. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery or its branches can produce sight-threatening conditions.

The corrugator supercilii muscle is a small, narrow, pyramidal muscle of the face. It arises from the medial end of the superciliary arch; it inserts into the deep surface of the skin of the eyebrow.

The orbicularis oculi is a muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. It arises from the nasal part of the frontal bone, from the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove, and from the anterior surface and borders of a short fibrous band, the medial palpebral ligament.

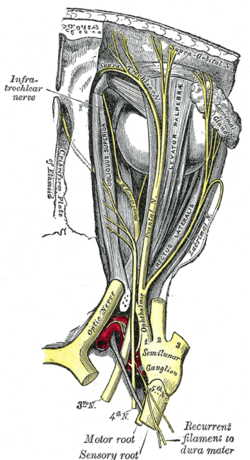
The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head.

The supraorbital foramen, is a bony elongated opening located above the orbit and under the forehead. It is part of the frontal bone of the skull. The supraorbital foramen lies directly under the eyebrow. In some people this foramen is incomplete and is then known as the supraorbital notch.
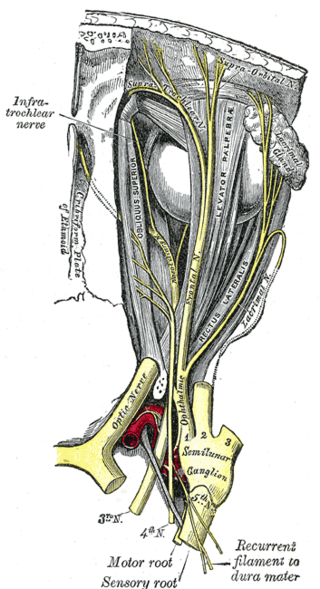
The frontal nerve is the largest branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It supplies sensation to the skin of the forehead, the mucosa of the frontal sinus, and the skin of the upper eyelid. It may be affected by schwannoma.

The lacrimal nerve is the smallest of the three main branches of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)).

The supratrochlear nerve is a branch of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) from the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the forehead and the upper eyelid.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.

The infratrochlear nerve is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)) in the orbit. It exits the orbit inferior to the trochlea of superior oblique. It provides sensory innervation to structures of the orbit and skin of adjacent structures.

The supraorbital vein is a vein of the forehead. It communicates with the frontal branch of the superficial temporal vein. It passes through the supraorbital notch, and merges with the angular vein to form the superior ophthalmic vein. The supraorbital vein helps to drain blood from the forehead, eyebrow, and upper eyelid.

The angular vein is a vein of the face. It is the upper part of the facial vein, above its junction with the superior labial vein. It is formed by the junction of the supratrochlear vein and supraorbital vein, and joins with the superior labial vein. It drains the medial canthus, and parts of the nose and the upper lip. It can be a route of spread of infection from the danger triangle of the face to the cavernous sinus.
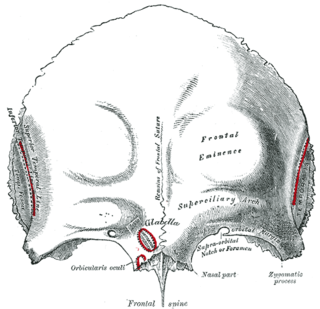
The squamous part of the frontal bone is the superior portion when viewed in standard anatomical orientation. There are two surfaces of the squamous part of the frontal bone: the external surface, and the internal surface.

The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The infraorbital nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa. It passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. It travels through the orbit, then enters and traverses the infraorbital canal, exiting the canal at the infraorbital foramen to reach the face. It provides sensory innervation to the skin and mucous membranes around the middle of the face.

The supraorbital artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It passes anteriorly within the orbit to exit the orbit through the supraorbital foramen or notch alongside the supraorbital nerve, splitting into two terminal branches which go on to form anastomoses with arteries of the head.

The supratrochlear artery is one of the terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It arises within the orbit. It exits the orbit alongside the supratrochlear nerve. It contributes arterial supply to the skin, muscles and pericranium of the forehead.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy: