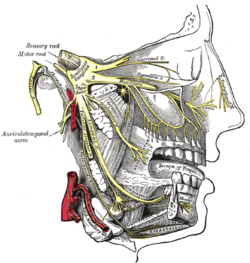
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.

In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication.

The buccinator is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.

The inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) (also the inferior dental nerve) is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) (which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). The nerve provides sensory innervation to the lower/mandibular teeth and their corresponding gingiva as well as a small area of the face (via its mental nerve).

The pterygopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck,.

The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, located in the maxilla. It drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the semilunar hiatus. It is located to the side of the nasal cavity, and below the orbit.

The greater petrosal nerve is a nerve of the head mainly containing pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres which ultimately synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion. It branches from the facial nerve and is derived from the parasympathetic part of the nervus intermedius component of CN VII, with its cell bodies located in the superior salivary nucleus. In the connective tissue substance of the foramen lacerum, the greater petrosal nerve unites with the (sympathetic) deep petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal which proceeds to the pterygopalatine ganglion.

In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face, and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.

The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head.

In human anatomy, the pterygopalatine fossa is a fossa in the skull. A human skull contains two pterygopalatine fossae—one on the left side, and another on the right side. Each fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep to the infratemporal fossa and posterior to the maxilla on each side of the skull, located between the pterygoid process and the maxillary tuberosity close to the apex of the orbit. It is the indented area medial to the pterygomaxillary fissure leading into the sphenopalatine foramen. It communicates with the nasal and oral cavities, infratemporal fossa, orbit, pharynx, and middle cranial fossa through eight foramina.

The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerve are for touch, pain and temperature (general sensation), and the ones from the facial nerve are for taste (special sensation).
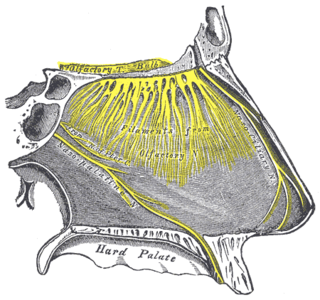
The nasopalatine nerve (also long sphenopalatine nerve) is a nerve of the head. It is a sensory branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) that passes through the pterygopalatine ganglion (without synapsing) and then through the sphenopalatine foramen to enter the nasal cavity, and finally out of the nasal cavity through the incisive canal and then the incisive fossa to enter the hard palate. It provides sensory innervation to the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum, and gingiva just posterior to the upper incisor teeth.

The zygomaticotemporal nerve (zygomaticotemporal branch, temporal branch) is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the head. It is a branch of the zygomatic nerve (itself a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2)). It arises in the orbit and exits the orbit through the zygomaticotemporal foramen in the zygomatic bone to enter the temporal fossa. It is distributed to the skin of the side of the forehead. It also contains a parasympathetic secretomotor component for the lacrimal gland which it confers to the lacrimal nerve (which then delivers it to the gland).

The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face.

The posterior superior alveolar artery is a branch of the maxillary artery. It is one of two or three superior alveolar arteries. It provides arterial suply to the molar and premolar teeth, maxillary sinus and adjacent bone, and the gingiva.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The anterior superior alveolar nerve (or anterior superior dental nerve) is a branch of the infraorbital nerve (itself a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2)). It passes through the canalis sinuosus to reach and innervate upper front teeth. Through its nasal branch, it also innervates parts of the nasal cavity.

The infraorbital nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa. It passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. It travels through the orbit, then enters and traverses the infraorbital canal, exiting the canal at the infraorbital foramen to reach the face. It provides sensory innervation to the skin and mucous membranes around the middle of the face.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The superior dental plexus is a nerve plexus that innervates the upper/maxillary teeth and as adjacent structures. It is formed by the anterior superior alveolar nerve (ASAN), middle superior alveolar nerve (MSAN), and the posterior superior alveolar nerve (PSAN). It issues dental branches and gingival branches.