A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia which contain the cell bodies of postganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons respectively.

A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers in the peripheral nervous system.
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison.

The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of the nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins and mechanical injuries.
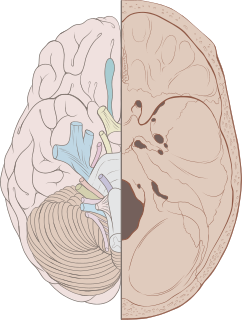
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain, of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing.

The vagus nerve, historically cited as the pneumogastric nerve, is the tenth cranial nerve or CN X, and interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It actually comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively in the singular. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus.

Bell's palsy is a type of facial paralysis that results in a temporary inability to control the facial muscles on the affected side of the face. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe. They may include muscle twitching, weakness, or total loss of the ability to move one or, in rare cases, both sides of the face. Other symptoms include drooping of the eyelid, a change in taste, and pain around the ear. Typically symptoms come on over 48 hours. Bell's palsy can trigger an increased sensitivity to sound known as hyperacusis.

In human anatomy, the arm is the part of the upper limb between the glenohumeral joint and the elbow joint. In common usage, the arm extends through the hand. The arm can be divided into the upper arm, which extends from the shoulder to the elbow, the forearm which extends from the elbow to the hand, and the hand. Anatomically the shoulder girdle with bones and corresponding muscles is by definition a part of the arm. The Latin term brachium may refer to either the arm as a whole or to the upper arm on its own.

Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the collection of symptoms and signs associated with median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel. Most CTS is related to idiopathic compression of the median nerve as it travels through the wrist at the carpal tunnel (IMNCT). Idiopathic means that there is no other disease process contributing to pressure on the nerve. Most CTS is due to IMNCT. As with most structural issues, it occurs in both hands, and the strongest risk factor is genetics.
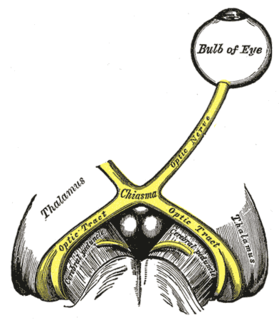
The optic nerve, also known as cranial nerve II, or simply as CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.

The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve, or simply CN VII. It emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerves typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.

The brainstem is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem.

The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.
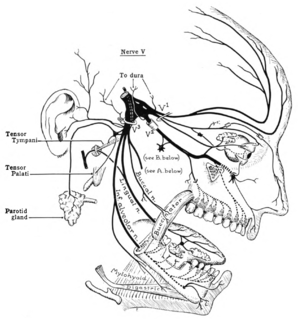
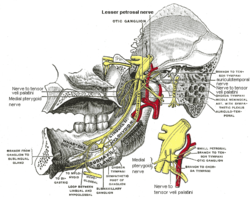
The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve, or simply CN V) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name ("trigeminal" = tri-, or three, and - geminus, or twin: thrice-twinned) derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it.

The accessory nerve is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is considered as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves, or simply cranial nerve XI, as part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain. The sternocleidomastoid muscle tilts and rotates the head, while the trapezius muscle, connecting to the scapula, acts to shrug the shoulder.

The hypoglossal nerve is the twelfth cranial nerve, or CN XII, and innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue, except for the palatoglossus which is innervated by the vagus nerve. It is a nerve with a solely motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, passes through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue.

In human anatomy, the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and produces saliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.