
The coronal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint that separates the two parietal bones from the frontal bone of the skull.
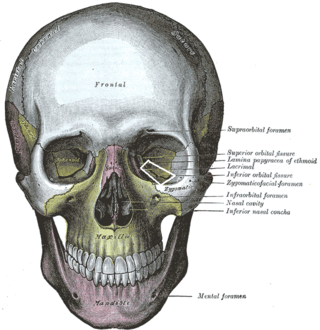
The inferior orbital fissure is a gap between the greater wing of sphenoid bone, and the maxilla. It connects the orbit (anteriorly) with the infratemporal fossa and pterygopalatine fossa (posteriorly).
The frontoethmoidal suture is the suture between the ethmoid bone and the frontal bone.

The squamosal suture, or squamous suture, arches backward from the pterion and connects the temporal squama with the lower border of the parietal bone: this suture is continuous behind with the short, nearly horizontal parietomastoid suture, which unites the mastoid process of the temporal with the region of the mastoid angle of the parietal bone. The term parietotemporal suture may refer to both of these sutures or exclusively to the parietomastoid suture and its use is, therefore, best avoided.

The sphenozygomatic suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the zygomatic bone.

The sphenofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone.

The zygomaticofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the zygomatic bone and the frontal bone. The suture can be palpated just lateral to the eye.

The zygomaticotemporal suture is the cranial suture between the zygomatic bone and the temporal bone. This is part of the zygomatic arch. Movement at the suture decreases with development during aging. It has a complex internal structure.

The occipitomastoid suture or occipitotemporal suture is the cranial suture between the occipital bone and the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.

Along the posterior part of the lateral margin of the carotid groove of the sphenoid bone, in the angle between the body and great wing, is a ridge of bone, called the lingula.

The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery to the dura mater.

The dorsum sellae is part of the sphenoid bone in the skull. Together with the basilar part of the occipital bone it forms the clivus.
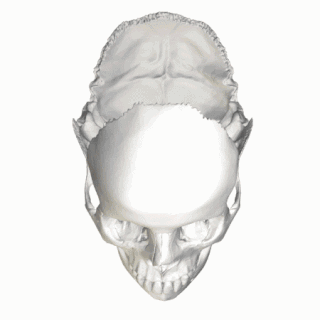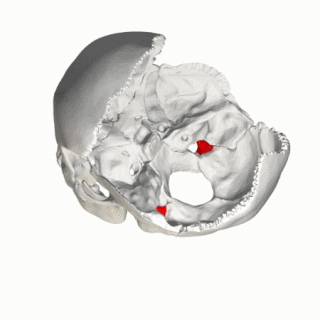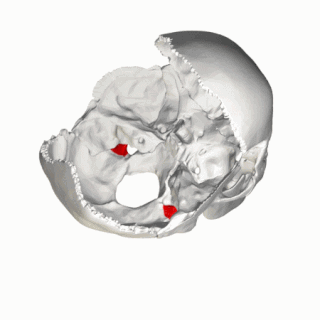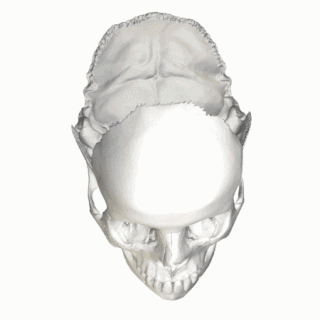
The jugular process is a quadrilateral or triangular bony plate projecting lateralward from the posterior half of the occipital condyle; it is a part of the lateral part of the occipital bone.
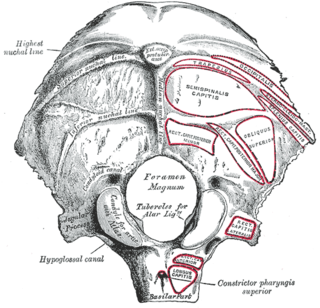
The jugular tubercle is a rounded prominence/oval elevation upon the superior surface of the occipital condyle at the junction of the basilar part and lateral part of the occipital bone, just medial to the jugular foramen on either side of the foramen magnum.

The tuberculum sellae is a slight median elevation upon the superior aspect of the body of sphenoid bone at the anterior boundary of the sella turcica and posterior boundary of the chiasmatic groove. A middle clinoid process flanks the tuberculum sellae on either side.

The carotid groove is an anatomical groove in the sphenoid bone located above the attachment of each great wing of the sphenoid bone. The groove is curved like the italic letter f, and lodges the internal carotid artery and the cavernous sinus.

The inner surface of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone presents a deep, curved groove, the sigmoid sulcus, which lodges part of the transverse sinus; in it may be seen the opening of the mastoid foramen.

Along the internal surface of the occipital bone, at the point of intersection of the four divisions of the cruciform eminence, is the internal occipital protuberance. Running transversely on either side is a groove for the transverse sinus.

The anterior nasal spine, or anterior nasal spine of maxilla, is a bony projection in the skull that serves as a cephalometric landmark. The anterior nasal spine is the projection formed by the fusion of the two maxillary bones at the intermaxillary suture. It is placed at the level of the nostrils, at the uppermost part of the philtrum. It rarely fractures.

The symphysis of the external surface of the mandible divides below and encloses a triangular eminence, the mental protuberance, the base of which is depressed in the center but raised on either side to form the mental tubercle. The size and shape of the bones making up this structure are responsible for the size and shape of a person's chin. Synonyms of mental protuberance include mental process and protuberantia mentalis.Mental in this sense derives from Latin mentum (chin), not mens (mind), source of the more common meaning of mental.



















