
The skull is a bone structure that forms the head in vertebrates. It supports the structures of the face and provides a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton.

The occipital bone is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput. It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord.

In anatomy, the zygomatic arch, or cheek bone, is a part of the skull formed by the zygomatic process of the temporal bone and the temporal process of the zygomatic bone, the two being united by an oblique suture ; the tendon of the temporal muscle passes medial to the arch, to gain insertion into the coronoid process of the mandible (jawbone).
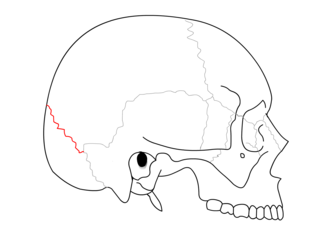
The lambdoid suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture.

The coronal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint that separates the two parietal bones from the frontal bone of the skull.

The asterion is a meeting point between three sutures between bones of the skull. It is an important surgical landmark.

The frontoethmoidal suture is the suture between the ethmoid bone and the frontal bone.

The sphenozygomatic suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the zygomatic bone.

The sphenoparietal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the parietal bone. It is one of the sutures that comprises the pterion.

The sphenofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone.

The sphenopetrosal fissure is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the petrous portion of the temporal bone.

The zygomaticofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the zygomatic bone and the frontal bone. The suture can be palpated just lateral to the eye.

The zygomaticotemporal suture is the cranial suture between the zygomatic bone and the temporal bone. This is part of the zygomatic arch. Movement at the suture decreases with development during aging. It has a complex internal structure.

The occipitomastoid suture or occipitotemporal suture is the cranial suture between the occipital bone and the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.
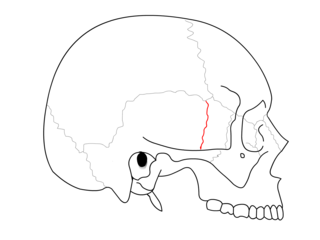
The sphenosquamosal suture is a cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the squama of the temporal bone.

The pterion is the region where the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones join. It is located on the side of the skull, just behind the temple.
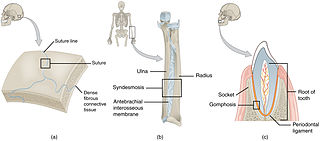
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are called sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthroses.
In arthropod and vertebrate anatomy, the vertex is the highest point of the head.

In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skullcap. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton.

Metopism is the condition of having a persistent metopic suture, or persistence of the frontal metopic suture in the adult human skull. The premature fusion of cranial sutures named craniosynostosis, it is “simple” when only one cranial suture is involved and “compound” when two or more cranial sutures are involved. Metopism is the opposite of craniosynostosis. The main factor of the metopic suture is to increase the volume of the anterior cranial fossa. The frontal bone includes the forehead, and the roofs of the orbits of the eyes. The frontal bone has vertical portion (squama) and horizontal portion. Some adults have a metopic or frontal suture in the vertical portion. In uterine period in right and left half of frontal region of the fetus there is a membrane tissue. On each half a primary ossification center appears about the end of the second month of the fetus. Primary ossification center extends to form the corresponding half of the vertical part (squama) and horizontal part of the frontal bone.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.


















