
Rhamnus is a genus of about 110 accepted species of shrubs or small trees, commonly known as buckthorns, in the family Rhamnaceae. Its species range from 1 to 10 m tall and are native mainly in east Asia and North America, but found throughout the temperate and subtropical Northern Hemisphere, and also more locally in the subtropical Southern Hemisphere in parts of Africa and South America. One species, the common buckthorn, is able to flourish as an invasive plant in parts of Canada and the U.S., where it has become naturalized.

The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western 'sounds' of North America, Central America, South America and West Antarctica.
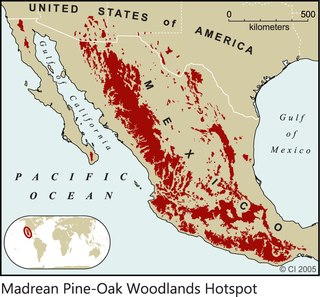
The Madrean pine–oak woodlands are subtropical woodlands found in the mountains of Mexico and the southwestern United States. They are a biogeographic region of the tropical and subtropical coniferous forests and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biomes, located in North America.

The Sierra Madre Occidental pine–oak forests are a Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of the Sierra Madre Occidental range from the southwest USA region to the western part of Mexico. They are home to a large number of endemic plants and important habitat for wildlife.

Alnus oblongifolia is a large alder growing up to 72 feet (22 m), from the southwestern United States and northern Sonora, Mexico. It grows across Arizona into western New Mexico mountain ranges. In central Arizona its range extends across the transition zone to the White Mountains region of eastern Arizona–western New Mexico border.

Fraxinus velutina, the velvet ash, Arizona ash or Modesto ash, is a species of Fraxinus native to southwestern North America, in the United States from southern California east to Texas, and in Mexico from northern Baja California east to Coahuila and Nuevo León.
The narrow-skulled pocket mouse is a species of rodent in the family Heteromyidae. It is endemic to western Mexico, living west of the Sierra Madre Occidental crest.
The Sierra San Luis range is a mountain range in northwest Chihuahua, northeast Sonora, Mexico at the northern region of the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera. The region contains sky island mountain ranges, called the Madrean Sky Islands, some separated from the Sierra Madre Occidental proper, and occurring in the northeastern Sonoran Desert, and extreme west-northwestern Chihuahuan Desert. Many of the ranges occur in southeast Arizona.
The Sierra San Antonio is a mountain range in southernmost Arizona state (U.S.) and northern Sonora state (México).

Yucca × schottii is a plant species in the genus Yucca, native to southern Arizona, southwestern New Mexico, and the northern parts of Sonora and Chihuahua. The common names are Schott's yucca, hoary yucca, and mountain yucca. The "×" in the name indicates that this is a nothospecies, regarded as being a natural hybrid between two other species. In this case, Yucca × schottii is believed to have originated as a hybrid between Y. baccata and Y. madrensis. Yucca × schottii is firmly established and does reproduce freely in the wild.

Arbutus arizonica, commonly known as Arizona madrone, is a tree species in the heath family that is native to the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. Its range extends along the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera from the Madrean Sky Islands of southeastern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico south as far as Jalisco. It has been found in Sonora, Chihuahua, Durango, and Sinaloa, with one isolated population in Tamaulipas.
Salix taxifolia, the yewleaf or yew-leaf willow, is a species of willow native to all of southern Mexico, also Pacific Coast regions, north to Sinaloa, and in the south Pacific Coast of Mexico into central Guatemala. Scattered populations are also reported from northern Mexico and from the US states of Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona.

Salix bonplandiana, , is a perennial species of willow tree native to southern and southwest Mexico and extending into central Guatemala; in western Mexico it is a tree of the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera, but also occurring in other small locales, for example Baja California Sur, northern Sonora, San Luis Potosi, etc. A core disjunct area occurs in central and southeast Arizona, in advantageous locales, especially associated with higher elevations and water.

Purshia mexicana is a species of perennial flowering small tree in the rose family known by the common name Mexican cliffrose. It is native to western-northern Mexico, the region of the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera.
Eysenhardtia orthocarpa is a species of small flowering tree, in the family Fabaceae. Its range is at the northern region of the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera of eastern Sonora; it is also in central Sonora, with the species ranging into southeast Arizona and the extreme southwest, bootheel region of New Mexico, the entire sky island region at the northern cordillera called Madrean Sky Islands.

Platanus wrightii, the Arizona sycamore, is a sycamore tree native to Arizona and New Mexico with its range extending south into the Mexican states of Sonora, Chihuahua, and Sinaloa.
The Sierra La Esmeralda range, are a mountain range in northern Sonora, Mexico at the northern region of the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera. The region contains sky island mountain ranges, called the Madrean Sky Islands, some separated from the Sierra Madre Occidental proper, and occurring in the northeastern Sonoran Desert, and extreme west-northwestern Chihuahuan Desert. Many of the ranges occur in southeast Arizona.

The Pajarito Mountains is a small mountain range of western Santa Cruz County, Arizona, United States, that extend south into Sonora, Mexico. The range is adjacent the Atascosa Mountains at its north, with both ranges in the center of a north-south sequence of ranges called the Tumacacori Highlands. The Highlands have the Tumacacori Mountains at the north, and south of the U.S.-Mexico border, the Sierra La Esmeralda range. The Tumacacori Highlands are part of a regional conservancy study of "travel corridors" for cats, called Cuatro Gatos, Four Cats, for mountain lions, ocelot, bobcat, and jaguar.
Magnolia tarahumara is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is endemic to Mexico, where it occurs in scattered locations in the Sierra Madre Occidental of southeastern Sonora, southwestern Chihuahua, Sinaloa, and northwestern Durango.
Quercus jonesii, commonly known as palo manzano, is a species of oak tree native to Mexico.














