
The Atlantic tripletail, also known as the black grunt, black perch, buoy fish, buoyfish, brown triple tail, brown tripletail, conchy leaf, dusky triple-tail, dusky tripletail, flasher, sleepfish, triple tail, triple-tail, tripletail, or tripple tail is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Lobotidae. This fish is found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world except for the eastern Pacific Ocean.

The black swallower is a species of deep sea fish in the family Chiasmodontidae. It is known for its ability to swallow fish larger than itself.

The European conger is a species of conger of the family Congridae. It is the heaviest eel in the world and native to the northeast Atlantic, including the Mediterranean Sea.

Cephalopholis fulva, the coney or the butterfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is in the family Serranidae which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in the western Atlantic. It is associated with reefs and is a quarry species for commercial and recreational fisheries. It can be found in the aquarium trade.

Synodus intermedius, the common sand diver, is a species of fish in the lizardfish family, the Synodontidae, a basal ray-finned fish in the class Actinopterygii. Sand divers inhabit subtropical marine ecosystems, (37-17°N), including sandy- bottom areas on continental shelves, coral reefs, estuaries, bays, and reef structures. They are demersal or benthic fish, which means they live on or close to the sea bed. Distribution ranges from the northern Gulf of Mexico south to the Guianas, and western Atlantic north to North Carolina and Bermuda. They are a common lizardfish in the West Indies. They grow to about 40 cm (16 in) total length, and weigh around 1 kg (2.2 lb).

The smallscale lizardfish(Saurida caribbaea) is a species of lizardfish that lives mainly in the Western Atlantic.

Cynoponticus is a genus of marine ray-fiined fishes belonging to the family Muraenesocidae, the pike congers. The fishes in this genus are found in the Eastern and Western Atlantic Oceans and the Eastern Pacific Ocean, with a single parapatric species in each region.
Gobioclinus gobio is a strictly marine ray finned fish, also called Gobioclinus gobio. Its common name is the palehead blenny, and is sometimes referred to as the goggle-eye blenny. It can be identified by its greenish top, red belly, and multicolored banding. L. gobio is a benthic organism with a wide range, taking up residence in a number of coastal environments from Florida to Brazil. This means the fish can live in equatorial, subtropical, and tropical climatic zones. It is native to coastal areas of the Caribbean. Its diet consists mainly of different molluscs and echinoderms.
Hoplunnis is a genus of eels in the duckbill eel family Nettastomatidae. It currently contains the following species:

The blackfin snapper, also known as the blackspot snapper, blackfin red snapper, gun-mouth backfin, gun-mouth snapper, redfish and wrenchman is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a snapper belonging to the family Lutjanidae. It is native to the western Atlantic Ocean. It is a commercially important species, though it has been reported to carry the ciguatera toxin.

The yellow conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by George Brown Goode and Tarleton Hoffman Bean in 1896. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Gulf of Mexico and the mouth of the Amazon River, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 26 to 183 meters, and inhabits soft sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 150 centimeters (59 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 30 centimeters (12 in).
The whiptail conger, also known as the conger eel in Cuba, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Isaac Ginsburg in 1951, originally under the genus Congrina. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States in the northern Gulf of Mexico and northern South America. It is known to dwell at a depth of 203 meters (666 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 61 centimeters (24 in).
The yellow pike conger is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Muraenesocidae, the pike congers. This fish is found in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.
The threadtail conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Isaac Ginsburg in 1954. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Guinea, the Gulf of Mexico and Suriname. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 44 to 384 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 38 centimeters (15 in).
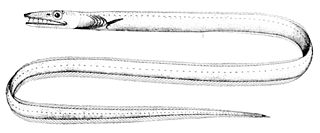
The blacktail pike-conger is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by George Brown Goode and Tarleton Hoffman Bean in 1896. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 203 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 36.6 centimeters.
The spotted pike-conger, also known as the conger eel in Cuba, is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Isaac Ginsburg in 1951. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Straits of Florida, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 130 to 420 meters, and inhabits benthic sediments of mud. Males can reach a maximum total length of 46 centimeters (18 in).

Dysommina rugosa is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Isaac Ginsburg in 1951. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western Atlantic and eastern central Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 260–775 metres, and is found off the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 37 centimetres.

The bigtooth cardinalfish or longtooth cardinalfish is a species of marine fish in the family Apogonidae and the only member of its genus. The bigtooth cardinalfish lives in the west-central Atlantic, off southern Florida, United States, and from the Bahamas to Venezuela, and as far south as Suriname. This species also is found in the east-central Atlantic and the Gulf of Guinea, and has been reported as far as Cape Verde. It is a pale orangeish colour.
Astronesthes richardsoni, or Richardson's snaggletooth, is a species of small, deep sea fish in the family Stomiidae. It occurs in the tropical western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. First described by the Cuban zoologist Felipe Poey in 1852, it was named Chauliodus richardsoni in honour of the Scottish explorer and naturalist John Richardson. It was later transferred to the genus Astronesthes.

Astronesthes niger, commonly known as snaggletooth, is a species of small, deep sea fish in the family Stomiidae. It occurs in the tropical and subtropical Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, as well as the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean, at depths to 1,000 m (3,300 ft).













