
The Bromeliaceae are a family of monocot flowering plants of about 80 genera and 3700 known species, native mainly to the tropical Americas, with several species found in the American subtropics and one in tropical west Africa, Pitcairnia feliciana.

Prunus is a genus of trees and shrubs, which includes the fruits plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots, and almonds.

Gibbons are apes in the family Hylobatidae. The family historically contained one genus, but now is split into four extant genera and 20 species. Gibbons live in subtropical and tropical rainforests from eastern Bangladesh to Northeast India to southern China and Indonesia.

Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophytasensu stricto. Bryophyta may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically 0.2–10 cm (0.1–3.9 in) tall, though some species are much larger. Dawsonia, the tallest moss in the world, can grow to 50 cm (20 in) in height. There are approximately 12,000 species.

A truffle is the fruiting body of a subterranean ascomycete fungus, predominantly one of the many species of the genus Tuber. In addition to Tuber, over one hundred other genera of fungi are classified as truffles including Geopora, Peziza, Choiromyces, and Leucangium. These genera belong to the class Pezizomycetes and the Pezizales order. Several truffle-like basidiomycetes are excluded from Pezizales, including Rhizopogon and Glomus. Truffles are ectomycorrhizal fungi, so they are usually found in close association with tree roots. Spore dispersal is accomplished through fungivores, animals that eat fungi. These fungi have significant ecological roles in nutrient cycling and drought tolerance.

The Pinaceae, or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as cedars, firs, hemlocks, piñons, larches, pines and spruces. The family is included in the order Pinales, formerly known as Coniferales. Pinaceae are supported as monophyletic by their protein-type sieve cell plastids, pattern of proembryogeny, and lack of bioflavonoids. They are the largest extant conifer family in species diversity, with between 220 and 250 species in 11 genera, and the second-largest in geographical range, found in most of the Northern Hemisphere, with the majority of the species in temperate climates, but ranging from subarctic to tropical. The family often forms the dominant component of boreal, coastal, and montane forests. One species, Pinus merkusii, grows just south of the equator in Southeast Asia. Major centres of diversity are found in the mountains of southwest China, Mexico, central Japan, and California.

A living fossil is an extant taxon that cosmetically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of origin of the extant clade. Living fossils commonly are of species-poor lineages, but they need not be. While the body plan of a living fossil remains superficially similar, it is never the same species as the remote relatives it resembles, because genetic drift would inevitably change its chromosomal structure.

Atta is a genus of New World ants of the subfamily Myrmicinae. It contains at least 17 known species.

Cupressaceae is a conifer family, the cypress, with worldwide distribution. The family includes 27–30 genera, which include the junipers and redwoods, with about 130–140 species in total. They are monoecious, subdioecious or (rarely) dioecious trees and shrubs up to 116 m (381 ft) tall. The bark of mature trees is commonly orange- to red-brown and of stringy texture, often flaking or peeling in vertical strips, but smooth, scaly or hard and square-cracked in some species.
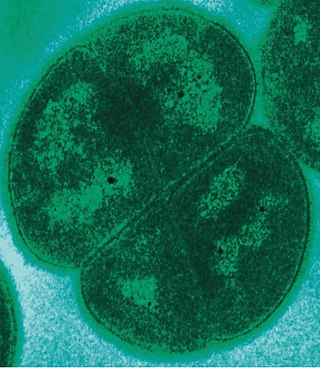
Deinococcota is a phylum of bacteria with a single class, Deinococci, that are highly resistant to environmental hazards, also known as extremophiles. These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them gram-positive stains, but they include a second membrane and so are closer in structure to those of gram-negative bacteria.

Moringa is the sole genus in the plant family Moringaceae. It contains 13 species, which occur in tropical and subtropical regions of Africa and Asia and that range in size from tiny herbs to massive trees. Moringa species grow quickly in many types of environments.
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript.

Phyllanthaceae is a family of flowering plants in the eudicot order Malpighiales. It is most closely related to the family Picrodendraceae.

A polydnavirus (PDV) or more recently, polydnaviriform is a member of the family Polydnaviridae of insect viruses. There are two genera in the family: bracoform and Ichnoviriform. Polydnaviruses form a symbiotic relationship with parasitoid wasps. Ichnoviriforms (IV) occur in Ichneumonid wasps and Bracoviriforms (BV) in Braconid wasps. The larvae of wasps in both of those groups are themselves parasitic on Lepidoptera, and the polydnaviruses are important in circumventing the immune response of their parasitized hosts. Little or no sequence homology exists between BV and IV, suggesting that the two genera have been evolving independently for a long time.

Chloranthaceae is a family of flowering plants (angiosperms), the only family in the order Chloranthales. It is not closely related to any other family of flowering plants, and is among the early-diverging lineages in the angiosperms. They are woody or weakly woody plants occurring in Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Madagascar, Central and South America, and the West Indies. The family consists of four extant genera, totalling about 77 known species according to Christenhusz and Byng in 2016. Some species are used in traditional medicine. The type genus is Chloranthus. The fossil record of the family, mostly represented by pollen such as Clavatipollenites, extends back to the dawn of the history of flowering plants in the Early Cretaceous, and has been found on all continents.

The painted tree-rat is a species of spiny rat from Brazil, restricted to north-eastern Bahia in eastern Brazil. It is the only species in the genus Callistomys.

A spermatophyte, also known as phanerogam or phaenogam, is any plant that produces seeds, hence the alternative name seed plant. Spermatophytes are a subset of the embryophytes or land plants. They include most familiar types of plants, including all flowering plants and gymnosperms, but exclude some other types of plants such as ferns, mosses, and algae.

Pecan scab is the most economically significant disease of pecan trees in the southeastern United States. Venturia effusa is a fungal plant pathogen that causes pecan scab. The fungus causes lesions and tissue death on pecan twigs, petioles, leaves, nuts and shucks beginning in early spring, with multiple cycles of infection repeating until late summer. Wind and rain spread the fungus to a susceptible host. Control of the disease is achieved by fungicide, sanitation and, in some cases, quarantine.

Citrus taxonomy refers to the botanical classification of the species, varieties, cultivars, and graft hybrids within the genus Citrus and related genera, found in cultivation and in the wild.

The Solanaceae, or the nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and ornamentals. Many members of the family contain potent alkaloids, and some are highly toxic, but many—including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell and chili peppers—are used as food. The family belongs to the order Solanales, in the asterid group and class Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons). The Solanaceae consists of about 98 genera and some 2,700 species, with a great diversity of habitats, morphology and ecology.


















