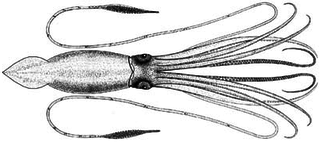
The giant squid is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around 12–13 m (39–43 ft) for females and 10 m (33 ft) for males, from the posterior fins to the tip of the two long tentacles. The mantle of the giant squid is about 2 m long, and the length of the squid excluding its tentacles rarely exceeds 5 m (16 ft). Claims of specimens measuring 20 m (66 ft) or more have not been scientifically documented.

The hooked squid, family Onychoteuthidae, currently comprise about 20–25 species, in six or seven genera. They range in mature mantle length from 7 cm (2.8 in) to a suggested length of 2 m for the largest member, Onykia robusta. The family is characterised by the presence of hooks only on the tentacular clubs, a simple, straight, funnel–mantle locking apparatus, and a 'step' inside the jaw angle of the lower beak. With the exception of the Arctic Ocean, the family is found worldwide.

Taoniinae is a subfamily containing ten genera of glass squids.

Taningia danae, the Dana octopus squid, is a species of squid in the family Octopoteuthidae. It is one of the largest known squid species, reaching a mantle length of 1.7 m (5.6 ft) and total length of 2.3 m (7.5 ft). The largest known specimen, a mature female, weighed 161.4 kg (356 lb).[nb a]

Cephalopods, which include squids and octopuses, vary enormously in size. The smallest are only about 1 centimetre (0.39 in) long and weigh less than 1 gram (0.035 oz) at maturity, while the giant squid can exceed 10 metres (33 ft) in length and the colossal squid weighs close to half a tonne (1,100 lb), making them the largest living invertebrates. Living species range in mass more than three-billion-fold, or across nine orders of magnitude, from the lightest hatchlings to the heaviest adults. Certain cephalopod species are also noted for having individual body parts of exceptional size.

Rossia palpebrosa, also known as the warty bobtail squid, is a species of bobtail squid native to the northern Atlantic Ocean.

The thorny whiplash squid, known as Asperoteuthis acanthoderma is a large species of squid belonging to the family Chiroteuthidae. It is characterised by the tiny, pointed tubercules present on its skin and a Y-shaped groove in the funnel locking apparatus.

Chiroteuthis veranii, commonly known as the long-armed squid, is a species of chiroteuthid squid. It grows to a mantle length of 12.5 cm (4.9 in) and a total length of 130 cm (51 in).
Moroteuthopsis longimana, also known as the giant warty squid or longarm octopus squid, is a large species of hooked squid. It attains a mantle length of at least 85 cm and probably over 1.15 m. The largest complete specimen of this species, measuring 2.3 m in total length, was found in Antarctica in 2000.

Galiteuthis armata, the armed cranch squid, is a large species of glass squid. It reaches a mantle length of 61 cm (24 in). The species is native to the Atlantic Ocean and has been recorded from Bermuda, Canada, Namibia, and Spain. Armed cranch squids often appear to have bloated bodies, short arms, with thin but muscular mantles. They also contain large buoyancy chambers.

The colossal squid is the largest member of its family Cranchiidae, the cockatoo or glass squids, with its second largest member being Megalocranchia fisheri. It is sometimes called the Antarctic cranch squid or giant squid and is believed to be the largest squid species in terms of mass. It is the only recognized member of the genus Mesonychoteuthis and is known from only a small number of specimens. The species is confirmed to reach a mass of at least 495 kilograms (1,091 lb), though the largest specimens—known only from beaks found in sperm whale stomachs—may perhaps weigh as much as 600–700 kilograms (1,300–1,500 lb), making it the largest known invertebrate. Maximum total length has been estimated between 10 metres (33 ft) and 14 metres (46 ft) but the former estimate is more likely. The colossal squid has the largest eyes of any known creature ever to exist, with an estimated diameter of 27–30 cm (11–12 in) to 40 cm (16 in) for the largest collected specimen.

Illex coindetii, commonly known as the southern shortfin squid or broadtail shortfin squid, is a species of neritic squids in the family Ommastrephidae. They are found in the Mediterranean Sea and on both sides of the north Atlantic Ocean.

Teuthowenia megalops, sometimes known as the Atlantic cranch squid, is a species of glass squid from the subarctic and temperate waters of the northern Atlantic Ocean. They are moderately sized squid with a maximum mantle length of 40 cm (16 in). Their very large eyes are the source for the specific name megalops. Like other members of the genus Teuthowenia, they are easily recognizable by the presence of three bioluminescent organs (photophores) on their eyeballs.

Galiteuthis glacialis is a species of glass squid from the Antarctic Convergence. It is in the family Cranchiidae and subfamily Taoniinae. They are endemic to the Antarctic and are found in the Southern Ocean, around the Weddell Sea and the South Shetland Islands. Galiteuthis glacialis are one of the most plentiful and widely dispersed species of Antarctic squid. These squids are found in the mesopelagic and bathypelagic layers of the open ocean and demonstrate vertical migration. They can reach a maximum mantle length of 500 mm (0.5m).
Gonatopsis okutanii is a species of squid from the family Gonatidae from the northern Pacific Ocean. It is of uncertain taxonomic status, the presence of remnant tentacles on spent females indicate that this species does not belong in the genus Gonatopsis and the differences between this species and Gonatus makodai have led to some authorities stating that G. okutanii is a junior synonym of Eogonatus tinro. However the World Register of Marine Species still recognises Gonatopsis okutanii as the valid name for this taxon.

Gonatopsis borealis, the Boreopacific armhook squid, is a species of squid from the North Pacific Ocean. It is a member of the family Gonatidae. It is an abundant species which is currently caught mainly as a bycatch by fishing boats targeting other quarry. It is an important prey species for many commercially important species of fish, as well as for marine mammals.
Gonatopsis japonicus is a species of squid from the family Gonatidae. This species is restricted to the western North Pacific in the seas around the Japanese Archipelago.
Nototeuthis is a monotypic genus of squid, in the family Neoteuthidae. The only species in this genus is Nototeuthis dimegacotyle . This species is characterised by short tentacular clubs, less than 40% of the length of the mantle, and relatively long fins, which are approximately 60% of the mantle length. The tentacle clubs have two greatly enlarged suckers on distal portion of the manus, which distinguish N. dimegacotyle from other members of the Neoteuthidae. Few specimens of this species are currently known. Specimens have been collected from the south eastern Pacific Ocean, off Chile, between the Southern Subtropical and the Antarctic Polar frontal zones. This species is mesopelagic to bathypelagic and can be found from near the surface to a depth of ~500m.

The Antarctic flying squid is a species of squid from the subfamily Todarodinae of the family Ommastrephidae, a family of pelagic squid from the order Oegopsida. It has a circumglobal distribution in the seas around the lower latitudes of the Southern Ocean.
















