
The Mexican tetra, also known as the blind cave fish, blind cave characin, and blind cave tetra, is a freshwater fish of the family Characidae of the order Characiformes. The type species of its genus, it is native to the Nearctic realm, originating in the lower Rio Grande and the Neueces and Pecos Rivers in Texas, as well as the central and eastern parts of Mexico.

The red garra, also known as the doctor fish or nibble fish, is a species of cyprinid that is native to a wide range of freshwater habitats in subtropical parts of Western Asia. This small fish typically is up to about 14 cm (5.5 in) in total length, but locally individuals can reach as much as 24 cm (9.5 in).

Jabal Hafeet is a mountain in the region of Tawam, on the border of the United Arab Emirates and Oman, which may be considered an outlier of Al Hajar Mountains in Eastern Arabia. Due to its proximity to the main Hajar range, the mountain may be considered as being part of the Hajar range, sensu lato. To the north is the UAE city of Al Ain, in the Eastern Region of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, and the adjacent Omani town of Al-Buraimi.

Priddy Pools is a 52.7-hectare (130-acre) geological Site of Special Scientific Interest at Priddy in the Mendip Hills, Somerset, notified in 1972.

The Roanoke logperch is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the family Percidae, which also contains the perches, ruffes and pikeperches. It is found in the Roanoke and Chowan drainages in Virginia and North Carolina in the United States. They inhabit low and moderate-gradient streams and rivers in warm, clear water in mostly unsilted gravel and rubble in runs, pools, and riffles. They are primarily insectivorous. This fish is a federally listed endangered species.

Garra is a genus of fish in the family Cyprinidae. These fish are one example of the "log suckers", sucker-mouthed barbs and other cyprinids commonly kept in aquaria to keep down algae. The doctor fish of Anatolia and the Middle East belongs in this genus. The majority of the more than 140 species of garras are native to Asia, but about one-fifth of the species are from Africa.
Garra dunsirei, the Tawi Atair garra, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Cyprinidae. This cavefish lacks pigmentation and is found only in pools near Tawi Atair in Dhofar, Oman. Unlike the cave form of the related Oman garra, G. dunsirei has normal eyes.
The Tennessee dace is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is found only in the United States; particularly in northeast Tennessee and southwest Virginia, and parts of extreme northwest Georgia. Until recently, they were considered a subspecies of mountain redbelly dace. They are commonly found in East Tennessee in spring fed first-order streams, often in silt and fine gravel pools, or undercut banks. These streams usually do not exceed two meters in width.
Typhlogarra widdowsoni or Garra widdowsoni, the Iraq blind barb or Haditha cave garra, is a species of cyprinid fish endemic to underground water systems near Haditha in Iraq. Although traditionally placed in its own genus Typhlogarra, this is not supported by genetic evidence, leading to its move to Garra. This cavefish is considered critically endangered because of water extraction, which has lowered the groundwater level. Once abundant, a survey in 2012 found that it now was very rare. Another species from the same place, Caecocypris basimi, may already be extinct. The only other known cavefish in Iraq is Eidinemacheilus proudlovei.

The Arabian toad is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to the Arabian Peninsula and is found in Oman, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen.

The flying fox is a Southeast Asian species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is commonly kept in the aquarium trade. Among other foods, it is known to eat green algae. It is sometimes mistakenly referred to as the Siamese algae eater.

The channel darter is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the family Percidae, which also contains the perches, ruffes and pikeperches. It is native to North America where it typically occurs in the sandy or gravelly shallows of lakes and in small and medium-sized rivers in riffles over sand, gravel or rock bottoms. It is a small fish ranging from 34 to 72 mm in length, olive brown with darker speckles and sometimes with a dark spot below the eye and dark blotches along the flank. It feeds mostly on insect larvae and other small invertebrates and breeds in small streams. This species is listed as threatened by the Canadian Species at Risk Act (SARA) but overall it has a wide range and numerous sub-populations and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it as a "least concern species".

Cavefish or cave fish is a generic term for fresh and brackish water fish adapted to life in caves and other underground habitats. Related terms are subterranean fish, troglomorphic fish, troglobitic fish, stygobitic fish, phreatic fish and hypogean fish.

The violet goby is a species of goby native to marine, fresh and brackish waters near the Atlantic coast of North and South America from South Carolina in the United States of America, to northern Brazil. It prefers bays, estuaries and river mouths with muddy substrates. It is often marketed as the dragon goby or dragon fish.
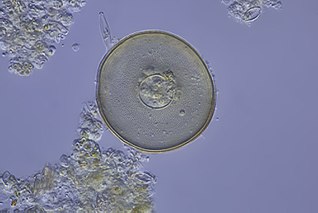
Arcella is a genus of testate amoebae in the order Arcellinida, usually found in freshwaters and mosses, and rarely in soils. A key characteristic of Arcella is the circular test with a hole on its center from where finger-like pseudopods emerge. It is one of the largest testacean genera.

Gyrinocheilus aymonieri is a freshwater fish native to large parts of Southeast Asia. It is of interest as a local food source and for the aquarium trade. Its common names include honey sucker, sucking loach and Chinese algae eater; the FAO-endorsed common name is Siamese algae eater. The black line on the side of a true Siamese algae eater ends at the back of its tail fin and not the beginning.

The creek chubsucker is a freshwater fish of the sucker family (Catostomidae).

Gökgöl Cave is a show cave in Zonguldak Province, Turkey. It is the fifth biggest cave of the country. It is close to a main highway and is well-decorated with stalactites and stalagmites and attracts many visitors.

The wildlife of Oman is the flora and fauna of this country in the southeastern corner of the Arabian Peninsula, with coasts on the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea. The climate is hot and dry, apart from the southeastern coast, and the country offers a variety of habitats for wildlife including mountains, valleys, deserts, coastal plains and sea coasts.
Garra tashanensis is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Garra. This cavefish is endemic to the Tashan Cave located in the Tashan region of Khuzestan Province, Iran.
















