
Obdurodon is a genus of extinct platypus-like Australian monotreme which lived from the Late Oligocene to the Late Miocene. Three species have been described in the genus, the type species Obdurodon insignis, plus Obdurodon dicksoni and Obdurodon tharalkooschild. The species appeared much like their modern day relative the platypus, except adults retained their molar teeth, and unlike the platypus, which forages on the lakebed, they may have foraged in the water column or surface.

Leptictidium is an extinct genus of small mammals that were likely bipedal. Comprising eight species, they resembled today's bilbies, bandicoots, and elephant shrews. They are especially interesting for their combination of characteristics typical of primitive eutherians with highly specialized adaptations, such as powerful hind legs and a long tail which aided in locomotion. They were omnivorous, their diet a combination of insects, lizards and small mammals. Lepticidium and other lepticids are not placentals, but are non-placentral eutherians, although closely related. They appeared in the Lower Eocene, a time of warm temperatures and high humidity, roughly fifty million years ago. Although they were widespread throughout Europe, they became extinct around thirty-five million years ago with no descendants, probably because they were adapted to live in forest ecosystems and were unable to adapt to the open plains of the Oligocene.

Gigantopithecus is an extinct genus of ape from roughly 2 million to 350,000 years ago during the Early to Middle Pleistocene of southern China, represented by one species, Gigantopithecus blacki. Potential identifications have also been made in Thailand, Vietnam, and Indonesia. The first remains of Gigantopithecus, two third molar teeth, were identified in a drugstore by anthropologist Ralph von Koenigswald in 1935, who subsequently described the ape. In 1956, the first mandible and more than 1,000 teeth were found in Liucheng, and numerous more remains have since been found in at least 16 sites. Only teeth and four mandibles are known currently, and other skeletal elements were likely consumed by porcupines before they could fossilise. Gigantopithecus was once argued to be a hominin, a member of the human line, but it is now thought to be closely allied with orangutans, classified in the subfamily Ponginae.

Paranthropus aethiopicus is an extinct species of robust australopithecine from the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2.7–2.3 million years ago. However, it is much debated whether or not Paranthropus is an invalid grouping and is synonymous with Australopithecus, so the species is also often classified as Australopithecus aethiopicus. Whatever the case, it is considered to have been the ancestor of the much more robust P. boisei. It is debated if P. aethiopicus should be subsumed under P. boisei, and the terms P. boisei sensu lato and P. boisei sensu stricto can be used to respectively include and exclude P. aethiopicus from P. boisei.

Dorudon ("spear-tooth") is a genus of extinct basilosaurid ancient whales that lived alongside Basilosaurus 40.4 to 33.9 million years ago in the Eocene. It was a small whale, with D. atrox measuring 5 metres (16 ft) long and weighing 1–2.2 metric tons. Dorudon lived in warm seas around the world and fed on small fish and mollusks. Fossils have been found along the former shorelines of the Tethys Sea in present-day Egypt and Pakistan, as well as in the United States, New Zealand and Western Sahara.

Archaeoindris fontoynontii is an extinct giant lemur and the largest primate known to have evolved on Madagascar, comparable in size to a male gorilla. It belonged to a family of extinct lemurs known as "sloth lemurs" (Palaeopropithecidae) and, because of its extremely large size, it has been compared to the ground sloths that once roamed North and South America. It was most closely related to Palaeopropithecus, the second largest type of sloth lemur. Along with the other sloth lemurs, Archaeoindris was related to the living indri, sifakas, and woolly lemurs, as well as the recently extinct monkey lemurs (Archaeolemuridae). The genus, Archaeoindris, translates to "ancient indri-like lemur", even though it probably became extinct recently, around 350 BCE.

A genet is a member of the genus Genetta, which consists of 17 species of small African carnivorans. The common genet is the only genet present in Europe and occurs in the Iberian Peninsula, Italy and France.

Nakalipithecus nakayamai, sometimes referred to as the Nakali ape, is an extinct species of great ape from Nakali, Kenya, from about 9.9–9.8 million years ago during the Late Miocene. It is known from a right jawbone with 3 molars and from 11 isolated teeth, and the specimen is presumed female as the teeth are similar in size to those of female gorillas and orangutans. Compared to other great apes, the canines are short, the enamel is thin, and the molars are flatter. Nakalipithecus seems to have inhabited a sclerophyllous woodland environment.

Lufengpithecus is an extinct genus of ape in the subfamily Ponginae. It is known from thousands of dental remains and a few skulls and probably weighed about 50 kg (110 lb). It contains three species: L. lufengensis, L. hudienensis and L. keiyuanensis. Lufengpithecus lufengensis is from the Late Miocene found in China, named after the Lufeng site and dated around 6.2 Ma. It is the latest Miocene fossil ape that has been discovered in the entire world. Some researchers believe that genus Lufengpithecus could be an ancestor to African apes.

Microgale macpheei is an extinct shrew tenrec from southeastern Madagascar. It is known only from two partial skulls found in Andrahomana cave, which radiocarbon dating of associated rodent remains suggests are about 3000 years old. It is the only known recently extinct tenrec. First described in 2007, it is most similar to the smaller Microgale brevicaudata of northern and western Madagascar. M. macpheei has a broad rostrum and, like M. brevicaudata, lacks a diastema (gap) between the premolars. A number of details of tooth morphology are characteristic of M. macpheei.

Hipposideros besaoka is an extinct bat from Madagascar in the genus Hipposideros. It is known from numerous jaws and teeth, which were collected in a cave at Anjohibe in 1996 and described as a new species in 2007. The site where H. besaoka was found is at most 10,000 years old; other parts of the cave have yielded H. commersoni, a living species of Hipposideros from Madagascar, and some material that is distinct from both species. H. besaoka was larger than H. commersoni, making it the largest insectivorous bat of Madagascar, and had broader molars and a more robust lower jaw. As usual in Hipposideros, the second upper premolar is small and displaced from the toothrow, and the second lower premolar is large.

Seorsumuscardinus is a genus of fossil dormice from the early Miocene of Europe. It is known from zone MN 4 in Oberdorf, Austria; Karydia, Greece; and Tägernaustrasse-Jona, Switzerland, and from zone MN 5 in a single site at Affalterbach, Germany. The MN 4 records are placed in the species S. alpinus and the sole MN 5 record is classified as the species S. bolligeri. The latter was placed in a separate genus, Heissigia, when it was first described in 2007, but it was reclassified as a second species of Seorsumuscardinus in 2009.
Miniopterus zapfei is a fossil bat in the genus Miniopterus from the middle Miocene of France. First described in 2002, it is known only from the site of La Grive M, where it occurs with another fossil Miniopterus species, the smaller and more common Miniopterus fossilis. M. zapfei is known from five mandibles and an isolated fourth upper premolar (P4). The fourth lower premolar is more slender than in M. fossilis and the cingulum shelf surrounding the P4 is less well-developed than in living Miniopterus. The length of the first lower molar is 1.57 to 1.60 mm.
Dermotherium is a genus of fossil mammals closely related to the living colugos, a small group of gliding mammals from Southeast Asia. Two species are recognized: D. major from the Late Eocene of Thailand, based on a single fragment of the lower jaw, and D. chimaera from the Late Oligocene of Thailand, known from three fragments of the lower jaw and two isolated upper molars. In addition, a single isolated upper molar from the Early Oligocene of Pakistan has been tentatively assigned to D. chimaera. All sites where fossils of Dermotherium have been found were probably forested environments and the fossil species were probably forest dwellers like living colugos, but whether they had the gliding adaptations of the living species is unknown.
Indraloris is a fossil primate from the Miocene of India and Pakistan in the family Sivaladapidae. Two species are now recognized: I. himalayensis from Haritalyangar, India and I. kamlialensis from the Pothohar Plateau, Pakistan. Other material from the Potwar Plateau may represent an additional, unnamed species. Body mass estimates range from about 2 kg (4.4 lb) for the smaller I. kamlialensis to over 4 kg (8.8 lb) for the larger I. himalayensis.
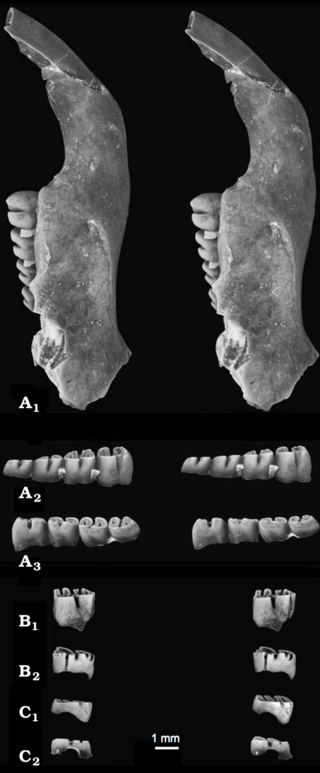
Apeomyoides savagei is a fossil rodent from the Miocene of the United States, the only species in the genus Apeomyoides. It is known from fragmentary jaws and isolated teeth from a site in the early Barstovian, around 15–16 million years ago, of Nevada. Together with other species from scattered localities in the United States, Japan, and Europe, Apeomyoides is classified in the subfamily Apeomyinae of the extinct rodent family Eomyidae. Apeomyines are a rare but widespread group that may have been adapted to a relatively dry habitat.

Hilarcotherium is an extinct genus of astrapotheriid mammals that lived in South America during the Middle Miocene (Laventan). The type species is H. castanedaii, found in sediments of the La Victoria Formation, part of the Honda Group in the department of Tolima in Colombia. In 2018, Carrillo et al. described a partial skull and mandible of a second species H. miyou from the Castilletes Formation in the Cocinetas Basin of northern Colombia, and estimated the body weight of the animal at 6,465 kilograms (14,253 lb).

Microleo attenboroughi is a very small species of the Thylacoleonidae family of marsupials from the Early Miocene of Australia, living in the wet forest that dominated Riversleigh about 18 million years ago. The genus Microleo is currently known from a broken palate and two pieces of jaw, containing some teeth and roots that correspond to those found in other species of thylacoleonids. The shape and structure of the blade-like P3 tooth, a premolar, distinguished the species as a new genus. It was found in Early Miocene-aged deposits of the Riversleigh fossil site in Queensland, regarded as one of the most significant palaeontological sites yet discovered, and named for the naturalist David Attenborough in appreciation of his support for its heritage listing. The anatomy of Microleo suggests the genus is basal to all the known thylacoleonids, known as the marsupial lions, although its relative size prompted one discoverer to describe it as the "feisty" kitten of the family.
Asilifelis is an extinct genus of small felid that lived in what is now Kenya during the Early Miocene. Despite its fragmentary remains, it is remarkable because of its small size and advanced dentition. It contains a single species, Asilifelis cotae.
Katifelis is an extinct genus of felids that lived in what is now Kenya during the Early Miocene and is notable for its dental features, which are intermediate between basal and modern cats. It contains a single species, Katifelis nightingalei.














