
Eryops is a genus of extinct, amphibious temnospondyls. It contains the single species Eryops megacephalus, the fossils of which are found mainly in early Permian rocks of the Texas Red Beds, located in Archer County, Texas. Fossils have also been found in late Carboniferous period rocks from New Mexico. Several complete skeletons of Eryops have been found in lower Permian rocks, but skull bones and teeth are its most common fossils.

The Lasiocampidae are a family of moths also known as eggars, tent caterpillars, snout moths, or lappet moths. Over 2,000 species occur worldwide, and probably not all have been named or studied. It is the sole family in superfamily Lasiocampoidea.
Aulacosphinctes is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopod that lived during the Late Jurassic and had a widespread distribution.

Allen's big-eared bat, also known as the lappet-browed bat, is a species of vesper bat in the monotypic genus Idionycteris. It occurs in Mexico and in Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Colorado in the United States.
The lappet-eared free-tailed bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is found in Benin, Burkina Faso, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, and Uganda. Its natural habitats are dry savanna and moist savanna.

Gobiosuchidae is a family of Cretaceous crocodyliforms known from Mongolia and Spain.

Sichuanosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform from the Late Jurassic and possibly Early Cretaceous of China.
Cadomoceras is an extinct cephalopod genus from the order Ammonitida that lived during the Bajocian Stage of the Middle Jurassic, approximately 178 to 175 million years ago.
Cleistosphinctes is an extinct cephalopod genus from the ammonite order that lived during the Middle Jurassic.
Phaulostephanus is an extinct genus from the ammonoid family Stephanoceratidae, which is part of the ammonitid superfamily Stephanoceratoidea, that lived during the early Middle Jurassic.
Oecoptychius is an extinct genus of fossil ammonite cephalopods. The species lived during the Middle Jurassic.
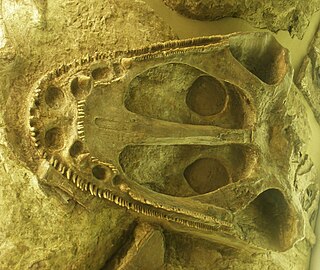
Mastodonsauridae is a family of capitosauroid temnospondyls. Fossils belonging to this family have been found in North America, Greenland, Europe, Asia, and Australia. The family Capitosauridae is synonymous with Mastodonsauridae.

Dissorophus (DI-soh-ROH-fus) is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian that lived during the Early Permian Period about 273 million years ago. Its fossils have been found in Texas and in Oklahoma in North America. Its heavy armor and robust build indicate Dissorophus was active on land, similar to other members of the clade Dissorophidae that are known from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Permian periods. Dissorphus is distinguished by its small body size, disproportionately large head and short trunk.

Tarjadia is an extinct genus of erpetosuchid pseudosuchian, distantly related to modern crocodilians. It is known from a single species, T. ruthae, first described in 1998 from the Middle Triassic Chañares Formation in Argentina. Partial remains have been found from deposits that are Anisian-Ladinian in age. Long known mostly from osteoderms, vertebrae, and fragments of the skull, specimens described in 2017 provided much more anatomical details and showed that it was a fairly large predator. Tarjadia predates known species of aetosaurs and phytosaurs, two Late Triassic groups of crurotarsans with heavy plating, making it one of the first heavily armored archosaurs. Prior to 2017, most studies placed it outside Archosauria as a member of Doswelliidae, a family of heavily armored and crocodile-like archosauriforms. The 2017 specimens instead show that it belonged to the Erpetosuchidae.
Haploceras is a genus of late Upper Jurassic ammonoid cephalopods and the type for the Haploceratidae, similar to Lissoceras but with a broader whorl section and small blunt lappets and a blunt rostrum; some species with feeble ventral folds on body chamber.
Neoaganides is a small, 1–2 cm diameter subdiscoidal to subglobular goniatitid belonging to the family Pseudohaloritidae that lived from the Late Pennsylvanian to the Late Permian, existing for some 56 million years.
Shouchangoceras is a genus of goniatitid pseudohaloritid ammonoids and is the type genus for the pseudohaloritid subfamily Shouchangoceratinae. The genus is characterized by a compressed shell as much as 5 cm in diameter, with a strongly constricted mature peristome that has shallow dorsolateral sinus, a moderately deep rounded ventral sinus, but without conspicuous lappets, and ornamented by moderately strong transverse ribs and numerous stronger longitudinal lirae, producing a weakly reticulate pattern. Lobes are attenuate. The siphuncle is within the dorsal septal flecture.
Ochetoceras is a genus of ammonites, belonging to the Oppeliidae, that lived during the Late Jurassic from the early Oxfordian to the early Tithonian, and type for the subfamily Ochetoceratinae.

Aerodactylus is a pterosaur genus containing a single species, Aerodactylus scolopaciceps, previously regarded as a species of Pterodactylus.

Kutorginates (Kutorginata) are an extinct class of early rhynchonelliform ("articulate") brachiopods. The class contains only a single order, Kutorginida (kutorginides). Kutorginides were among the earliest rhynchonelliforms, restricted to the lower-middle part of the Cambrian Period.









