
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the world's second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land. With an area of nearly 9.6 million square kilometers (3,700,000 sq mi), it is the third-largest country by total land area. The country is divided into 33 province-level divisions: 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center.

Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their taxonomy, genetics, biochemical properties, and use by humans. Fungi can be a source of tinder, food, traditional medicine, as well as entheogens, poison, and infection. Mycology branches into the field of phytopathology, the study of plant diseases. The two disciplines are closely related, because the vast majority of plant pathogens are fungi. A biologist specializing in mycology is called a mycologist.

Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae and the Ochotonidae (pikas). There are 110 recent species of lagomorph of which 109 are extant, including 10 genera of rabbits, 1 genus of hare and 1 genus of pika. The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek lagos + morphē.

Clupeiformes is the order of ray-finned fish that includes the herring family, Clupeidae, and the anchovy family, Engraulidae. The group includes many of the most important forage and food fish.
2024 (MMXXIV) is the current year, and is a leap year starting on Monday of the Gregorian calendar, the 2024th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 24th year of the 3rd millennium and the 21st century, and the 5th year of the 2020s decade.

Firs are evergreen coniferous trees belonging to the genus Abies in the family Pinaceae. There are approximately 48–65 extant species, found on mountains throughout much of North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The genus is most closely related to Cedrus (cedar). The genus name is derived from the Latin "to rise" in reference to the height of its species. The common English name originates with the Old Norse, fyri, or the Old Danish, fyr.

Coots are medium-sized water birds that are members of the rail family, Rallidae. They constitute the genus Fulica, the name being the Latin term for "coot". Coots have predominantly black plumage, and—unlike many rails—they are usually easy to see, often swimming in open water.

Tagetes is a genus of 50 species of annual or perennial, mostly herbaceous plants in the family Asteraceae. They are among several groups of plants known in English as marigolds. The genus Tagetes was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.

Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus Carya, which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mexico, and two to four are native to Canada. A number of hickory species are used for their edible nuts, lumber or other wood and woodcraft products.
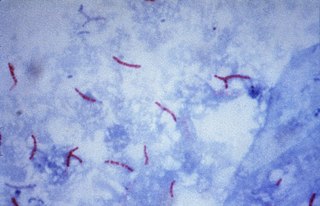
The Ziehl-Neelsen stain, also known as the acid-fast stain, is a bacteriological staining technique used in cytopathology and microbiology to identify acid-fast bacteria under microscopy, particularly members of the Mycobacterium genus. This staining method was initially introduced by Paul Ehrlich (1854–1915) and subsequently modified by the German bacteriologists Franz Ziehl (1859–1926) and Friedrich Neelsen (1854–1898) during the late 19th century.

Cycas is a genus of cycad, and the only genus in the family Cycadaceae with all other genera of cycad being divided between the Stangeriaceae and Zamiaceae families. Cycas circinalis, a species endemic to India, was the first cycad species to be described in western literature, and is the type species of the genus.

The body whorl is part of the morphology of the shell in those gastropod mollusks that possess a coiled shell. The term is also sometimes used in a similar way to describe the shell of a cephalopod mollusk.

Vampyressa is a genus of bats in the family Phyllostomidae, the leaf-nosed bats. They are known commonly as the yellow-eared bats or yellow-eared vampire bats.
Martinichthys is an extinct genus of plethodid fish from the Cretaceous of North America. It is known from the Niobrara Chalk, in which it is exceedingly rare. It is named after one H. T. Martin, who collected the most complete specimen at the time of description.

Carabinae is a subfamily of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. There are about 10 genera and more than 1,400 described species in Carabinae. The Carabinea include 2 tribes, the Cychrini Laporte, 1834 and Carabini Latreille, 1802. The Carabini Latreille is divided into 2 sub-tribes, the Carabina Latreille, 1802 and Ceroglossina Vacher de Lapouge, 1927.

Pycnodontidae is an extinct family of ray-finned fishes, ranging from the Jurassic period until the Eocene. It was the largest and most derived family of the successful Mesozoic fish order Pycnodontiformes, and the only member of it to survive into the Cenozoic.
Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC) rankings, which were introduced in February 2013, are generated by a voting panel made up of media members. These media members are asked to vote for whom they feel are the top fighters in the UFC by weight class and pound-for-pound. A fighter is only eligible to be voted on if they are of active status in the UFC. A fighter can appear in more than one weight division at a time. The champion and interim champion are considered to be in top positions of their respective divisions and therefore are not eligible for voting by weight class. However, the champions can be voted on for the pound-for-pound rankings.














