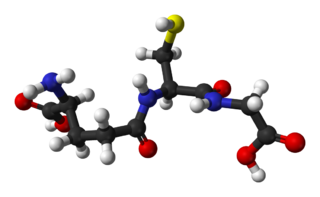
Glutathione is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine.

Glutathione disulfide (GSSG) is a disulfide derived from two glutathione molecules.

Glutathione reductase (GR) also known as glutathione-disulfide reductase (GSR) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSR gene. Glutathione reductase catalyzes the reduction of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) to the sulfhydryl form glutathione (GSH), which is a critical molecule in resisting oxidative stress and maintaining the reducing environment of the cell. Glutathione reductase functions as dimeric disulfide oxidoreductase and utilizes an FAD prosthetic group and NADPH to reduce one molar equivalent of GSSG to two molar equivalents of GSH:

Sulfur assimilation is the process by which living organisms incorporate sulfur into their biological molecules. In plants, sulfate is absorbed by the roots and then be transported to the chloroplasts by the transipration stream where the sulfur are reduced to sulfide with the help of a series of enzymatic reactions. Furthermore, the reduced sulfur is incorporated into cysteine, an amino acid that is a precursor to many other sulfur-containing compounds. In animals, sulfur assimilation occurs primarily through the diet, as animals cannot produce sulfur-containing compounds directly. Sulfur is incorporated into amino acids such as cysteine and methionine, which are used to build proteins and other important molecules. Besides, With the rapid development of economy, the increase emission of sulfur results in environmental issues, such as acid rain and hydrogen sulfilde.
Ascorbate peroxidase (or L-ascorbate peroxidase, APX) (EC 1.11.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Glutaredoxins are small redox enzymes of approximately one hundred amino-acid residues that use glutathione as a cofactor. In humans this oxidation repair enzyme is also known to participate in many cellular functions, including redox signaling and regulation of glucose metabolism. Glutaredoxins are oxidized by substrates, and reduced non-enzymatically by glutathione. In contrast to thioredoxins, which are reduced by thioredoxin reductase, no oxidoreductase exists that specifically reduces glutaredoxins. Instead, glutaredoxins are reduced by the oxidation of glutathione. Reduced glutathione is then regenerated by glutathione reductase. Together these components compose the glutathione system.
In enzymology, a methylarsonate reductase (EC 1.20.4.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-ascorbate oxidase (EC 1.10.3.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Adenylyl-sulfate reductase (glutathione) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Bis-gamma-glutamylcystine reductase (EC 1.8.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CoA-glutathione reductase (EC 1.8.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an enzyme-thiol transhydrogenase (glutathione-disulfide) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathione—CoA-glutathione transhydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathione—homocystine transhydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDAR) (EC 1.6.5.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protein-disulfide reductase (EC 1.8.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protein-disulfide reductase (glutathione) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyrimidodiazepine synthase (EC 1.5.4.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a thiosulfate-thiol sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The ascorbate-glutathione cycle, sometimes Foyer-Halliwell-Asada pathway, is a metabolic pathway that detoxifies hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a reactive oxygen species that is produced as a waste product in metabolism. The cycle involves the antioxidant metabolites: ascorbate, glutathione and NADPH and the enzymes linking these metabolites.








