
The Guarani are a group of culturally-related indigenous peoples of South America. They are distinguished from the related Tupi by their use of the Guarani language. The traditional range of the Guarani people is in what is now Paraguay between the Paraná River and lower Paraguay River, the Misiones Province of Argentina, southern Brazil once as far east as Rio de Janeiro, and parts of Uruguay and Bolivia.

The Río de la Plata, also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and forms a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf, or a marginal sea. If considered a river, it is the widest in the world, with a maximum width of 220 kilometres (140 mi).
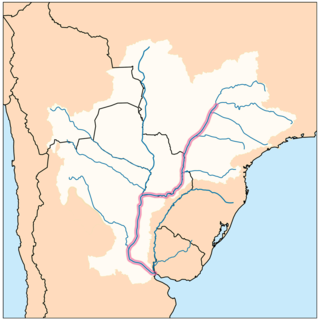
The Paraná River is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some 4,880 kilometres (3,030 mi). Among South American rivers, it is second in length only to the Amazon River. It merges with the Paraguay River and then farther downstream with the Uruguay River to form the Río de la Plata and empties into the Atlantic Ocean.

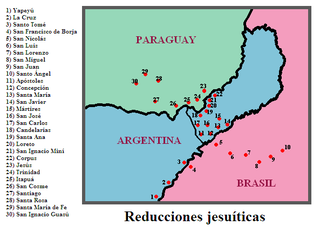
The Jesuit missions among the Guaraní were a type of settlement for the Guaraní people in an area straddling the borders of present-day Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay. The missions were established by the Jesuit Order of the Catholic Church early in the 17th century and ended in the late 18th century after the expulsion of the Jesuit order from the Americas. The missions have been called an experiment in "socialist theocracy" or a rare example of "benign colonialism". Others have argued that "the Jesuits took away the Indians' freedom, forced them to radically change their lifestyle, physically abused them, and subjected them to disease".

Bandeirantes were settlers in colonial Brazil who participated in expeditions to expand the colony's borders and subjugate indigenous Brazilians during the early modern period. They played a major role in expanding the colony to the modern-day borders of independent Brazil, beyond the boundaries demarcated by the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas. Bandeirantes also enslaved thousands of indigenous people, which ultimately played a major role in the genocide of Indigenous peoples in Brazil.

Alto Paraná is a department in Paraguay. The capital is Ciudad del Este.

Guairá is one of the seventeen departments of Paraguay. Its capital and most populous city is Villarrica. It is located to the southern half of the country and to the center of the Eastern Region. Guaira is the second smallest department of Paraguay after Central and the fourth most densely populated after Central, Alto Parana and Cordillera. It was created in 1906.

The Governorate of the Río de la Plata (1549−1776) was one of the governorates of the Spanish Empire. It was created in 1549 by Spain in the area around the Río de la Plata.
Banda Oriental, or more fully Banda Oriental del Río Uruguay, was the name of the South American territories east of the Uruguay River and north of Río de la Plata that comprise the modern nation of Uruguay, the modern state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, and part of the modern state of Santa Catarina, Brazil. It was the easternmost territory of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata.
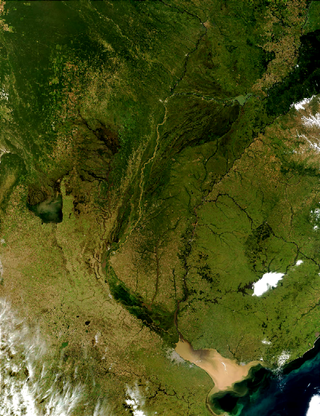
The Río de la Plata basin, more often called the River Plate basin in scholarly writings, sometimes called the Platine basin or Platine region, is the 3,170,000-square-kilometre (1,220,000 sq mi) hydrographical area in South America that drains to the Río de la Plata. It includes areas of southeastern Bolivia, southern and central Brazil, the entire country of Paraguay, most of Uruguay, and northern Argentina. Making up about one fourth of the continent's surface, it is the second largest drainage basin in South America and one of the largest in the world.

São Miguel das Missões is a municipality in Rio Grande do Sul state, southern Brazil. Important 17th century Spanish Jesuit mission ruins are located in the municipality. San Miguel Mission is within Santo Ângelo Microregion, and the Riograndense Northwest Mesoregion. The city covers 1,246 square kilometres (481 sq mi) and had a population of 7,683 residents.
The Guaraní War of 1756, also called the War of the Seven Reductions, took place between the Guaraní tribes of seven Jesuit Missions and joint Spanish-Portuguese forces. It was a result of the 1750 Treaty of Madrid, which set a line of demarcation between Spanish and Portuguese colonial territory in South America.

San Ignacio Miní was one of the many missions founded in 1610 in Argentina, by the Jesuits in what the colonial Spaniards called the Province of Paraguay of the Americas during the Spanish colonial period. It is located near present-day San Ignacio valley, some 60 kilometers (37 mi) north of Posadas, Misiones Province, Argentina. In 1984, it was one of four reducciones in Argentina to be designated by UNESCO as World Heritage Sites.
Gonzalo de Mendoza was a Spanish conquistador and colonizer.
Long before Spanish conquistadors discovered Paraguay for King Charles V in 1524, semi-nomadic Chaco Indian tribes populated Paraguay's rugged landscape. Although few relics or physical landmarks remain from these tribes, the fact that nearly 90 percent of Paraguayans still understand the indigenous Guarani language is testament to Paraguay's Indian lineage. The Spanish conquistadors arrived in 1524 and founded Asunción in 1537. Paraguay's colonial experience differed from that of neighboring countries, such as Bolivia and Argentina, because it did not have gold and other mineral deposits that the Spanish were searching for. Because of its lack of mineral wealth and its remoteness, Paraguay remained underpopulated and economically underdeveloped. Early governor Domingo Martínez de Irala took an Indian wife and a series of Indian concubines and encouraged other male settlers to do likewise. Intermarriage fused Indian culture with that of the Europeans, creating the mestizo class that dominates Paraguay today. From the beginning, however, Indians retained their Guaraní language, even as Spanish influence was accepted, and embraced, in other aspects of society.
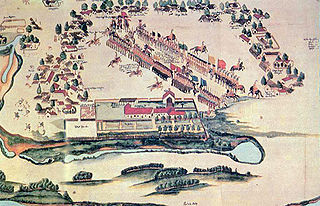
The Battle of Mbororé, which occurred on 11 March 1641, was a conflict between the Guaraníes inhabiting the Jesuit Missions and the bandeirantes, Portuguese explorers and slavers based in São Paulo. The location of the battle is near the coordinates 27°43′29″S 54°54′56″W, in the vicinity of Cerro Mbororé, today the municipality of Panambí in the Province of Misiones, Argentina. The battle ended in a Guarani victory. It took place at the beginning of the Portuguese Restoration War.

The history of yerba mate stretches back to pre-Columbian Paraguay. It is marked by a rapid expansion in harvest and consumption in the Spanish South American colonies but also by its difficult domestication process that began in the mid 17th century and again later when production was industrialized around 1900.

The Governorate of Paraguay, originally called the Governorate of Guayrá, was a governorate of the Spanish Empire and part of the Viceroyalty of Peru. Its seat was the city of Asunción; its territory roughly encompassed the modern day country of Paraguay.
Sopa correntina is a traditional food of the Corrientes Province and part of the Chaco Province, a product of the absorption of the Guaraní culture and mainly of Paraguay. Its invention is attributed to the typical Sopa paraguaya.

Itatín was a 17th century region, corresponding to the western half of the 21st century Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul. The indigenous people inhabiting the region gave their name to Itatín. The Itatínes were related to the Guaraní who lived to their south in Paraguay. In 1631, the Jesuit Order of the Roman Catholic church began founding missions in Itatín but the missions failed in 1648 because of slave raids by the Bandeirantes of Brazil and revolts against the Jesuits. Considered part of colonial Paraguay, Itatín was ceded to Brazil in 1750 by the Treaty of Madrid. The name has fallen out of use.


















