Related Research Articles
HD 169830 is a star in the southern constellation of Sagittarius. It has a yellow-white hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.90. The star is located at a distance of 120 light years from the Sun based on parallax. It is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −17.3 km/s, and is predicted to come as close as 20.7 ly (6.4 pc) in 2.08 million years. HD 169830 is known to be orbited by two large Jupiter-like exoplanets.

HD 108147, also known as Tupã, is a 7th magnitude star in the constellation of Crux in direct line with and very near to the bright star Acrux or Alpha Crucis. It is either a yellow-white or yellow dwarf, slightly brighter and more massive than the Sun. The spectral type is F8 V or G0 V. The star is also younger than the Sun. Due to its distance, about 126 light years, it is too dim to be visible with unaided eye; with binoculars it is an easy target. However, due to its southerly location it is not visible in the northern hemisphere except for the tropics.
HD 6434 is a star in the southern constellation of Phoenix. Yellow dwarfs such as this are not very luminous, so at a distance of 138 light years it is not visible to the unaided eye. However, with binoculars it is readily visible under ideal observing conditions, having an apparent visual magnitude of 7.71. The star is drifting further from the Sun with a radial velocity of +23 km/s.
HD 216770 is an 8th-magnitude star located approximately 124 light-years away in the constellation of Piscis Austrinus. It is an orange dwarf, and is somewhat dimmer and cooler than the Sun.
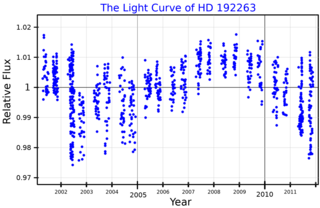
HD 192263 is an 8th magnitude star about 64 light years away in the constellation of Aquila. The spectral type of the star is K2V, meaning that it is an orange dwarf, a type of star somewhat cooler and less luminous than the Sun. It is not visible to the unaided eye, but with good binoculars or small telescope it should be easy to spot.
HD 10647 is a 6th-magnitude yellow-white dwarf star, 57 light-years away in the constellation of Eridanus. The star is visible to the unaided eye under very dark skies. It is slightly hotter and more luminous than the Sun, and at 1.75 billion years old, it is also younger. An extrasolar planet was discovered orbiting this star in 2003.
HD 202206 is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Capricornus. With an apparent visual magnitude of +8.1, it is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. It is located at a distance of 150 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +14.7 km/s.
HD 1237 is a binary star system approximately 57 light-years away in the constellation of Hydrus.
HD 224693, also named Axólotl, is a star in the equatorial constellation of Cetus, and is positioned near the western constellation border with Aquarius. It can be viewed with a small telescope but is too faint to be seen with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 8.23. Based on parallax measurements, the object is located at a distance of approximately 306 light years from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of 1.5 km/s.
HD 106252 is a star with a brown dwarf companion in the constellation Virgo. An apparent visual magnitude of 7.41 means this star is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. It is located at a distance of 210 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is receding with a radial velocity of 15 km/s.
HD 111232 is a star in the southern constellation of Musca. It is too faint to be visible with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 7.59. The distance to this star is 94.5 light years based on parallax. It is drifting away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +104 km/s, having come to within 14.1 light-years some 264,700 years ago. The absolute magnitude of this star is 5.25, indicating it would have been visible to the naked eye at that time.
HD 141937 is a star in the southern zodiac constellation of Libra, positioned a couple of degrees to the north of Lambda Librae. It is a yellow-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 7.25, which means it is too faint to be seen with the naked eye. This object is located at a distance of 108.9 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −2.2 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of 4.71.
HD 142415 is a single star in the southern constellation of Norma, positioned next to the southern constellation border with Triangulum Australe and less than a degree to the west of NGC 6025. With an apparent visual magnitude of 7.33, it is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. The distance to this star is 116 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but it is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −12 km/s. It is a candidate member of the NGC 1901 open cluster of stars.
HD 162020 is a star in the southern constellation of Scorpius with a likely red dwarf companion. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 9.10, which is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. The distance to this system is 101 light years based on stellar parallax. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −27 km/s, and is predicted to come to within ~18 light-years in 1.1 million years.

HD 108147 b, also named Tumearandu, is a gas giant exoplanet with a minimum mass about half that of Jupiter. It orbits the star in a very tight "torch orbit". The distance between the planet and the star is only a tenth of the distance between Earth and the Sun (0.1AU). A number of such worlds are known to exist, but the eccentricity of this planet is unusually high. Planets orbiting very close to their parent stars usually have round orbits because of the tidal forces between the bodies.
HD 65216 b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 115 light-years away in the constellation of Carina, orbiting the star HD 65216. This planet was discovered by the Geneva Extrasolar Planet Search Team in 2003. Like most planet candidates so far, it was detected with the radial velocity method.
HD 147018 is a star in the southern constellation of Triangulum Australe. It has a yellow-orange hue with an apparent visual magnitude of 8.30, which is too faint to be seen with the naked eye but can be viewed with a small telescope. The star is located at a distance of 132 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −27.5 km/s.
HD 220689 is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is a challenge to view with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of +7.74, but is readily viewed with a pair of binoculars. The star is located at a distance of 153 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +12 km/s. A survey in 2015 has ruled out the existence of any additional stellar companions at projected distances from 26 to 305 astronomical units.
HD 166724 is a star in the southern constellation of Corona Australis. It is invisible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +9.33. The star is located at a distance of 148 light-years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −18 km/s. It is predicted to come as close as 97.0 light-years in around 1.2 million years from now. The star has an absolute magnitude of 6.20.
HD 106515 is a binary star in the constellation of Virgo.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365 . Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 . Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Pepe, F.; et al. (2002). "The CORALIE survey for southern extra-solar planets VII. Two short-period Saturnian companions to HD 108147 and HD 168746". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 388 (2): 632–638. arXiv: astro-ph/0202457 . Bibcode:2002A&A...388..632P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020433. S2CID 13942987.
- ↑ "HD 168746". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2018-04-05.
- ↑ "Exoplanets Galore!" (Press release). Garching, Germany: European Southern Observatory. April 15, 2000. Retrieved December 30, 2012.