Related Research Articles
HD 27274, also known as Gliese 167, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern constellation Dorado. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.63, making it readily visible in binoculars, but not to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the star is known to be located 42.5 light-years away from the Solar System However, it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −23 km/s. At its current distance, HD 27274 is dimmed down by 0.05 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 24479, also designated as HR 1204, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. The star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.04. Based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, it is located 385 light years from the Sun. However, it is receding with a somewhat constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 4.6 km/s. At its current distance, HD 24479's brightness is diminished by 0.29 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

Kappa2 Coronae Australis, Latinized from κ2 Coronae Australis, is the primary of a probable binary system located in the southern constellation Corona Australis. It is visible to the naked eye as a bluish-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.59. The distance to this star is roughly 710 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements. The radial velocity is poorly constrained, but the star appears to be moving closer with a radial velocity of around −15 km/s. At its current distance, Kappa2 CrA's brightness is diminished by 0.45 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 26764, also known as HR 1314 or rarely 14 H. Camelopardalis, is a solitary white hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.19, making it faintly to the naked eye if viewed under good conditions. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 266 light years and is drifting closer with a poorly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 3 km/s. At its current distance, HD 26764's brightness is diminished by 0.26 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

Zeta Octantis, Latinized from ζ Octantis, is a solitary, yellowish-white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.42, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. The star is located relatively close at a distance of only 156 light-years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −3.6 km/s. At its current distance, Zeta Octantis' brightness is diminished by 0.25 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

7 Trianguli is a solitary star located in the northern constellation Triangulum. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.25, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. The star is situated at distance of 360 light years but is approaching with a heliocentric radial velocity of −1.3 km/s, which is poorly constrained.
HD 89571 is a binary star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent magnitude of 5.51 and is estimated to be 142 light years away from the Solar System. However, it is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 3.5 km/s.

42 Leonis Minoris is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the northern constellation Leo Minor. It has a visual apparent magnitude of 5.35, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. Parallax measurements place it at a distance of 412 light years. The object has a heliocentric radial velocity of 12 km/s, indicating that it is drifting away from the Solar System.
CD−34°8618, also known as KELT-13 or WASP-167, is a yellowish-white hued star located in the southern constellation of Centaurus. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.52, making it readily visible in medium sized telescopes, but not to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is estimated to be approximately 1,350 light years away from the Solar System. It appears to be drifting closer to it, having a radial velocity of −0.53 km/s.
HD 34255, also known HR 1720, is a star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis, the giraffe. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.60, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The object is located relatively far at a distance of about 1.65 kly but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −7.7 km/s.
HD 10455, also known as HR 4595, is a star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.02, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia Data Release 3, it is estimated to be 336 light years distant. It appears to be receding from the Solar System, having a heliocentric radial velocity of 17.1 km/s.
HD 26670, also known as HR 1305, is a star located in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis, the giraffe. The object has been designated as 26 H. Camelopardalis, but is not commonly used in modern times. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.70, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, the object is estimated to be 491 light years away from the Solar System. It appears to be slowly receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 0.4 km/s.
HD 50885, also known as HR 2581, is a star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis, the giraffe. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.69, making it faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under ideal conditions. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, the object is estimated to be 513 light years distant. It appears to be approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −17.8 km/s.
HD 43899, also designated as HR 2263, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern constellation Columba, the dove. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.53, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is estimated to be 284 light years distant. It appears to be rapidly receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 66.5 km/s. Eggen (1993) lists HD 43899 as an old disk star and its kinematics match with that of the ζ Herculis moving group.
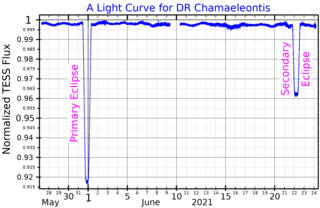
DR Chamaeleontis, also known as HD 93237, is a star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. The system has an average apparent magnitude of 5.97, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. DR Cha is located relatively far at a distance of 1,060 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, but is receding with a poorly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 18 km/s.

40 Leonis Minoris is a white hued star located in the northern constellation Leo Minor. It is rarely called 14 H. Leonis Minoris, which is the designation given by Polis astronomer Johann Hevelius.
HD 191220, also known as HR 7698, is a solitary white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.14, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 245 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is slowly receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 0.1 km/s. At its current distance, HD 191220's brightness is diminished by 0.22 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 22764, also known as HR 1112, is an orange hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.78, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The object is located relatively far at a distance of approximately 1,770 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −12.5 km/s. At its current distance, HD 22764's brightness is diminished by 0.66 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 27322, also known as HR 1342, is a binary star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. The visible component is faintly visible to the naked eye as a white-hued point of light with an apparent magnitude of 5.92. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 313 light-years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, and it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of approximately −13 km/s. At its current distance, HD 27322's brightness is diminished by 0.24 magnitudes due to interstellar extinction and it has an absolute magnitude of +0.98.

HD 28780, also known as HR 1440, is a solitary white-hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.91, making it faintly viisble to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements imply a distance of 488 light-years, and it is currently drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −22.6 km/s. At its current distance, HD 28780's brightness is diminished by 0.33 magnitudes due to interstellar extinction and it has an absolute magnitude of +0.26.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia Collaboration) (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . arXiv: 2208.00211 . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 . Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (March 2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27–L30. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H. ISSN 0004-6361.
- 1 2 Jaschek, Mercedes; Jaschek, Carlos (December 1960). "Southern Stars with Abnormal Spectra". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 72 (429): 500. Bibcode:1960PASP...72..500J. doi: 10.1086/127590 . eISSN 1538-3873. ISSN 0004-6280.
- 1 2 Feinstein, A. (November 1974). "Photoelectric UBVRI observations of AM stars". The Astronomical Journal. 79: 1290. Bibcode:1974AJ.....79.1290F. doi: 10.1086/111675 . ISSN 0004-6256.
- 1 2 Kharchenko, N.V.; Scholz, R.-D.; Piskunov, A.E.; Röser, S.; Schilbach, E. (November 2007). "Astrophysical supplements to the ASCC-2.5: Ia. Radial velocities of ~55000 stars and mean radial velocities of 516 Galactic open clusters and associations". Astronomische Nachrichten. 328 (9): 889–896. arXiv: 0705.0878 . Bibcode:2007AN....328..889K. doi:10.1002/asna.200710776. eISSN 1521-3994. ISSN 0004-6337. S2CID 119323941.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (May 2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331–346. arXiv: 1108.4971 . Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. eISSN 1562-6873. ISSN 1063-7737. S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 Stassun, Keivan G.; et al. (9 September 2019). "The Revised TESS Input Catalog and Candidate Target List". The Astronomical Journal. 158 (4): 138. arXiv: 1905.10694 . Bibcode:2019AJ....158..138S. doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/ab3467 . eISSN 1538-3881.
- 1 2 Chandler, Colin Orion; McDonald, Iain; Kane, Stephen R. (17 February 2016). "The Catalog of Earth-Like Exoplanet Survey Targets (CELESTA): A Database of Habitable Zones Around Nearby Stars". The Astronomical Journal. 151 (3): 59. arXiv: 1510.05666 . Bibcode:2016AJ....151...59C. doi: 10.3847/0004-6256/151/3/59 . eISSN 1538-3881.
- 1 2 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365 . Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 . Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Watson, R. A. (15 June 2017). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Tycho–Gaia stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 471 (1): 770–791. arXiv: 1706.02208 . Bibcode:2017MNRAS.471..770M. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stx1433 . eISSN 1365-2966. ISSN 0035-8711.
- 1 2 Bai, Yu; Liu, JiFeng; Bai, ZhongRui; Wang, Song; Fan, DongWei (2 August 2019). "Machine-learning Regression of Stellar Effective Temperatures in the Second Gaia Data Release". The Astronomical Journal. 158 (2): 93. arXiv: 1906.09695 . Bibcode:2019AJ....158...93B. doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/ab3048 . eISSN 1538-3881.
- ↑ Gould, Benjamin Apthorp (1878). "Uranometria Argentina : brillantez y posicion de las estrellas fijas, hasta la septima magnitud, comprendidas dentro de cien grados del polo austral : con atlas". Resultados del Observatorio Nacional Argentino. 1. Bibcode:1879RNAO....1.....G.
- ↑ "HD 167714". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved September 14, 2022.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (11 September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 389 (2): 869–879. arXiv: 0806.2878 . Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x . eISSN 1365-2966. ISSN 0035-8711.