
HD 24479, also designated as HR 1204, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. The star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.04. Based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, it is located 385 light years from the Sun. However, it is receding with a somewhat constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 4.6 km/s. At its current distance, HD 24479's brightness is diminished by 0.29 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
HD 86267, also known as HR 3932, is a solitary orange-hued star located in the southern constellation Antlia. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.82, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. Parallax measurements place it a distance of 514 light years and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 3.7 km/s.
HD 133981, also known as HR 5628, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation of Apus. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.02, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye in ideal conditions. The object is located relatively far at a distance of 856 light years based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3 but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −13.7 km/s.
HD 121439, also known as HR 5240, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Apus. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.08, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The object is located relatively far at a distance of 774 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is receding with a fairly constrained radial velocity of 4 km/s. At its current distance, HD 121439's brightness is diminished by 0.57 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 154972, also known as HR 6373 or rarely 56 G. Apodis, is a solitary, bluish-white-hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Apus. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.23, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements place the object 336 light years away, and it is currently drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −3.1 km/s. At its current distance, HD 154972's brightness is diminished by 0.23 magnitudes due to extinction from interstellar dust. It has an absolute magnitude of +1.11.
HD 39901 is an orange hued star located in the constellation Columba. It is also called HR 2069, which is the star's Bright Star Catalog designation. Eggen (1989) lists it as a member of the old disk population.
1 Trianguli, also known as HD 10407, is a star located in the northern constellation Triangulum. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.52, making it readily visible in binoculars but not to the naked eye. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements imply a distance of 723 light years and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 7 km/s. At its current distance 1 Trianguli's brightness is diminished by a quarter of a magnitudes due to interstellar dust and it has an absolute magnitude of +0.78. Even though it has a Flamsteed designation, 1 Trianguli is one of the 220 Flamsteed stars that are not in the Yale Bright Star Catalogue.
HD 75116, also known as HR 3491, is a solitary, orange hued star in the southern circumpolar constellation Volans, the flying fish. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.31, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft place the star relatively far at a distance of 930 light years. It appears to be approaching the Solar System, having a heliocentric radial velocity of −17.5 km/s.
HD 66920, also known as HR 3171, is a solitary, white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Volans, the flying fish. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.33, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the star is estimated to be 428 light years distant. It appears to be receding from the Solar System, having a heliocentric radial velocity of 23.8 km/s. Pauzen et al. (2001) listed it as a λ Boötis star, but is now considered a non member.

HD 171819, also known as HR 6986 or rarely 22 G. Telescopii, is a solitary star located in the southern constellation Telescopium. It is faintly visible to the naked eye as a white-hued object with an apparent magnitude of 5.84. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 313 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, but it is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −9 km/s. At its current distance, HD 171819's brightness is diminished by one-quarter of a magnitude due to interstellar dust and it has an absolute magnitude of +0.65.
HD 194612 is a solitary orange hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.9, making it visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Parallax measurements place it at a distance of 760 light years and it has a low heliocentric radial velocity of 0.3 km/s.
HD 31529, also known as HR 1584, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern constellation Caelum, the chisel. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.09, making it faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under ideal conditions. This object is located relatively far at a distance of 932 light years based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 28.4 km/s. Eggen (1989) lists it as a member of the old disk population.

HD 98617, also known HR 4385, is a double star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. The system has a combined apparent magnitude of 6.35, placing it near the limit for naked eye. The system is located relatively close at a distance of 206 light years but is approaching the Solar System with a fairly constrained radial velocity of −4 km/s. At its current distance, HD 98617 brightness is diminished by 0.29 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
HD 191220, also known as HR 7698, is a solitary white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.14, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 245 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is slowly receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 0.1 km/s. At its current distance, HD 191220's brightness is diminished by 0.22 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 198716, also known as HR 7987 or 33 G. Microscopii, is a solitary star located in the southern constellation Microscopium. Eggen (1993) lists it as a member of the Milky Way's old disk population.
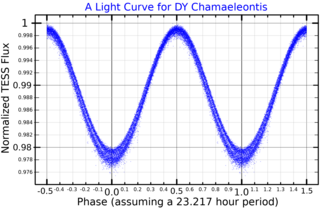
HD 118285, also known as HR 5115, is a variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. DY Chamaeleontis is its variable star designation. It has an average apparent magnitude of 6.32, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. The object is located relatively far at a distance of 864 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 18 km/s. At its current distance, HD 118285's brightness is diminished by 0.58 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 168592, also designated as HR 6862 or rarely 7 G. Coronae Australis, is a solitary star located in the southern constellation Corona Australis. It is faintly visible to the naked eye as an orange-hued star with an apparent magnitude of 5.07. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements place it at a distance of 490 light years and is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 18 km/s. At its current distance, HD 168592's brightness is diminished by 0.38 magnitudes due to interstellar dust. It has an absolute magnitude of −0.76.
HD 99015, also known as HR 4397 or rarely 31 G. Chamaeleontis, is a solitary white-hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.42, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility even in ideal conditions. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 243 light years and is drifting closer with a somewhat constrained heliocentric radial velocity of −5.9 km/s. At its current distance, HD 99015's brightness is diminished by 0.31 magnitudes due to interstellar dust. It has an absolute magnitude of +2.08.

HD 170873, also known as HR 6954 or rarely 19 G. Telescopii, is a solitary orange-hued star located in the southern constellation Telescopium. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.20, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements imply a distance of 551 light years and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 23.8 km/s. At its current distance, HD 170873's brightness is diminished by 0.39 magnitudes due to interstellar dust, and it has an absolute magnitude of −0.31.

HD 186756, also known as HR 7521 or rarely 68 G. Telescopii, is a solitary orange hued star located in the southern constellation Telescopium. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.25, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility, even under ideal conditions. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements imply a distance of 743 light years; it is currently approaching with a heliocentric radial velocity of −21.2 km/s. At its current distance, HD 186756's brightness is diminished by 0.34 magnitudes due to extinction from interstellar dust and it has an absolute magnitude of −0.96.







