 A visual band light curve for RZ Chamaeleontis, plotted from data published by Jørgensen & Gyldenkerne (1975) [1] | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Chamaeleon |
| Right ascension | 10h 42m 24.10884s [2] |
| Declination | −82° 02′ 14.1832″ [2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.1 –8.5 [3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F5 IV-V + F5 IV-V [4] |
| B−V color index | +0.45 [5] |
| Variable type | Algol [6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 20±0.6 [7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −13.536 mas/yr [2] Dec.: −45.153 mas/yr [2] |
| Parallax (π) | 5.7404±0.0186 mas [2] |
| Distance | 568 ± 2 ly (174.2 ± 0.6 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +1.72 [8] (combined) |
| Orbit [9] | |
| Primary | RZ Cha A |
| Companion | RZ Cha B |
| Period (P) | 2.8320896±0.0000013 d |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 0.05631 ± 0.00013 AU |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.00 |
| Inclination (i) | 83.292±0.006° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 107.8±0.4 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 108.2±0.4 km/s |
| Details [9] | |
| RZ Cha A | |
| Mass | 1.488±0.011 M☉ |
| Radius | 2.1499±0.0058 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 7.9 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.9458±0.0018 cgs |
| Temperature | 6,596±150 K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 38.41±0.10 km/s |
| Age | 2.3 Gyr |
| RZ Cha B | |
| Mass | 1.482±0.011 M☉ |
| Radius | 2.2708±0.0058 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 8.6 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.8967±0.0017 cgs |
| Temperature | 6,564±150 K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 40.57±0.10 km/s |
| Age | 2.3 Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| RZ Cha, CD−81°391, CPD−81°467, GC 14785, HD 93486, HIP 52381, SAO 258590 [10] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
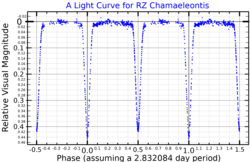
HD 93486, also known as HIP 52381, is a binary star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon near the border with Octans. Its variable star designation is RZ Chamaeleontis (RZ Cha). It has an apparent magnitude ranging from 8.2 to 9.1, [6] which is below the limit for naked eye visibility. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements place the system 568 light years away, [2] and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 20 km/s . [7] At its current distance, HD 93486's average brightness is diminished by 0.53 magnitudes due to interstellar dust. [11] The system has a combined absolute magnitude of +1.72. [8]
In 1964, HD 93486 was discovered to be an eclipsing binary by astronomer W. Strohmeier and colleagues. [12] Four years later, the system was found to be an Algol variable [13] and was given the variable star designation RZ Chamaeleontis in 1974. [14] J. Andersen et al. (1975) calculated a circular orbit of 2.8321 days, [4] which is also its variability period. During this time, RZ Cha drops from photographic magnitude 8.2 to 9.1 when the smaller component is eclipsed, and to 8.8 when the larger one is eclipsed. [6]
Both components have a stellar classification of F5 IV-V, indicating that they are slightly evolved F-type stars with luminosity classes intermediate between a subgiant and a main-sequence star. The primary has 149% the mass of the Sun and 2.15 times the Sun's radius. The secondary has 148% the mass of the Sun and 2.27 times the radius of the Sun. [9] Together, both stars radiate 7.94 times the luminosity of the Sun [15] from their photospheres at an effective temperature of 6,450 K , giving it a combined yellowish-white hue. The system is metal enriched with an iron abundance and is estimated to be 2 to 3 billion years old. [16] Both stars spin modestly, with projected rotational velocities of 38.4 km/s and 40.6 km/s respectively. [9]