
Portable Network Graphics is a raster-graphics file format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) — unofficially, the initials PNG stood for the recursive acronym "PNG's not GIF".

In computer graphics and digital photography, a raster graphic is a mechanism that represents a two-dimensional image as a rectangular matrix or grid of square pixels, viewable via a computer display, paper, or other display medium. A raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixel. Raster images are stored in image files with varying dissemination, production, generation, and acquisition formats.

Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML-based vector image format for two-dimensional graphics with support for interactivity and animation. The SVG specification is an open standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) since 1999.
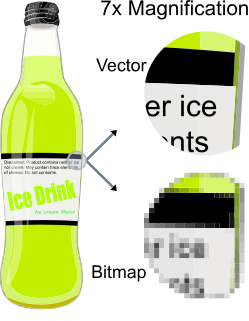
Vector graphics, as a form of computer graphics, is the set of mechanisms for creating visual images directly from geometric shapes defined on a Cartesian plane, such as points, lines, curves, and polygons. These mechanisms may include vector display and printing hardware, vector data models and file formats, and software based on these data models. Vector graphics are an alternative to raster graphics, each having advantages and disadvantages in general and in specific situations.
Interchange File Format (IFF), is a generic container file format originally introduced by the Electronic Arts company in 1985 in order to facilitate transfer of data between software produced by different companies.
The Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF) is a generic file container format for storing data in tagged chunks. It is primarily used to store multimedia such as sound and video, though it may also be used to store any arbitrary data.

Adobe Illustrator is a vector graphics editor and design program developed and marketed by Adobe Inc. Originally designed for the Apple Macintosh, development of Adobe Illustrator began in 1985. Along with Creative Cloud, Illustrator CC was released. The latest version, Illustrator 2022, was released on October 26, 2021, and is the 25th generation in the product line. Adobe Illustrator was reviewed as the best vector graphics editing program in 2018 by PC Magazine.
The BMP file format, also known as bitmap image file, device independent bitmap (DIB) file format and bitmap, is a raster graphics image file format used to store bitmap digital images, independently of the display device, especially on Microsoft Windows and OS/2 operating systems.

Pixel art is a form of digital art, created through the use of software, where images are edited on the pixel level. The aesthetic for this kind of graphics comes from 8-bit and 16-bit computers and video game consoles, in addition to other limited systems such as graphing calculators. In most pixel art, the color palette used is extremely limited in size, with some pixel art using only two colors.
Cairo is an open source graphics library that provides a vector graphics-based, device-independent API for software developers. It provides primitives for two-dimensional drawing across a number of different back ends. Cairo uses hardware acceleration when available.
A computer font is implemented as a digital data file containing a set of graphically related glyphs. A computer font is designed and created using a font editor. A computer font specifically designed for the computer screen, and not for printing, is a screen font.

Digital illustration or computer illustration is the use of digital tools to produce images under the direct manipulation of the artist, usually through a pointing device such as a tablet or a mouse. It is distinguished from computer-generated art, which is produced by a computer using mathematical models created by the artist. It is also distinct from digital manipulation of photographs, in that it is an original construction "from scratch". Photographic elements such as background or texture may be incorporated into such works, but they are not necessarily the primary basis.
The ICO file format is an image file format for computer icons in Microsoft Windows. ICO files contain one or more small images at multiple sizes and color depths, such that they may be scaled appropriately. In Windows, all executables that display an icon to the user, on the desktop, in the Start Menu, or in Windows Explorer, must carry the icon in ICO format.
A number of vector graphics editors exist for various platforms. Potential users of these editors will make a comparison of vector graphics editors based on factors such as the availability for the user's platform, the software license, the feature set, the merits of the user interface (UI) and the focus of the program. Some programs are more suitable for artistic work while others are better for technical drawings. Another important factor is the application's support of various vector and bitmap image formats for import and export.
Image file formats are standardized means of organizing and storing digital images. An image file format may store data in an uncompressed format, a compressed format, or a vector format. Image files are composed of digital data in one of these formats so that the data can be rasterized for use on a computer display or printer. Rasterization converts the image data into a grid of pixels. Each pixel has a number of bits to designate its color. Rasterizing an image file for a specific device takes into account the number of bits per pixel that the device is designed to handle.

The shapefile format is a geospatial vector data format for geographic information system (GIS) software. It is developed and regulated by Esri as a mostly open specification for data interoperability among Esri and other GIS software products. The shapefile format can spatially describe vector features: points, lines, and polygons, representing, for example, water wells, rivers, and lakes. Each item usually has attributes that describe it, such as name or temperature.
Apple's Macintosh computer supports a wide variety of fonts. This support was one of the features that initially distinguished it from other systems.
In computing, a bitmap is a mapping from some domain to bits. It is also called a bit array or bitmap index.
The history of Haiku, a free, open-source operating system, began in 2001. As of January 2016, as refactoring FLOSS effort of BeOS named initially "OpenBeOS". It used open sourced code of a Tracker file browser and NewOS kernel. Today, after 4 alpha and 2 beta versions, work on Haiku continues with a third beta planned and 'Nightly' builds available between releases.
This is a glossary of terms relating to computer graphics.






