
Amphicyonidae is an extinct family of terrestrial carnivorans belonging to the suborder Caniformia. They first appeared in North America in the middle Eocene, spread to Europe by the late Eocene, and further spread to Asia and Africa by the early Miocene. They had largely disappeared worldwide by the late Miocene, with the latest recorded species at the end of the Miocene in Africa. They were among the first carnivorans to evolve large body size. Amphicyonids are colloquially referred to as "bear-dogs".

Amphicyon is an extinct genus of large carnivorans belonging to the family Amphicyonidae, subfamily Amphicyoninae, from the Miocene epoch. Members of this family received their vernacular name for possessing bear-like and dog-like features. They ranged over North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa.

Quercygale is an extinct genus of placental mammals from the clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in Europe during the early to late Eocene.

Daphoenodon is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore, which lived in the early Miocene and belonged to the family Amphicyonidae of the suborder Caniformia. The species of Daphoenodon are characterized by limbs that are specialized in fore and aft movement, as well as a body alignment that results in a lengthened stride.

Agnotherium is a genus of large sized carnivoran mammals, belonging to the Amphicyonidae, which has been found in Western Europe, and possibly China and Northern Africa, and lived during the Late Miocene epoch. Despite only being known from fragmentary remains, the genus notable for hypercarnivorous adaptions, which have been said to represent the "apex" among its family.
Brachycyon is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, family Amphicyonidae, which inhabited Eurasia and North America.
Haplocyon is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the Carnivoran suborder Caniformia, family Amphicyonidae named by Schlosser in 1901. It lived in Europe between 28.4 and 23.03 Mya, during the Late Oligocene.
Haplocyonoides is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, family Amphicyonidae, and which inhabited Europe from the Early Miocene subepoch —(16.9 Mya). Haplocyonoides existed for approximately 3.1 million years.
Pseudarctos is a member of the extinct family Amphicyonidae of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, which inhabited Eurasia in the Middle Miocene subepoch 16.9—11.1 Ma, existing for approximately 5.8 million years.
Pseudocyonopsis is a member of the extinct family Amphicyonidae, a terrestrial carnivore belonging to the order Caniformia.

Ysengrinia is an extinct genus of carnivoran in the family Amphicyonidae, that lived during the Late Oligocene to Early Miocene. Fossil remains have been discovered in Western Europe, the United States and possibly China. The European species are among the earliest known members of the Thaumastocyoninae, a group of aberrant amphicyonids showcasing hypercarnivorous adations, but are only known from fragmentary remains. The American species is much better preserved and shows a robust, black-bear sized predator. These fossils play an important role in our understanding of the biotic interchange between Eurasia and North America during the earliest Miocene. However, more recent research suggests that the genus might be polyphyletic, and that several of its species should be excluded from Ysengrinia.
Afrocyon is an extinct genus of large, mostly carnivorous bone-crushing mammals known as bear dogs, of the family Amphicyonidae endemic to Africa during the Miocene to Pliocene living from 11.6 to 5.3 Ma and existed for approximately 6.3 million years.
Harpagophagus is an extinct genus of large, mostly carnivorous bone-crushing mammals of the family Amphicyonidae endemic to Europe during the Oligocene living from 33.9 to 23.03 Ma and existed for approximately 10.87 million years.

Amphicyoninae is a subfamily of extinct amphicyonids, large terrestrial carnivores sometimes called "bear-dogs", belonging to the suborder Caniformia, which inhabited North America, Eurasia, and Africa from the middle Eocene to the late Miocene.
Amphicyanis is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, family Amphicyonidae, and which inhabited Eurasia and North America.
Daphoenictis is an extinct cat-like genus of the family Amphicyonidae (bear-dogs), subfamily Daphoeninae, endemic to North America during the Late Eocene subepoch, existing for approximately 3.3 million years. Daphoenictis' geographical range was mid-western North America; from central Canada, to Texas, U.S. Only one species is known, Daphoenictis tedfordi.

Angelarctocyon is an extinct genus of Amphicyonidae, which belongs to the order Carnivora.
Goupilictis minor is a prehistoric species of mammal in the family Amphicyonidae. There is only one known species in the genus Goupilictis.
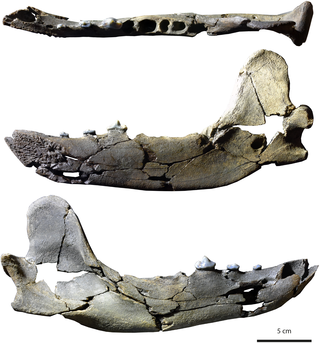
Tartarocyon is an extinct genus of Amphicyonidae, who lived during the late Middle Miocene. It was described after fossilized remains found in Sallespisse, France. Despite the scarceness of its fossil remains, being only known from the holotype mandible, its body mass has been estimated to be close to 200 kilograms, far from its closest relative, Cynelos, and making it one of the largest terrestrial predators of Miocene Europe. T. cazanavei is the only species included in the genus. The genus was named after a southwestern French Pyrenees legend of a man eating giant ; the species name honors the owner of the terrain in which the holotype has been discovered.

Thaumastocyoninae is an extinct subfamily of amphicyonids, large terrestrial carnivores, which inhabited what is now Europe during the Miocene epoch. The subfamily was erected by Hürzeler (1940), and is defined by the complete suppression of m1 metaconid, reduction of the premolars, except the p4, which is reinforced, and the oblique abrasion of the teeth, and the possession of hypercarnivorous tendencies. Thaumastocyonines are poorly known, with only about 65 dental specimens, most of those isolated teeth, being known as of 2020, although more complete remains have recently been discovered.









