
Amphicyonidae is an extinct family of terrestrial carnivorans belonging to the suborder Caniformia. They first appeared in North America in the middle Eocene, spread to Europe by the late Eocene, and further spread to Asia and Africa by the early Miocene. They had largely disappeared worldwide by the late Miocene, with the latest recorded species at the end of the Miocene in Africa. They were among the first carnivorans to evolve large body size. Amphicyonids are colloquially referred to as "bear-dogs".

Miacidae is a former paraphyletic family of extinct primitive placental mammals that lived in North America, Europe and Asia during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs, about 65–33.9 million years ago. These mammals were basal to order Carnivora, the crown-group within the Carnivoraformes.

Miacis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to middle Eocene.

Amphicyon is an extinct genus of large carnivorans belonging to the family Amphicyonidae, subfamily Amphicyoninae, from the Miocene epoch. Members of this family received their vernacular name for possessing bear-like and dog-like features. They ranged over North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa.

The John Day Formation is a series of rock strata exposed in the Picture Gorge district of the John Day River basin and elsewhere in north-central Oregon in the United States. The Picture Gorge exposure lies east of the Blue Mountain uplift, which cuts southwest–northeast through the Horse Heaven mining district northeast of Madras. Aside from the Picture Gorge district, which defines the type, the formation is visible on the surface in two other areas: another exposure is in the Warm Springs district west of the uplift, between it and the Cascade Range, and the third is along the south side of the Ochoco Mountains. All three exposures, consisting mainly of tuffaceous sediments and pyroclastic rock rich in silica, lie unconformably between the older rocks of the Clarno Formation below and Columbia River basalts above.

Paroodectes is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in Europe during the middle Eocene.

Miocyon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to late Eocene.
Messelogale is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in Europe during the middle Eocene.

Quercygale is an extinct genus of placental mammals from the clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in Europe during the early to late Eocene.
Quercylurus major is an extinct, cat-like nimravid carnivora from the early Oligocene of France. Its fossils were found in Early Oligocene strata in Quercy. Q. major was possibly the largest nimravid ever known, as its fossils suggest it was similar in size to the modern-day lion.

Agnotherium is a genus of large sized carnivoran mammals, belonging to the Amphicyonidae, which has been found in Western Europe, and possibly China and Northern Africa, and lived during the Late Miocene epoch. Despite only being known from fragmentary remains, the genus notable for hypercarnivorous adaptions, which have been said to represent the "apex" among its family.

Ysengrinia is an extinct genus of carnivoran in the family Amphicyonidae, that lived during the Late Oligocene to Early Miocene. Fossil remains have been discovered in Western Europe, the United States and possibly China. The European species are among the earliest known members of the Thaumastocyoninae, a group of aberrant amphicyonids showcasing hypercarnivorous adations, but are only known from fragmentary remains. The American species is much better preserved and shows a robust, black-bear sized predator. These fossils play an important role in our understanding of the biotic interchange between Eurasia and North America during the earliest Miocene. However, more recent research suggests that the genus might be polyphyletic, and that several of its species should be excluded from Ysengrinia.

Arctoidea is a clade of mostly carnivorous mammals which include the extinct Hemicyonidae (dog-bears), and the extant Musteloidea, Pinnipedia, and Ursidae (bears), found in all continents from the Eocene, 46 million years ago, to the present. The oldest group of the clade is the bears, as their CMAH gene is still intact. The gene became non-functional in the common ancestor of the Mustelida. Arctoids are caniforms, along with dogs (canids) and extinct bear dogs (Amphicyonidae). The earliest caniforms were superficially similar to martens, which are tree-dwelling mustelids. Together with feliforms, caniforms compose the order Carnivora; sometimes Arctoidea can be considered a separate suborder from Caniformia and a sister taxon to Feliformia.

Aeluroidea, Ailuroidea or Feloidea is the name of a taxon comprising cat-like Carnivora. More specifically the taxon comprises:

Lesmesodon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct family Proviverridae within extinct superfamily Hyaenodontoidea, that lived during the Early to Middle Eocene. It was found in France and in the Messel Pit in Germany. Lesmesodon was a weasel-sized carnivorous mammal.
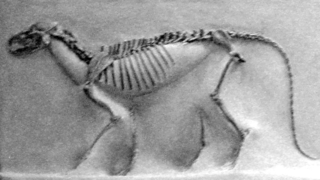
Brachyrhynchocyon is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore, which belonged to the family Amphicyonidae of the suborder Caniformia.

Angelarctocyon is an extinct genus of Amphicyonidae, which belongs to the order Carnivora.
Goupilictis minor is a prehistoric species of mammal in the family Amphicyonidae. There is only one known species in the genus Goupilictis.

Proviverrinae is an extinct subfamily of placental mammals within the extinct order Hyaenodonta. Fossil remains of these mammals are known from early to late Eocene deposits in Europe.

Thaumastocyoninae is an extinct subfamily of amphicyonids, large terrestrial carnivores, which inhabited what is now Europe during the Miocene epoch. The subfamily was erected by Hürzeler (1940), and is defined by the complete suppression of m1 metaconid, reduction of the premolars, except the p4, which is reinforced, and the oblique abrasion of the teeth, and the possession of hypercarnivorous tendencies. Thaumastocyonines are poorly known, with only about 65 dental specimens, most of those isolated teeth, being known as of 2020, although more complete remains have recently been discovered.
















