
Amphicyonidae is an extinct family of terrestrial carnivorans belonging to the suborder Caniformia. They first appeared in North America in the middle Eocene, spread to Europe by the late Eocene, and further spread to Asia and Africa by the early Miocene. They had largely disappeared worldwide by the late Miocene, with the latest recorded species at the end of the Miocene in Africa. They were among the first carnivorans to evolve large body size. Amphicyonids are colloquially referred to as "bear-dogs".

Trilophosaurs are lizard-like Triassic allokotosaur reptiles related to the archosaurs. The best known genus is Trilophosaurus, a herbivore up to 2.5 metres long. It had a short, unusually heavily built skull, equipped with massive, broad flattened cheek teeth with sharp shearing surfaces for cutting up tough plant material. Teeth are absent from the premaxilla and front of the lower jaw, which in life were probably equipped with a horny beak.
Herbstosaurus is the name given to a genus of pterosaurs that lived during the Late Jurassic period, in what is now Argentina. In 1969 Argentine paleobotanist Rafael Herbst in the province Neuquén at Picun Leufú dug up a piece of sandstone holding a number of disarticulated bones of a small reptile. At the time it was assumed the rock dated to the Middle Jurassic (Callovian), about 163 million years ago.

Quercygale is an extinct genus of placental mammals from the clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in Europe during the early to late Eocene.

Daphoenodon is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore, which lived in the early Miocene and belonged to the family Amphicyonidae of the suborder Caniformia. The species of Daphoenodon are characterized by limbs that are specialized in fore and aft movement, as well as a body alignment that results in a lengthened stride.
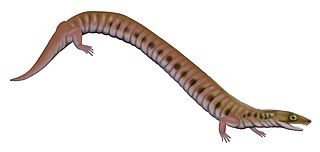
Rhynchonkos is an extinct genus of rhynchonkid microsaur. Originally known as Goniorhynchus, it was renamed in 1981 because the name had already been given to another genus; the family, likewise, was originally named Goniorhynchidae but renamed in 1988. The type and only known species is R. stovalli, found from the Early Permian Fairmont Shale in Cleveland County, Oklahoma. Rhynchonkos shares many similarities with Eocaecilia, an early caecilian from the Early Jurassic of Arizona. Similarities between Rhynchonkos and Eocaecilia have been taken as evidence that caecilians are descendants of microsaurs. However, such a relationship is no longer widely accepted.
Macrocephalochelys is an extinct genus of turtles in the family Chelydridae. It was first described from a partial skull from the Pliocene found in Ukraine by Piboplichko and Taraschchuk in 1960. It was assigned to the family Chelydridae by R. L. Carroll in 1988 although it had been hypothesised to belong in Chelydridae by Chkhikvadze in 1971.
Planiplastron is an extinct genus of snapping turtle. It was first described by Chkhikvadze in 1971. It was assigned to the family Chelydridae by R. L. Carroll in 1988.

Pseudocyon is a genus of amphicyonid which inhabited Eurasia and North America during the Miocene epoch living approximately 3.22 million years.
Brachycyon is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, family Amphicyonidae, which inhabited Eurasia and North America.
Haplocyonoides is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, family Amphicyonidae, and which inhabited Europe from the Early Miocene subepoch —(16.9 Mya). Haplocyonoides existed for approximately 3.1 million years.
Haplocyonopsis is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, family Amphicyonidae.
Pseudarctos is a member of the extinct family Amphicyonidae of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, which inhabited Eurasia in the Middle Miocene subepoch 16.9—11.1 Ma, existing for approximately 5.8 million years.

Pseudhesperosuchus is a genus of sphenosuchian, a type of basal crocodylomorph, the clade that comprises the crocodilians and their closest kin. It is known from a partial skeleton and skull found in rocks of the Late Triassic (Norian-age) Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina.

Proplatyarthrus is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Megalonychidae, endemic to Chubut Province, Argentina in South America.
Afrocyon is an extinct genus of large, mostly carnivorous bone-crushing mammals known as bear dogs, of the family Amphicyonidae endemic to Africa during the Miocene to Pliocene living from 11.6 to 5.3 Ma and existed for approximately 6.3 million years.
Harpagophagus is an extinct genus of large, mostly carnivorous bone-crushing mammals of the family Amphicyonidae endemic to Europe during the Oligocene living from 33.9 to 23.03 Ma and existed for approximately 10.87 million years.

Arctoidea is a clade of mostly carnivorous mammals which include the extinct Hemicyonidae (dog-bears), and the extant Musteloidea, Pinnipedia, and Ursidae (bears), found in all continents from the Eocene, 46 million years ago, to the present. The oldest group of the clade is the bears, as their CMAH gene is still intact. The gene became non-functional in the common ancestor of the Mustelida. Arctoids are caniforms, along with dogs (canids) and extinct bear dogs (Amphicyonidae). The earliest caniforms were superficially similar to martens, which are tree-dwelling mustelids. Together with feliforms, caniforms compose the order Carnivora; sometimes Arctoidea can be considered a separate suborder from Caniformia and a sister taxon to Feliformia.
Amphicyanis is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia, family Amphicyonidae, and which inhabited Eurasia and North America.

Thaumastocyoninae is an extinct subfamily of amphicyonids, large terrestrial carnivores, which inhabited what is now Europe during the Miocene epoch. The subfamily was erected by Hürzeler (1940), and is defined by the complete suppression of m1 metaconid, reduction of the premolars, except the p4, which is reinforced, and the oblique abrasion of the teeth, and the possession of hypercarnivorous tendencies. Thaumastocyonines are poorly known, with only about 65 dental specimens, most of those isolated teeth, being known as of 2020, although more complete remains have recently been discovered.










