
The Humboldt Current, also called the Peru Current, is a cold, low-salinity ocean current that flows north along the western coast of South America. It is an eastern boundary current flowing in the direction of the equator, and extends 500–1,000 km (310–620 mi) offshore. The Humboldt Current is named after the German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt even though it was discovered by José de Acosta 250 years before Humboldt. In 1846, von Humboldt reported measurements of the cold-water current in his book Cosmos.

The big-eared brown bat is a species of vesper bat found in Argentina, Paraguay, and Chile.

Haplopappus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae found in South America, mostly restricted to the dry regions of the Southern Andes, Chilean Matorral, and Patagonia.

Ceanothus foliosus is a species of flowering shrub known by the common name wavyleaf ceanothus.

Erigeron foliosus, known by the common names leafy daisy and leafy fleabane, is a North American species of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.

The southern pudu is a species of South American deer native to the Andes of Chile and Argentina. It is found in high-altitude forests and is classified as Near Threatened in the IUCN Red List.

Ennealophus is a genus of perennial, herbaceous and bulbous plants in the family Iridaceae. It consists in five species distributed from Ecuador to Northern Brazil and Northwest Argentina. The genus name is derived from the Greek words ennea, meaning "nine", and lophus, meaning "crest".
Lophopappus is a genus of South American flowering plants in the daisy family.
Stanfieldia is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family. The single species, Stanfieldia nealleyi, was based on Haplopappus nealleyi J.M. Coulter,. Existing compilations consider the application of these names to be unresolved, but annotations on the type specimen of Haplopappus nealleyi in the US National Herbarium suggest that they may be synonyms of Clappia suaedifolia.
Clappia suaedifolia is the sole species in the North American genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, Clappia.

Potamogeton foliosus is a species of aquatic plant known by the common name leafy pondweed. It is native to nearly all of North America and parts of Central America, where it grows in water bodies such as ponds, lakes, ditches, and slow-moving streams. It has been reported from every state in the United States except Hawaii as well as from every Canadian province and territory except Newfoundland and Nunavut.

Sporobolus foliosus is a species of grass known by the common name California cordgrass. It was reclassified from Spartina foliosa after a taxonomic revision in 2014. It is native to the salt marshes and mudflats of coastal California and Baja California, especially San Francisco Bay. It is a perennial grass growing from short rhizomes. It produces single stems or clumps of thick, fleshy stems that grow up to 1.5 meters tall. They are green or purple-tinged. The long, narrow leaves are flat or rolled inward. The inflorescence is a narrow, dense, spike-like stick of branches appressed together, the unit reaching up to 25 centimeters long. The lower spikelets are sometimes enclosed in the basal sheaths of upper leaves.
Narcissus foliosus is a species of the genus Narcissus (Daffodils) in the family Amaryllidaceae. It is classified in Section Bulbocodium.
Ericameria zionis, the subalpine goldenbush or cedar breaks goldenbush, is a rare North American species of flowering plants in the daisy family. It has been found only at high elevations in the mountains in the southern part of the state of Utah in the western United States. Some of the populations lie inside Cedar Breaks National Monument and Bryce Canyon National Park.

Leucopogon foliosus is a plant in the family Ericaceae native to Western Australia. It was first described in 2016 by Michael Hislop. The species epithet, foliosus describes the leafy inflorescence.
Raymond "Ray" Carl Jackson was an American botanist, known "for his work in cytogenetics, particularly on polyploidy, and for his discovery of low chromosome numbers in angiosperms."

Haplopappus glutinosus, known also by the common name sticky haplopappus is a species of plant in the genus Haplopappus in the family Asteraceae. It is native to Chile and Argentina.

Symphyotrichum glabrifolium is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to Argentina and Chile where it inhabits wet meadows and stream edges. It is a perennial, herbaceous plant that grows 5 to 25 centimetres tall. Its flowers have white or lilac ray florets and yellow disk florets.

Symphyotrichum peteroanum is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae endemic to Argentina and Chile. It is a perennial, herbaceous plant that grows 20 to 60 centimetres tall. Its flowers have white ray florets in one series that are 6–8 millimetres long. It grows in tall forests with trees that exceed 15 metres at elevations of 1,000–2,200 metres in humid montane ecosystems.
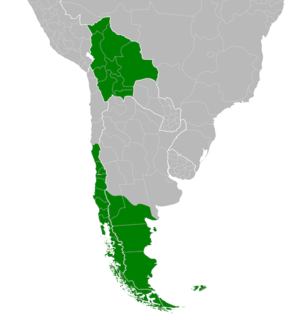
Symphyotrichum vahlii is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to South America, specifically Bolivia, Chile, Argentina, and the Falkland Islands. It is herbaceous and grows 10 to 60 centimetres tall. Its flowers have white ray florets of length 6 millimetres. It grows in wetland areas of tall forests with trees that exceed 15 metres. One infraspecies is accepted, Symphyotrichum vahlii var. tenuifolium, in addition to the autonym S. vahlii var. vahlii.














