
The rodent subfamily Sigmodontinae includes New World rats and mice, with at least 376 species. Many authorities include the Neotominae and Tylomyinae as part of a larger definition of Sigmodontinae. When those genera are included, the species count numbers at least 508. Their distribution includes much of the New World, but the genera are predominantly South American, such as brucies. They invaded South America from Central America as part of the Great American Interchange near the end of the Miocene, about 5 million years ago. Sigmodontines proceeded to diversify explosively in the formerly isolated continent. They inhabit many of the same ecological niches that the Murinae occupy in the Old World.

The New World rats and mice are a group of related rodents found in North and South America. They are extremely diverse in appearance and ecology, ranging in from the tiny Baiomys to the large Kunsia. They represent one of the few examples of muroid rodents in North America, and the only example of muroid rodents to have made it into South America.

The Strongylida suborder includes many of the important nematodes found in the gastrointestinal tracts of ruminants, horses, and swine, as well as the lungworms of ruminants and the hookworms of dogs and cats.
Oecomys auyantepui, also known as the Guianan oecomys and north Amazonian arboreal rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oecomys from South America. It is found in Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and nearby regions of Venezuela and Brazil. It is an arboreal rodent known from the understory of primary rainforest, found at altitudes from sea level to 1100 m.

Oryzomys dimidiatus, also known as the Nicaraguan oryzomys, Thomas's rice rat, or the Nicaraguan rice rat, is a rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is known from only three specimens, all collected in southeastern Nicaragua since 1904. Placed in Nectomys upon its discovery, it was later classified in its own subgenus of Oryzomys and finally recognized as closely related to other species now placed in Oryzomys, including the marsh rice rat and Coues' rice rat, which occurs in the same region.

Oryzomyini is a tribe of rodents in the subfamily Sigmodontinae of the family Cricetidae. It includes about 120 species in about thirty genera, distributed from the eastern United States to the southernmost parts of South America, including many offshore islands. It is part of the clade Oryzomyalia, which includes most of the South American Sigmodontinae.
In mammals, ungual tufts are tufts of hairs at the base of claws of the forefeet and hindfeet. Their presence has been used as a character in cladistic studies of the Cricetidae, a large family of rodents.
Hassalstrongylus forresteri is a nematode worm of the genus Hassalstrongylus that infects the marsh rice rat in the United States. It was first described as Hassalstrongylus musculi by Marie-Claude Durette-Desset in 1972, but she later recognized it as a different species, H. forresteri. The females cannot be distinguished from those of the other species in the marsh rice rat, H. musculi and H. lichtenfelsi.
Hassalstrongylus musculi is a nematode worm of the genus Hassalstrongylus that infects the marsh rice rat and house mouse in the United States and Oryzomys couesi, Oligoryzomys fulvescens, and Handleyomys melanotis in San Luis Potosí, Mexico. It was first described as Longistriata musculi by Dikmans in 1935, but transferred to Hassalstrongylus in 1971 and 1972 by Marie-Claude Durette-Desset. She later renamed the material she had used to describe H. musculi in 1972 as H. forresteri. The females cannot be distinguished from those of the other species in the marsh rice rat, H. forresteri and H. lichtenfelsi.
Hassalstrongylus lichtenfelsi is a nematode worm of the genus Hassalstrongylus that infects the marsh rice rat in Florida. The females cannot be distinguished from those of the other species in the marsh rice rat, H. forresteri and H. musculi.
Monodontus is a genus of parasitic nematodes in the subfamily Bunostominae of family Ancylostomatidae. Most of its species occur in rodents and suids, but Monodontus louisianensis is from the white-tailed deer and Monodontus giraffae from the giraffe. An unspecified Monodontus has been recorded from the marsh rice rat in Florida.
Laelaps manguinhosi is a species of parasitic mite in the family Laelapidae. In the United States, it has been found on the marsh rice rat in Florida, Texas, and South Carolina. Other recorded hosts include the sigmodontine rodents Scapteromys aquaticus, Akodon azarae, Oligoryzomys flavescens, and Holochilus brasiliensis in Argentina and Oryzomys couesi and Handleyomys melanotis in Mexico. In Venezuela, it mainly infects the oryzomyines Holochilus sciureus and Nectomys, but it has also been recorded on a variety of other mammals and even on a bird. A separate subspecies, Laelaps manguinhosi calvescens, has been described from the ichthyomyine rodent Neusticomys venezuelae.

Alain Chabaud was a French parasitologist, mainly a specialist of nematodes and sporozoa. He was the Director of the Laboratoire de Zoologie (Vers) in the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle in Paris from 1960 to 1989. He was one of the founders of the Société Française de Parasitologie in 1962 and its president until 1975, and president of the Société zoologique de France in 1967.

Trichostrongyloidea is a superfamily of nematodes under the order Strongylida.

Odilia is a genus of nematode worms established by Marie-Claude Durette-Desset in 1973 that infect mostly murid rodents of the Australasian region (species of Melomys, Rattus and Uromys from mainland Australia and Tasmania.
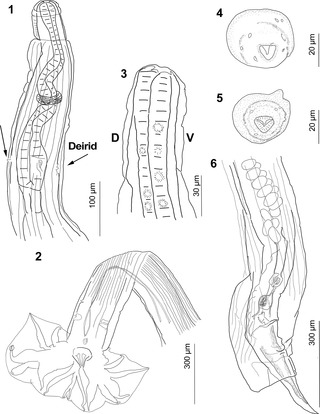
Guerrerostrongylus is a genus of nematode worms. Species of Guerrerostrongylus infect mostly the digestive tract of sigmodontine and caviomorph rodents from South America. The genus is part of the subfamily Nippostrongylinae.
Trichostrongylidae is a family of nematode in the suborder Strongylida.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialises on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research is mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.

Robert-Philippe Dollfus was a French zoologist and parasitologist.

Hassalstrongylus dollfusi is a nematode worm of the genus Hassalstrongylus, first described under the name Longistriata dollfusi by Carlos Díaz-Ungría in 1963 who named it dollfusi as an homage to French parasitologist Robert-Philippe Dollfus. The species was transferred to the genus Hassalstrongylus in 1971 by Marie-Claude Durette-Desset. Serrano et al. redescribed the species in 2021.












