
The cryptomonads are a group of algae, most of which have plastids. They are traditionally considered a division of algae among phycologists, under the name of Cryptophyta. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some may exhibit mixotrophy. They are classified as clade Cryptomonada, which is divided into two classes: heterotrophic Goniomonadea and phototrophic Cryptophyceae. The two groups are united under three shared morphological characteristics: presence of a periplast, ejectisomes with secondary scroll, and mitochondrial cristae with flat tubules. Genetic studies as early as 1994 also supported the hypothesis that Goniomonas was sister to Cryptophyceae. A study in 2018 found strong evidence that the common ancestor of Cryptomonada was an autotrophic protist.
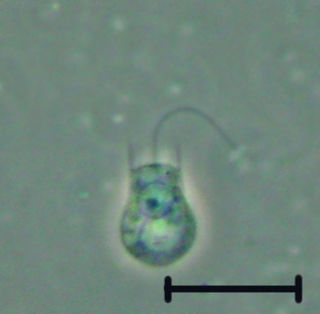
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconnected microvilli at the base of a flagellum. Choanoflagellates are capable of both asexual and sexual reproduction. They have a distinctive cell morphology characterized by an ovoid or spherical cell body 3–10 μm in diameter with a single apical flagellum surrounded by a collar of 30–40 microvilli. Movement of the flagellum creates water currents that can propel free-swimming choanoflagellates through the water column and trap bacteria and detritus against the collar of microvilli, where these foodstuffs are engulfed. This feeding provides a critical link within the global carbon cycle, linking trophic levels. In addition to their critical ecological roles, choanoflagellates are of particular interest to evolutionary biologists studying the origins of multicellularity in animals. As the closest living relatives of animals, choanoflagellates serve as a useful model for reconstructions of the last unicellular ancestor of animals. According to a 2021 study, crown group craspedids appeared 422.78 million years ago, Although a previous study from 2017 recovered the divergence of the crown group choanoflagellates (craspedids) at 786.62 million years.
Cryptomonas is the name-giving genus of the Cryptomonads established by German biologist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1831. The algae are common in freshwater habitats and brackish water worldwide and often form blooms in greater depths of lakes. The cells are usually brownish or greenish in color and are characteristic of having a slit-like furrow at the anterior. They are not known to produce any toxins. They are used to feed small zooplankton, which is the food source for small fish in fish farms. Many species of Cryptomonas can only be identified by DNA sequencing. Cryptomonas can be found in several marine ecosystems in Australia and South Korea.
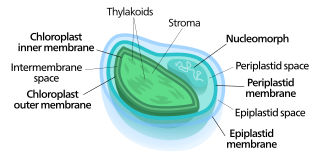
Nucleomorphs are small, vestigial eukaryotic nuclei found between the inner and outer pairs of membranes in certain plastids. They are thought to be vestiges of primitive red and green algal nuclei that were engulfed by a larger eukaryote. Because the nucleomorph lies between two sets of membranes, nucleomorphs support the endosymbiotic theory and are evidence that the plastids containing them are complex plastids. Having two sets of membranes indicate that the plastid, a prokaryote, was engulfed by a eukaryote, an alga, which was then engulfed by another eukaryote, the host cell, making the plastid an example of secondary endosymbiosis.
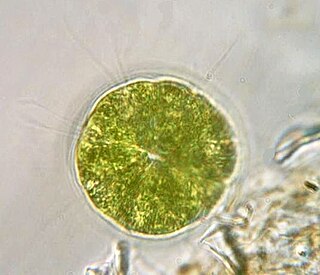
Pandorina is a genus of green algae composed of 8, 16, or sometimes 32 cells, held together at their bases to form a sack globular colony surrounded by mucilage. The cells are ovoid or slightly narrowed at one end to appear keystone- or pear-shaped. Each cell has two flagella with two contractile vacuoles at its base, an eyespot, and a large cup-shaped chloroplast with at least one pyrenoid.

Tetraselmis is a genus of phytoplankton. Tetraselmis is a green algal genus within the order Chlorodendrales, and they are characterized by their intensely-colored green chloroplast, their flagellated cell bodies, the presence of a pyrenoid within the chloroplast, and a scale-produced thecal-wall. Species within this genus are found in both marine and freshwater ecosystems across the globe; their habitat range is mainly limited by water depth due to their photosynthetic nature. Thus, they live in diverse water environments if enough nutrients and light are available for net photosynthetic activity. Tetraselmis species have proven to be useful for both research and industry. Tetraselmis species have been studied for understanding plankton growth rates, and recently a colonial species is being used to gain an understanding of multicellularity evolution. Additionally, many species are currently being examined for their use as biofuels due to their high lipid content.

The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 230 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella.

Telonemia is a phylum of microscopic eukaryotes commonly known as telonemids. They are unicellular free-living flagellates with a unique combination of cell structures, including a highly complex cytoskeleton unseen in other eukaryotes.
Lobocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiosiphonaceae. It contains the single species Lobocharacium coloradoense. It has been isolated from a pond in Colorado, United States.
Katablepharis is a genus of single-celled eukaryotes comprising five to six species. They are heterotrophic and live in both freshwater and seawater. They have two flagella and a feeding apparatus consisting of a mouth and two arrays of microtubules.

Rhodomonas is a genus of cryptomonads. It is characterized by its red colour, the square-shaped plates of its inner periplast, its short furrow ending in a gullet, and a distinctly shaped chloroplast closely associated with its nucleomorph. Historically, Rhodomonas was characterized by its red chloroplast alone, but this no longer occurs as its taxonomy has become increasingly based on molecular and cellular data. Currently, there is some debate about the taxonomic validity of Rhodomonas as a genus and further research is needed to verify its taxonomic status. Rhodomonas is typically found in marine environments, although freshwater reports exist. It is commonly used as a live feed for various aquaculture species.
Goniomonas is a genus of Cryptomonads and contains five species. It is a genus of single-celled eukaryotes, including both freshwater and marine species. It lacks plastids, which is very unusual among all of the Cryptophyte genera. It may reflect one of only a small number of times that the Cryptophytes evolved into freshwater habitats. Goniomonas seems to have a number of freshwater relatives which have not yet been cultured and named.
Geminigera /ˌdʒɛmɪnɪˈdʒɛɹə/ is a genus of cryptophyte from the family Geminigeraceae. Named for its unique pyrenoids, Geminigera is a genus with a single mixotrophic species. It was discovered in 1968 and is known for living in very cold temperatures such as under the Antarctic ice. While originally considered to be part of the genus Cryptomonas, the genus Geminigera was officially described in 1991 by D. R. A. Hill.

Guillardia is a genus of marine biflagellate cryptomonad algae with a plastid obtained through secondary endosymbiosis of a red alga.

The kathablepharids or katablepharids are a group of heterotrophic flagellates closely related to cryptomonads. First described by Heinrich Leonhards Skuja in 1939, kathablepharids were named after the genus Kathablepharis. This genus is corrected to Katablepharis under botanical nomenclature, but the original spelling is maintained under zoological nomenclature. They are single-celled protists with two anteriorly directed flagella, an anterior cytostome for ingesting eukaryotic prey, and a sheath that covers the cell membrane. They have extrusomes known as ejectisomes, as well as tubular mitochondrial cristae.
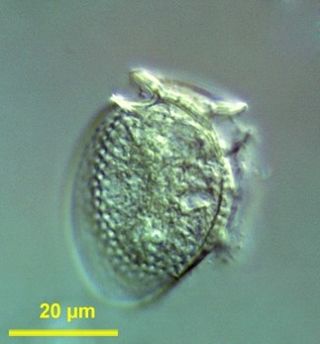
Dinophysis is a genus of dinoflagellates common in tropical, temperate, coastal and oceanic waters. It was first described in 1839 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.

Phacus is a genus of unicellular excavates, of the phylum Euglenozoa, characterized by its flat, leaf-shaped structure, and rigid cytoskeleton known as a pellicle. These eukaryotes are mostly green in colour, and have a single flagellum that extends the length of their body. They are morphologically very flat, rigid, leaf-shaped, and contain many small discoid chloroplasts.

Klebsormidium is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae comprising 20 species. The name was proposed in 1972 to resolve confusion in application and status of Hormidium and was given for the German botanist Georg Albrecht Klebs.
Mesodinium chamaeleon is a ciliate of the genus Mesodinium. It is known for being able to consume and maintain algae endosymbiotically for days before digesting the algae. It has the ability to eat red and green algae, and afterwards using the chlorophyll granules from the algae to generate energy, turning itself from being a heterotroph into an autotroph. The species was discovered in January 2012 outside the coast of Nivå, Denmark by professor Øjvind Moestrup.

Pyrenomonadaceae is a family of cryptomonads which includes three or four known genera. They are distinguished from other cryptomonads by their nucleomorphs being imbedded into the pyrenoid, and the presence of distinctive pigment phycoerythrin 545.











