
Balanus is a genus of barnacles in the family Balanidae of the subphylum Crustacea.

Thoracica is an infraclass of crustaceans which contains the most familiar species of barnacles found on rocky coasts, such as Semibalanus balanoides and Chthamalus stellatus. They have six well-developed limbs, and may be either stalked or sessile. The carapace is heavily calcified. The group includes free-living and commensal species.

Thecostraca is a class of marine invertebrates containing over 2,200 described species. Many species have planktonic larvae which become sessile or parasitic as adults.

The Balanidae comprise a family of barnacles of the order Balanomorpha. As a result of research published in 2021 by Chan et al., the members of the family Archaeobalanidae were merged with this family.

The Balanomorpha are an order of barnacles, containing familiar acorn barnacles of the seashore. The order contains these families:

Megabalanus is a genus of barnacles in the family Balanidae. Members of the genus grow to 7 cm (2.8 in) in length and inhabit the lower intertidal zone.
Calantica is a genus of barnacles in the family Calanticidae, containing the following species:

Calanticidae is a family of acorn barnacles in the order Calanticomorpha. There are about 12 genera and more than 60 described species in Calanticidae.

Paralepas is a genus of goose barnacles in the family Heteralepadidae.

Concavus is a genus of barnacles.

Poecilasmatidae is a family of goose barnacles.
Dianajonesia is a genus of goose barnacles in the family Poecilasmatidae. The taxon is a replacement name for the previously used Temnaspis, which by precedence is now accorded to a genus of megalopodid beetles. The type species of the genus is D. fissum, originally described by Charles Darwin as Poecilasma fissa. The genus contains the following species:

The clade Multicrustacea constitutes the largest superclass of crustaceans, containing approximately four-fifths of all described crustacean species, including crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, barnacles, copepods, amphipods, mantis shrimp and others. The largest branch of multicrustacea is the class Malacostraca.
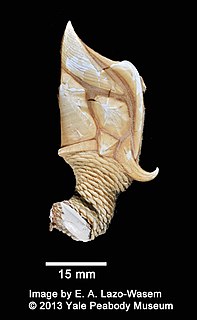
Scalpellidae is a family of acorn barnacles in the order Scalpellomorpha. There are about 25 genera and 220 described species in Scalpellidae.

Lepadiformes is an order of crustaceans belonging to the class Maxillopoda.
Verrucidae is a family of asymmetrical sessile barnacles in the order Verrucomorpha. There are about 14 genera and more than 90 described species in Verrucidae.

Scalpellomorpha is an order of acorn barnacles in the class Thecostraca. There are about 11 families in 3 superfamilies and more than 450 described species in Scalpellomorpha.
Lithoglyptida is an order of barnacles in the class Thecostraca. There are 2 families and more than 40 described species in Lithoglyptida.

Verruca is a genus of asymmetrical sessile barnacles in the family Verrucidae. There are about 20 described species in Verruca, around half of them extinct.













