
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.

Magnolia fraseri, commonly known as Fraser magnolia, mountain magnolia, earleaf cucumbertree, or mountain-oread, is a species of magnolia native to the south-eastern United States in the southern Appalachian Mountains and adjacent Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain from West Virginia south to northern Florida and west to eastern Texas. The Appalachian plants are classified as Magnolia fraseri var. fraseri, and the more coastal plants as M. fraseri var. pyramidata. These two kinds of magnolia are often recognized as distinct species, M. fraseri and M. pyramidata, respectively.

Rosa arkansana, the prairie rose or wild prairie rose, is a species of rose native to a large area of central North America, between the Appalachian and Rocky Mountains from Alberta, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan south to New Mexico, Texas and Indiana. There are two varieties:

Heuchera is a genus of largely evergreen perennial plants in the family Saxifragaceae, all native to North America. Common names include alumroot and coral bells.

Tiarella cordifolia, the heart-leaved foamflower, is a species of flowering plant in the family Saxifragaceae. The specific name cordifolia means "with heart-shaped leaves", a characteristic shared by all taxa of Tiarella in eastern North America. It is also referred to as Allegheny foamflower, false miterwort, and coolwort.

North Fork Mountain is a quartzite-capped mountain ridge in the Ridge and Valley physiographic province of the Allegheny Mountains of eastern West Virginia. Kile Knob, at 4,588 feet, is the mountain's highest point, and Panther Knob and Pike Knob are nearly as high.

In the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern United States, balds are mountain summits or crests covered primarily by thick vegetation of native grasses or shrubs occurring in areas where heavy forest growth would be expected.

Mirabilis laevis, the desert wishbone-bush, is a recently redefined species of flowering plant in the four o'clock family. Distribution is in the Southwestern United States and northwest Mexico.

Geum radiatum is a rare species of flowering plant in the rose family known by the common names spreading avens, Appalachian avens, and cliff avens. It is native to the region of the border between Tennessee and North Carolina in the southeastern United States, where there are eleven known populations remaining. The plant was federally listed as an endangered species in 1990.

Androsace villosa is an alpine plant, widespread in the mountains of Europe and Asia. It is frequently grown by alpine gardeners.

Veratrum hybridum is a species of flowering plant in the Melanthiaceae known by the common names slender bunchflower and crisped bunchflower. Many publications use the synonyms Melanthium latifolium and Veratrum latifolium, but the "hybridum" epithet is 9 years older than the "latifolium," so Veratrum hybridum is now the accepted name.

Heuchera parviflora is a species of flowering plant in the saxifrage family known by the common names cave alumroot and littleflower alumroot. It is native to the eastern United States, where it is found primarily in the Ozark Mountains, Appalachian Mountains, and Cumberland Plateau. It is found in deeply shaded areas such as under rock overhangs and cliffs, almost always where no direct sunlight falls. In this habitat, it is often the only vascular plant found. H. parviflora is an uncommon species throughout its range. It flowers in late summer through fall.
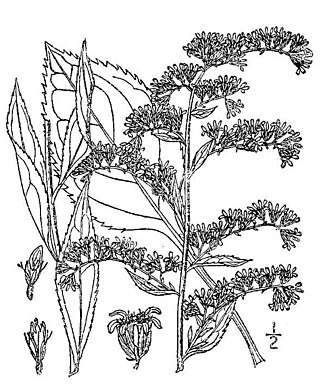
Solidago arguta, commonly called Atlantic goldenrod, cut-leaf goldenrod, and sharp-leaved goldenrod, is a species of flowering plant native to eastern and central North America. It grows along the Gulf and Atlantic states of the United States from Texas to Maine, inland as far as Ontario, Illinois, and Kansas. It is primarily found in areas of woodland openings, such as outcrops or clearings.

Gonolobus suberosus is a species of plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native to eastern North America, where it is primarily found in the southeastern United States. Its natural habitat is mesic to wet forests and thickets.

Solidago curtisii, commonly called Curtis' goldenrod and mountain decumbent goldenrod, is a North American species of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. It is the eastern part of the United States from Pennsylvania to Mississippi and Alabama, primarily in the southern Appalachian Mountains.

Heterotheca villosa, called the hairy goldenaster, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae found in central and western North America.

Cardamine flagellifera, commonly known as Blue Ridge bittercress, is a species of herbaceous plant in the mustard family. It is native to eastern North America, where it is found primarily in the southern Blue Ridge. It is a perennial that produces white flowers in the spring.

The Garden Mountain Cluster is a region in the Jefferson National Forest recognized by The Wilderness Society for its diversity of habitats extending along the east, south and west of Burke's Garden. The cluster, part of the Appalachian Mountains in southwest Virginia, connects wildlands in the high country of Garden Mountain and adjacent streams and ridges in one of the most remote areas of Virginia.




















