
The damsel in distress is a narrative device in which one or more men must rescue a woman who has been kidnapped or placed in other peril. Kinship, love, lust or a combination of those motivate the male protagonist to initiate the narrative.

Beneficial insects are any of a number of species of insects that perform valued services like pollination and pest control. The concept of beneficial is subjective and only arises in light of desired outcomes from a human perspective. In agriculture, where the goal is to raise selected crops, insects that hinder the production process are classified as pests, while insects that assist production are considered beneficial. In horticulture and gardening, beneficial insects are often considered those that contribute to pest control and native habitat integration.

The Miridae are a large and diverse insect family at one time known by the taxonomic synonym Capsidae. Species in the family may be referred to as capsid bugs or "mirid bugs". Common names include plant bugs, leaf bugs, and grass bugs. It is the largest family of true bugs belonging to the suborder Heteroptera; it includes over 10,000 known species, and new ones are being described constantly. Most widely known mirids are species that are notorious agricultural pests that pierce plant tissues, feed on the sap, and sometimes transmit viral plant diseases. Some species however, are predatory.

The insect family Nabidae contains the damsel bugs. There are over 500 species in 20 genera. They are soft-bodied, elongate, winged terrestrial predators. Many damsel bugs catch and hold prey with their forelegs, similar to mantids. They are considered helpful species in agriculture because of their predation on many types of crop pests.

The insect family Coenagrionidae is placed in the order Odonata and the suborder Zygoptera. The Zygoptera are the damselflies, which although less known than the dragonflies, are no less common. More than 1,300 species are in this family, making it the largest damselfly family. The family Coenagrionidae has six subfamilies: Agriocnemidinae, Argiinae, Coenagrioninae, Ischnurinae, Leptobasinae, and Pseudagrioninae.
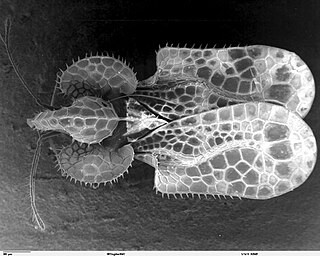
The Cimicomorpha are an infraorder of insects in the order Hemiptera, the true bugs. The rostrum and other morphology of all members apparently is adapted to feeding on animals as their prey or hosts. Members include bed bugs, bat bugs, assassin bugs, and pirate bugs.

In science fiction and fantasy literature, the term insectoid ("insect-like") denotes any fantastical fictional creature sharing physical or other traits with ordinary insects. Most frequently, insect-like or spider-like extraterrestrial life forms is meant; in such cases convergent evolution may presumably be responsible for the existence of such creatures. Occasionally, an earth-bound setting — such as in the film The Fly (1958), in which a scientist is accidentally transformed into a grotesque human–fly hybrid, or Kafka's famous novella The Metamorphosis (1915), which does not bother to explain how a man becomes an enormous insect — is the venue.

Thaumatoneura inopinata is a species of damselfly, sometimes called the cascade damselfly or giant waterfall damsel, and the only member of the genus Thaumatoneura. It is unusual in flying among the falling water and spray from waterfalls in moist tropical or subtropical forests in Costa Rica.

Nabis pseudoferus is a species of damsel bug in the family Nabidae.

Himacerus mirmicoides, common name ant damsel bug, is a species of damsel bugs belonging to the family Nabidae, subfamily Nabinae.

Himacerus apterus, known as the tree damsel bug, is a species of damsel bug belonging to the family Nabidae, subfamily Nabinae.

Nabis rugosus, the common damsel bug, is a predatory true bug. The species is found in the Palearctic. It is found in Europe from the North edge of the Mediterranean to southern Scandinavia. Further east, the distribution extends east across the Palearctic to Central Asia and Siberia. The species occurs everywhere in Central Europe and is found in the lowlands, as well as in the central uplands and in the Alps up to about 1500 meters above sea level. It is Central Europe's most common species of sickle bug and it is found in many different habitats, open, dry, shaded and moist; but it prefers moderately moist, half shady places with dominant grass. Adjacent woodland vegetation is equally important.

Himacerus boops is a species of damsel bug in the family Nabidae. It is found from South Scandinavia and the South of the British Isles over Western and Central Europe and East across the Palearctic to Siberia and in the Caspian region. They are not present in most parts of the Mediterranean.

Himacerus major is a species damsel bug in the family Nabidae. It is found in the Holarctic. The range is from South Scandinavia and the South of the British Isles over West Europe including the Western Mediterranean, Central Europe and Eastern Europe and in the Caucasus. It is also found in North America. Himacerus major occurs in many different habitats with grass, regardless of the level of humidity. The species occurs on very dry dune habitats, and nutrient-poor grasslands,as well as wet shores of waters without woody vegetation and salt places inland. The species occurs in very large numbers near the coast of the Northern Baltic Sea. It is absent from woodland.
Damsel is a synonym for mademoiselle.

Prostemmatinae is a subfamily of damsel bugs in the family Nabidae.

Nabis americoferus, the common damsel bug, is a species of damsel bug in the family Nabidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Nabis capsiformis, the pale damsel bug, is a species of damsel bug in the family Nabidae. It is found in Africa, the Caribbean, Europe and Northern Asia, Central America, North America, Oceania, and South America.

















