Related Research Articles
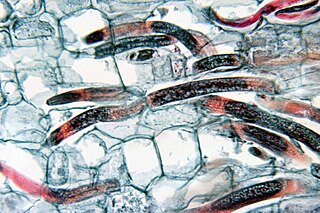
Radopholus similis is a species of nematode known commonly as the burrowing nematode. It is a parasite of plants, and it is a pest of many agricultural crops. It is an especially important pest of bananas and citrus, and it can be found on coconut, avocado, coffee, sugarcane, other grasses, and ornamentals. It is a migratory endoparasite of roots, causing lesions that form cankers. Infected plants experience malnutrition.
Belonolaimus longicaudatus is a common parasite of grasses and other plant crops and products. It is the most destructive nematode pest of turf grass, and it also attacks a wide range of fruit, vegetable, and fiber crops such as citrus, cotton, ornamentals, and forage. The sting nematode is a migratory ectoparasite of roots. It is well established in many golf courses and presents a problem in turf management. The sting nematode is only present in very sandy soils. It cannot reproduce in heavier or clay soils.
Rotylenchulus reniformis, the reniform nematode, is a species of parasitic nematode of plants with a worldwide distribution in the tropical and subtropical regions.
Paratrichodorus minor is a species of nematode in the family Trichodoridae, the stubby-root nematodes. It occurs in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. It damages plants by feeding on the roots and it is a vector of plant viruses. It is a pest of some agricultural crops.
Pratylenchus brachyurus is a plant parasitic nematode.

Pratylenchus penetrans is a species of nematode in the genus Pratylenchus, the lesion nematodes. It occurs in temperate regions worldwide, regions between the subtropics and the polar circles. It is an animal that inhabits the roots of a wide variety of plants and results in necrotic lesions on the roots. Symptoms of P. penetrans make it hard to distinguish from other plant pathogens; only an assay of soil can conclusively diagnose a nematode problem in the field. P. penetrans is physically very similar to other nematode species, but is characterized by its highly distinctive mouthpiece. P. penetrans uses its highly modified mouth organs to rupture the outer surface of subterranean plant root structures. It will then enter into the root interior and feed on the plant tissue inside. P. penetrans is considered to be a crop parasite and farmers will often treat their soil with various pesticides in an attempt to eliminate the damage caused by an infestation. In doing this, farmers will also eliminate many of the beneficial soil fauna, which will lead to an overall degradation of soil quality in the future. Alternative, more environmentally sustainable methods to control P. penetrans populations may be possible in certain regions.
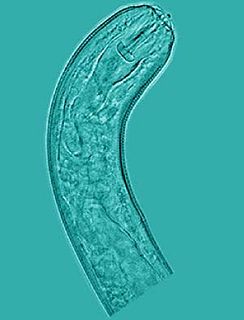
Pratylenchus zeae is a plant-pathogenic nematode found on potatoes, corn, cereal, tobacco, coffee, blackberry, and found most often on sugarcane.
Ditylenchus destructor is a plant pathogenic nematode commonly known as the potato rot nematode. Other common names include the iris nematode, the potato tuber eelworm and the potato tuber nematode. It is an endoparasitic, migratory nematode commonly found in areas such as the United States, Europe, central Asia and Southern Africa.

Ditylenchus dipsaci is a plant pathogenic nematode that primarily infects onion and garlic. It is commonly known as the stem nematode, the stem and bulb eelworm, or onion bloat. Symptoms of infection include stunted growth, discoloration of bulbs, and swollen stems. D. dipsaci is a migratory endoparasite that has a five-stage lifecycle and the ability to enter into a dormancy stage. D. dipsaci enters through stomata or plant wounds and creates galls or malformations in plant growth. This allows for the entrance of secondary pathogens such as fungi and bacteria. Management of disease is maintained through seed sanitation, heat treatment, crop rotation, and fumigation of fields. D. dipsaci is economically detrimental because infected crops are unmarketable.
Meloidogyne brevicauda is a plant-parasitic nematode. It is also called Tea root-knot nematode, Mature tea nematode or Indian root-knot nematode. It is a member of the root-knot nematodes, which was identified by C. A. Loos in 1953 in Sri Lanka.

Paratylenchus hamatus, the fig pin nematode, is a species of migratory plant endoparasites, that causes lesions on plant roots resulting in symptoms of chlorosis, wilting and ultimately yield losses. They move and feed on different parts of host tissue throughout their life cycle in order to find enough susceptible host tissue to survive and reproduce. A wide range of host plant species are susceptible to the fig pin nematode, including many valuable fruit and vegetable crops such as figs, carrots and celery. They are also commonly found associated with woody perennials in California. P. hamatus inhabits soils in both Europe and North America, and was originally isolated from fig in central California in 1950.
Xiphinema americanum is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes. It is one of many species that belongs to the genus Xiphinema. It was first described by N. A. Cobb in 1913, who found it on both sides of the United States on the roots of grass, corn, and citrus trees. Not only is Xiphinema americanum known to vector plant viruses, but also X. americanum has been referred to as "the most destructive plant parasitic nematode in America", and one of the four major nematode pests in the Southeastern United States.
Xiphinema index is a species of plant-parasitic nematodes.
Mesocriconema xenoplax is a species of plant parasitic nematodes. Nematodes of this particular species are collectively called ring nematodes.
Heterodera sacchari mitotic parthenogenic sedentary endoparasitic nematode. This plant-parasitic nematode infects the roots of sugarcane, and the female nematode eventually becomes a thick-walled cyst filled with eggs. Aboveground symptoms are species specific and are similar to those caused by other Heterodera species. Symptoms include: stunted and chlorotic plants, and reduced root growth. Seedlings may be killed in heavily infested soils.
Belonolaimus is a genus of nematodes. They are known commonly as sting nematodes. They are ectoparasites that feed on plant roots, sometimes becoming agricultural pests. They are found in the United States, Mexico, and Puerto Rico.

Pratylenchus is a genus of nematodes known commonly as lesion nematodes. They are parasitic on plants and are responsible for root lesion disease on many taxa of host plants in temperate regions around the world. Lesion nematodes are migratory endoparasites that feed and reproduce in the root and move around, unlike the cyst or root-knot nematodes, which may stay in one place. They usually only feed on the cortex of the root. Species are distinguished primarily by the morphology of the stylets.
Helicotylenchus is a genus of nematodes in the family Hoplolaimidae. They are known generally as spiral nematodes. They are found worldwide because they can live and survive in a wide range of habitats. They are among the most common parasitic nematodes of plants; found in corn, bananas, grass, soybeans.
Hoplolaimus galeatus is a plant pathogenic nematode.
Dolichodorus is a genus of nematodes known commonly as awl nematodes. They are distributed worldwide. They are ectoparasites of plant roots, and some are pests of agricultural crops.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Hoplolaimus. Nemaplex. University of California, Davis.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Bae, C. H., et al. (2008). Molecular Analysis of the lance nematode, Hoplolaimus spp., using the first internal transcribed spacer and the D1-D3 expansion segments of 28S ribosomal DNA. Journal of Nematology 40(3), 201-09.
- ↑ Hoplolaimus Host Range. Nemaplex. University of California, Davis.
- ↑ Handoo, Z. A. and A. M. Golden. (1992). A key and diagnostic compendium to the species of the genus Hoplolaimus Daday, 1905 (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae). Journal of Nematology 24(1), 45-53.
| | This Secernentea roundworm- related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |