
Agnostida are an order of extinct arthropods which have classically been seen as a group of highly modified trilobites, though some recent research has doubted this placement. Regardless, they appear to be close relatives as part of the Artiopoda. They are present in the Lower Cambrian fossil record along with trilobites from the Redlichiida, Corynexochida, and Ptychopariida orders, and were highly diverse throughout the Cambrian. Agnostidan diversity severely declined during the Cambrian-Ordovician transition, and the last agnostidans went extinct in the Late Ordovician.

Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.

Asaphida is a large, morphologically diverse order of trilobites found in marine strata dated from the Middle Cambrian until their extinction during the Silurian. Asaphida contains six superfamilies, but no suborders. Asaphids comprise some 20% of described fossil trilobites.

Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three related suborders.

Ptychopariida is a large, heterogeneous order of trilobite containing some of the most primitive species known. The earliest species occurred in the second half of the Lower Cambrian, and the last species did not survive the Ordovician–Silurian extinction event.

Richard Alan Fortey is a British palaeontologist, natural historian, writer and television presenter, who served as president of the Geological Society of London for its bicentennial year of 2007.

Arachnomorpha is a proposed subdivision or clade of Arthropoda, comprising the group formed by the trilobites and their close relatives (Artiopoda), Megacheira and chelicerates. Under this proposed classification scheme, Arachnomorpha is considered the sister group to Mandibulata.

Terataspis is a comparatively huge, 60 centimetre long lichid trilobite genus from the Early Devonian, about 397 million years ago. It lived in a shallow sea in what is now New York State and Ontario. No whole specimens have been found, only disarticulated fragments of its exoskeleton, but enough fragments have been found to allow researchers to form reconstructions of the whole animal. The genus only contains one species, T. grandis.

Arctinurus boltoni is a large lichid trilobite of the mid-Silurian. This trilobite reached about eight inches in length, though the normal adult carapace was about four inches. It lived in moderately deep-water in semi-tropical regions. Arctinurus fossils have been found in Europe and North America.
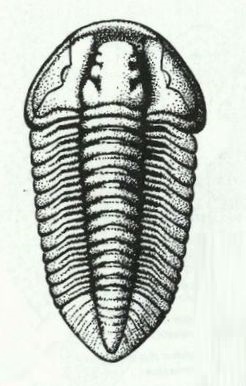
Flexicalymene Shirley, 1936. is a genus of trilobites belonging to the order Phacopida, suborder Calymenina and Family Calymenidae. Flexicalymene specimens can be mistaken for Calymene, Gravicalymene, Diacalymene and a few other Calymenina genera. They are used as an index fossil in the Ordovician. Ohio and North America are particularly known for being rich with Flexicalymene fossils.

Ronald Pearson Tripp FRSE was a British palaeontologist specializing in trilobites. He was self-taught in palaeontology and became an authority on the taxonomy of the trilobite order Lichida and the trilobite family Encrinuridae.

Encrinurus is a long-lived genus of phacopid trilobites that lived in what are now Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America from the middle Ordovician to the early Devonian from 472 to 412.3 mya, existing for approximately 59.7 million years.

Ceratarges was a genus of lichid Trilobite from the Middle Devonian to late Devonian. It lived in what is now western Europe and Morocco.

Acanthopyge is an extinct genus of lichid trilobite that lived during the Devonian. Very few A. consanguinea from the Devonian of Oklahoma have been found, and only a handful of complete specimens from Morocco, and many so-called Acanthopyge-specimens from Morocco are fake.

Odontopleurida is an order of very spinose trilobites closely related to the trilobites of the order Lichida. Some experts group the Odontopleurid families, Odontopleuridae and Damesellidae, within Lichida. Odontopleurids tend to have convex, bar-shaped cephalons, and lobed, knob-shaped glabella that extend to, or almost to the anterior margin. Many, if not almost all odontopleurids have long spines that are derived either from the margins of the exoskeleton, or from granular or tubercular ornamentation, or both. Many odontopleurids are so spinose so as to be described as having "spines on (their) spines." Odontopleurids have 8 to 13 thoracic segments, with Odontopleuridae odontopleurids having no more than 10, and Damesellidae odontopleurids having no more than 13. The pygidium tends to be very small, and invariably has long spines emanating from it in all known genera.
The cephalon is the head section of an arthropod. It is a tagma, i.e., a specialized grouping of arthropod segments. The word cephalon derives from the Greek κεφαλή (kephalē), meaning "head".
Cambrian Series 2 is the unnamed 2nd series of the Cambrian. It lies above the Terreneuvian series and below the Miaolingian. Series 2 has not been formally defined by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, lacking a precise lower boundary and subdivision into stages. The proposed lower boundary is the first appearance of trilobites which is estimated to be around 521 million years ago.

Lichas is a genus of lichid trilobites from Ordovician-Devonian-aged marine strata of Europe and Morocco.

Librostoma is a subclass of trilobites defined by having a natant hypostome, which is a hypostome that is free from the anterior doublure and aligned with the anterior of the glabella, this is unlike a conterminant hypostome, which is attached to the exoskeleton.
















