
Caracas, officially Santiago de León de Caracas, abbreviated as CCS, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas. Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the northern part of the country, within the Caracas Valley of the Venezuelan coastal mountain range. The valley is close to the Caribbean Sea, separated from the coast by a steep 2,200-meter-high (7,200 ft) mountain range, Cerro El Ávila; to the south there are more hills and mountains. The Metropolitan Region of Caracas has an estimated population of almost 5 million inhabitants.

Colonia Tovar is a town of Venezuela, capital of the municipality Tovar in Aragua state. It is located about 65.5 km (41 mi) west of Caracas. Founded on April 8, 1843, by a group of 390 immigrants from the then independent state of the Grand Duchy of Baden, it is characterized by the maintenance of the cultural imprint of their origin, so it is called "the Germany of the Caribbean". The economy depends primarily on agriculture and tourism. The Colonia Tovar is known for its temperate crops and their derivatives. Since 1990 it has shown a high rate of population growth, rising from 3,373 to 21,000 inhabitants in 2016.
Hungarian Canadians are persons in Canada of Hungarian ancestry. According to the 2016 Census, there are 348,085 Canadians of Hungarian ancestry. The Hungarian minority is the 24th largest ethnic group of Canada. The bulk of Hungarian immigration occurred after World War II, with the wave peaking after the 1956 Hungarian revolution against communist rule, when over 100,000 Hungarian refugees went to Canada. The Hungarian Canadian community is among the country's multiple ethnicities; Canada is one of the top five countries of the Hungarian diaspora.

Chacao is one of the five political and administrative subdivisions of the city of Caracas, Venezuela. The other four are Baruta, El Hatillo, Libertador and Sucre. This legal entity is known as the Caracas Metropolitan District. Chacao is also one of the 21 municipalities that make up the State of Miranda, Venezuela.
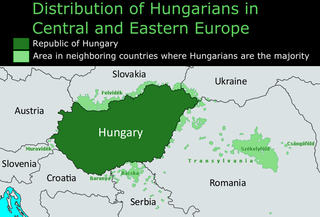
Hungarian diaspora is a term that encompasses the total ethnic Hungarian population located outside current-day Hungary.

Italian Venezuelans are Venezuelan citizens of Italian descent. The word may refer to someone born in Venezuela of Italian descent or to someone who has emigrated to Venezuela from Italy. Among European Venezuelans. Italians are one of the largest groups of immigrants to settle in the country. Approximately from 1,5 to 5 million Venezuelans have some degree of Italian ancestry.

Armenian Uruguayans number around 15,000–20,000 of the population, making Uruguay to have one of the largest Armenian populations around the world. The Armenian community in Uruguay is one of the oldest communities in South America, with most of them residing in the capital Montevideo. The majority of Armenians in Uruguay are either third or fourth-generation descendants of the first wave of immigrants coming from the Ottoman Empire between the end of the 19th century and the Armenian genocide.

Venezuelan people are people identified with Venezuela. Venezuelans are predominantly Roman Catholic and speak Spanish. The majority of Venezuelans are the result of a mixture of Europeans, Africans and Amerindians. Approximately 51.6% of the population are Pardos of mixed European, African, and Amerindian ancestry; 43.6% of Venezuelans identify as European, 3.6% identify as being Afro-Venezuelan and 2.7% identify as being Amerindian.
Arab Venezuelans refers to Venezuelan citizens of Arab origin or descent. There are around 1,600,000 Venezuelans of Arab origin, mainly from Lebanon, Syria and Palestine. Most Arab Venezuelans are of Syrian descent with their number between 400,000 and 1 million inhabitants, and Lebanese descent with their number between 341,000 and 500,000.

Éva Farkas is a Hungarian tapestry artist.
Polish Venezuelans are Venezuelan citizens of full or partial Polish ancestry. The Polish colony in Venezuela is well dispersed throughout the country, but most of the Poles and their descendants live in big cities like Caracas, Maracaibo and Valencia.
Russian Venezuelans are Venezuelan persons of full, partial, or predominantly Russian ancestry, or Russian-born persons residing in Venezuela. The term can also refer to someone with a Venezuelan mother and Russian father, or vice versa.
The Hungarian people and Hungarian Americans immigrated to Metro Detroit in the 20th century. Historically they populated Delray in Detroit but moved to the Downriver area in the 1960s. There were four historic waves of Hungarian immigration to Detroit.

Romanian Venezuelans are Venezuelans of Romanian descent or a Romania-born person who resides in Venezuela.
Scandinavian Venezuelan is a Venezuelan person of full or partial Scandinavian ancestry, or a Scandinavian-born person residing in Venezuela. Nevertheless, the Scandinavian settlement in Venezuela are almost unknown with little information about their colonization.
Greek Venezuelans are Venezuelan residents who are either fully or partially of Greek descent, or a Greece-born person who resides in Venezuela. They are mostly located in the north-center of Venezuela, concentrated in Caracas and Valencia.
Colegio Agustín Codazzi is an Italian international school in La Florida, Caracas, Venezuela.
Croatian Venezuelans are Venezuelans of full, partial, or predominantly Croat descent, or Croat-born people residing in Venezuela.

József Lenz was a Hungarian Fruit Distributor, tradesman of exotic fruits, commercial adviser, reserve hussar captain, decorated with the Order of Pro Ecclesia et Pontifice, Chairman of the National Association of Fruit, Vegetable and Food Traders of Hungary, Chairman of the Fruit Exporters and Importers Association of Hungary, member of the Hungarian Trade Statistics and Valuation Committee, and Vice-President of the "Association of Merchants of Fruits of Hungary", member of the organizing committee of the "Hungarian Fruit Export Association", urban palace owner, landowner in Nyékládháza, Bükkaranyos and Kesznyéten, art collector.













