
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Venezuela:
Contents
- General reference
- Geography of Venezuela
- Environment of Venezuela
- Regions of Venezuela
- Government and politics of Venezuela
- Branches of the government of Venezuela
- Foreign relations of Venezuela
- Law and order in Venezuela
- Military of Venezuela
- Local government in Venezuela
- History of Venezuela
- History of Venezuela, by period
- History of Venezuela, by region
- History of Venezuela, by subject
- Culture of Venezuela
- Art in Venezuela
- Sports in Venezuela
- Economy and infrastructure of Venezuela
- Education in Venezuela
- See also
- References
- External links
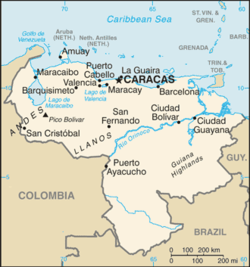
Venezuela – sovereign country located in northern South America. [1] It comprises a continental mainland and numerous islands located off the Venezuelan coastline in the Caribbean Sea. The country borders Guyana to the east, Brazil to the south, and Colombia to the west. Trinidad and Tobago, Grenada, St. Lucia, Barbados, Curaçao, Bonaire, Aruba, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and the Leeward Antilles lie just north, off the Venezuelan coast. Falling within the tropics, Venezuela sits close to the equator, in the Northern Hemisphere. A former Spanish colony, which has been an independent republic since 1821, Venezuela holds territorial disputes with Guyana, largely concerning the Essequibo area, and with Colombia concerning the Gulf of Venezuela. In 1895, after the dispute over the Guyana border flared up, it was submitted to a neutral commission, which in 1899 decided it mostly in Guyana's favour. [2] Today, the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela is known widely for its petroleum industry, the environmental diversity of its territory, and its natural features. Venezuela is considered to be among the world's 17 most biodiverse countries. [3]