
Aster is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. Its circumscription has been narrowed, and it now encompasses around 170 species, all but one of which are restricted to Eurasia; many species formerly in Aster are now in other genera of the tribe Astereae. Aster amellus is the type species of the genus and the family Asteraceae.

The Pucciniaceae are a family of rust fungi that cause plant diseases, mainly on cereals such as wheat. The family contains 20 genera and over 4900 species.
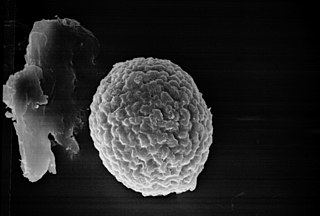
Tilletia is a genus of smut fungi in the Tilletiaceae family. Species in this genus are plant pathogens that affect various grasses. Tilletia indica, which causes Karnal bunt of wheat, and Tilletia horrida, responsible for rice kernel smut, are examples of species that affect economically important crops.

Capnodiales is a diverse order of Dothideomycetes, initially based on the family Capnodiaceae, also known as sooty mold fungi. Sooty molds grow as epiphytes, forming masses of black cells on plant leaves and are often associated with the honeydew secreted by insects feeding on plant sap. This diverse order has been expanded by the addition of several families formerly thought unrelated and now also includes saprobes, endophytes, plant pathogens, lichens and rock-inhabiting fungi. The new additions include the genus Mycosphaerella containing the causal agents of several economically important crop and tree diseases. A small number of these fungi are also able to parasitise humans and animals, including species able to colonise human hair shafts.

The Botryosphaeriaceae are a family of sac fungi (Ascomycetes), which is the type representative of the order Botryosphaeriales. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 26 genera and over 1500 species. Members of this order include notable plant pathogens.

Phyllachoraceae is a family of sac fungi.

Pucciniastrum is a genus of Basidiomycota fungi. Pucciniastrum species, like all rust fungi, are obligate plant parasites.

Lenzites is a widespread genus of wood-decay fungi in the family Polyporaceae. It was circumscribed by Elias Magnus Fries in 1835. The generic name honours German naturalist Harald Othmar Lenz (1798–1870).
Graphium is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae. Many species are known as plant pathogens. Graphium belongs to the group hyphomycetes and has about 20 species. They are found in soil, plant debris, woody substrate, manure, and polluted water. The sporulating structures of Graphium form synnema, which are a gathering of conidiophores into a sort of flower bouquet. Graphium spp. are recognized by their distinctive, erect, black synnemata, each bearing a single, terminal, ball of one-celled, hyaline conidia produced from annellides.

Bulgaria is a genus of fungi in the family Phacidiaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1822 by Elias Magnus Fries, with Bulgaria inquinans assigned as the type species.
Cintractia is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Anthracoideaceae. It was first described by Marie Maxime Cornu in 1883.
Dothidea is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Dothideaceae. The genus was first described in 1818 by Elias Magnus Fries. The type species is Dothidea sambuci.










