
Newton's parakeet, also known as the Rodrigues parakeet or Rodrigues ring-necked parakeet, is an extinct species of parrot that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues in the western Indian Ocean. Several of its features diverged from related species, indicating long-term isolation on Rodrigues and subsequent adaptation. The rose-ringed parakeet of the same genus is a close relative and probable ancestor. Newton's parakeet may itself have been ancestral to the endemic parakeets of nearby Mauritius and Réunion.

The plum-headed parakeet is a species of parakeet in the family Psittacidae. It is endemic to the Indian Subcontinent and was once thought to be conspecific with the blossom-headed parakeet before being elevated to a full species. Plum-headed parakeets are found in flocks, the males having a pinkish purple head and the females, a grey head. They fly swiftly with twists and turns accompanied by their distinctive calls.

The Blossom-headed parakeet, Psittacula roseata or Himalayapsitta roseata, is a parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It has a lime green body and a pink or bluish grey-head and is found in Southeast Asia. This species is sometimes also referred to as Rosy-headed parakeet. Biswamoy Biswas, an Indian ornithologist, is credited as the authority on this species due to his contributions researching the birds of Nepal and Bhutan.

Psittacula, also known as Afro-Asian ring-necked parrots, is a genus of parrots from Africa and Southeast Asia. It is a widespread group with a clear concentration of species in south Asia, but also with representatives in Africa and the islands of the Indian Ocean. This is the only genus of parrot which has the majority of its species in continental Asia. Of all the extant species only Psittacula calthropae, Psittacula caniceps and Psittacula echo do not have a representative subspecies in any part of mainland continental Asia. The rose-ringed parakeet, Psittacula krameri, is one of the most widely distributed of all parrots.

The slaty-headed parakeet is the only psittacid species to exhibit altitudinal migration. The species' range extends from Pakistan, to Western Himalayas in India through Nepal and Bhutan and up to the Eastern Himalayas in the northeastern Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. They descend to the valleys in winter, approximately during the last week of October.

Lord Derby's parakeet, also known as Derbyan parakeet, is a parrot species, which is confined to a small pocket of moist evergreen forest in the hills and mountains of the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam, and adjoining parts of Tibet, Sichuan and Yunnan in China. The species suffers from cutting of old trees and poaching for the illegal wildlife trade. In 2011, its status was updated from least concern to near threatened on the IUCN Red List. The adult male and female are easily distinguished because they have different beak colours and slightly different plumage.

The Seychelles parakeet or Seychelles Island parrot is an extinct species of parrot that was endemic to the Seychelles in the Indian Ocean. It was scientifically named Palaeornis wardi by the British ornithologist Edward Newton in 1867, and the specific name honours the British civil commissioner Swinburne Ward who procured the specimens that formed the basis for the description. It was found on the islands of Mahé, Silhouette, and possibly Praslin. Ten skin specimens exist today, but no skeletons. Though the species was later moved to the genus Psittacula, genetic studies have led some researchers to suggest it should belong in a reinstated Palaeornis along with the closely related Alexandrine parakeet (P. eupatria) of Asia.

Swartzia rediviva is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in Suriname.

Urocordylus is an extinct genus of nectridean tetrapodomorphs. It is the type genus of the family Urocordylidae. Fossils have been found from Ireland that date back to the Westphalian stage of the late Carboniferous. It had total length of about 19.5 in (500 mm), but the skull was only about 1.3 in (33 mm) long.

Cassiopea andromeda is one of many cnidarian species called the upside-down jellyfish. It usually lives in intertidal sand or mudflats, shallow lagoons, and around mangroves. This jellyfish, often mistaken for a sea anemone, usually keeps its mouth facing upward. Its yellow-brown bell, which has white or pale streaks and spots, pulsates to run water through its arms for respiration and to gather food.
Mesobuthus is an Asian genus of scorpions in the family Buthidae.
Palaeospinax is an extinct genus of synechodontiform cartilaginous fish. Although several species have been described, the genus is considered nomen dubium because the type-specimen of the type species, Palaeospinax priscus, from the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic of Europe lacks appropriate diagnostic characters to define the genus.
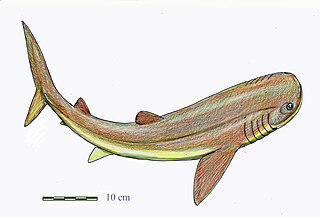
Gladbachus is an possible genus of extinct chondrichthyan.

Otobius is a genus in the soft-bodied tick family, Argasidae. While similar to the genus Ornithodoros it is characterized by a vestigial hypostome in adults, despite being developed in nymphs, in addition to the absence of both eyes and hood.

Otoba novogranatensis is a species of tree distributed from S. Nicaragua to Ecuador found in lowland to submontane forests up to 1300 m asl. It can reach heights of up to 30 m tall with a bole of 45 cm in diameter and has low buttresses.

Compsoneura is a genus comprising 23 species of trees found in tropical lowland forests of the New World. It can be distinguished from other Neotropical Myristicaceae by its conspicuous parallel tertiary venation that is nearly perpendicular to the costa.

Butia campicola is a very small species of Butia palm with an underground trunk; native to the cerrados of central Paraguay and south-central Brazil.
Compsosaurus is an extinct genus of phytosaur, a crocodile-like reptile that lived during the Triassic. Its fossils have been found in North Carolina. The type species, Compsosaurus priscus, was named by American paleontologist Joseph Leidy in 1856, although other sources say 1857. Compsosaurus may have been the same animal as the related Belodon.

Spondylis buprestoides is bark and wood-boring beetle from the genus Spondylis. These beetles are shiny black and have a cylindrical shape and have large mandibles.

Nhandu cerradensis is a species of spider from the genus Nhandu. The species is originally described by Rogério Bertani in 2001.
















