
Aerobatics is the practice of flying maneuvers involving aircraft attitudes that are not used in conventional passenger-carrying flights. The term is a portmanteau of "aerial" and "acrobatics". Aerobatics are performed in aeroplanes and gliders for training, recreation, entertainment, and sport. Additionally, some helicopters, such as the MBB Bo 105, are capable of limited aerobatic manoeuvres. An example of a fully aerobatic helicopter, capable of performing loops and rolls, is the Westland Lynx.

A model aircraft is a small unmanned aircraft. Many are replicas of real aircraft. Model aircraft are divided into two basic groups: flying and non-flying. Non-flying models are also termed static, display, or shelf models.

Control line is a simple and light way of controlling a flying model aircraft. The aircraft is connected to the operator by a pair of lines, attached to a handle, that work the elevator of the model. This allows the model to be controlled in the pitch axis. It is constrained to fly on the surface of a hemisphere by the control lines.

In flight dynamics a spin is a special category of stall resulting in autorotation about the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a shallow, rotating, downward path approximately centred on a vertical axis. Spins can be entered intentionally or unintentionally, from any flight attitude if the aircraft has sufficient yaw while at the stall point. In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying. It is possible for both wings to stall, but the angle of attack of each wing, and consequently its lift and drag, are different.

The Pitts Special is a series of light aerobatic biplanes designed by Curtis Pitts. It has accumulated many competition wins since its first flight in 1944. The Pitts biplanes dominated world aerobatic competition in the 1960s and 1970s and, even today, remain potent competition aircraft in the lower categories.

Jurgis Kairys is a Lithuanian aerobatic pilot and aeronautical engineer. He has won many awards for his flying and has invented several maneuvers, including the "Kairys Wheel." He helped develop the Sukhoi Su-26, -29, and -31 aerobatic aircraft, and also has manufactured his own aerobatic aircraft, called the "Juka."

Aerobatic maneuvers are flight paths putting aircraft in unusual attitudes, in air shows, dogfights or competition aerobatics. Aerobatics can be performed by a single aircraft or in formation with several others. Nearly all aircraft are capable of performing aerobatics maneuvers of some kind, although it may not be legal or safe to do so in certain aircraft.
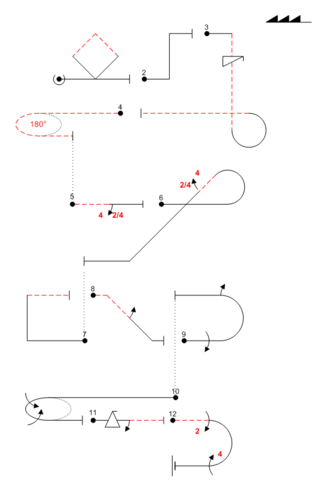
The Aresti Catalog is the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) standards document enumerating the aerobatic manoeuvers permitted in aerobatic competition. Designed by Spanish aviator Colonel José Luis Aresti Aguirre (1919–2003), each figure in the catalog is represented by lines, arrows, geometric shapes and numbers representing the precise form of a manoeuver to be flown.

A radio-controlled helicopter is model aircraft which is distinct from a RC airplane because of the differences in construction, aerodynamics, and flight training. Several basic designs of RC helicopters exist, of which some are more maneuverable than others. The more maneuverable designs are often harder to fly, but benefit from greater aerobatic capabilities.
Competition aerobatics is an air sport in which ground-based judges rate the skill of pilots performing aerobatic flying. It is practised in both piston-powered single-engine airplanes and also gliders.

A barrel roll is an aerial maneuver in which an airplane makes a complete rotation on both its longitudinal and lateral axes, causing it to follow a helical path, approximately maintaining its original direction. It is sometimes described as a "combination of a loop and a roll". The g-force is kept positive on the object throughout the maneuver, commonly between 2 and 3g, and no less than 0.5g. The barrel roll is commonly confused with an aileron roll.

A radio-controlled glider is a type of radio-controlled aircraft that normally does not have any form of propulsion. They are able to sustain continuous flight by exploiting the lift produced by slopes and thermals, controlled remotely from the ground with a transmitter. They can be constructed from a variety of materials, including wood, plastic, polymer foams, and composites, and can vary in wing loading from very light to relatively heavy, depending on their intended use.

Wayne Handley is an American airshow performer, former naval aviator, agricultural pilot, Aerobatic Competency Evaluator (ACE), and coach for upcoming and current airshow stars. Handley and his wife Karen are former residents of the Salinas Valley of California, who currently reside in Groveland, California.
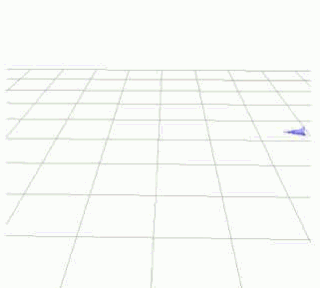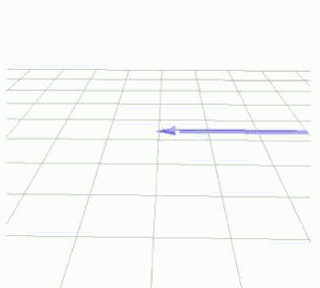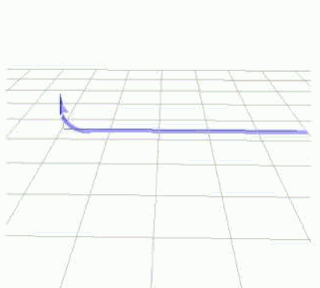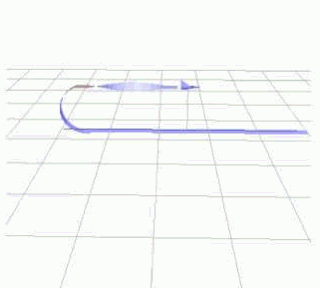
The term Immelmann turn, named after German World War I Eindecker fighter ace Lieutnant Max Immelmann, refers to two different aircraft maneuvers. In World War I aerial combat, an Immelmann turn was a maneuver used after an attack on another aircraft to reposition the attacking aircraft for another attack. In modern aerobatics, an Immelmann turn is an aerobatic maneuver that results in level flight in the opposite direction at a higher altitude.

A Cuban eight or Cuban 8 is a figure eight aerobatic maneuver for both full-scale and radio-controlled fixed-wing aircraft.

The aileron roll is an aerobatic maneuver in which an aircraft does a full 360° revolution about its longitudinal axis. When executed properly, there is no appreciable change in altitude and the aircraft exits the maneuver on the same heading as it entered. This is commonly one of the first maneuvers taught in basic aerobatics courses. The aileron roll is commonly confused with a barrel roll.

Radio-controlled aerobatics is the practice of flying radio-controlled aircraft in maneuvers involving aircraft attitudes that are not used in normal flight.
3D Aerobatics or 3D flying is a form of flying using flying aircraft to perform specific aerial maneuvers. They are usually performed when the aircraft had been intentionally placed in a stalled position.

A slow roll is a roll made by an airplane, in which the plane makes a complete rotation around its roll axis while keeping the aircraft flying a straight and level flightpath. A slow roll is performed more slowly than an aileron roll; although it is not necessarily performed very slowly, it is performed slowly enough to allow the pilot to maintain balance, keeping a steady flightpath, pitch angle, and height (altitude) throughout the maneuver. The maneuver is performed by rolling the airplane at a controlled rate with the ailerons, and moving the elevators and rudder in opposition, or "cross-controlling," to keep the plane on a steady, level flightpath.
Rob Holland is a highly accomplished aerobatic pilot from the United States. currently residing in Nashua, New Hampshire. Holland is one of the most decorated aerobatic pilots in U.S. history, with an impressive list of accomplishments that includes multiple championship titles and groundbreaking innovations in the field of aerobatics.

















