
Kayayei or Kaya Yei is a Ghanaian term for a female porter or bearer. Many of these women have migrated from a rural community to any of Ghana's urban cities in search of work. [1] [2] They generally carry their burdens on their heads.

Kayayei or Kaya Yei is a Ghanaian term for a female porter or bearer. Many of these women have migrated from a rural community to any of Ghana's urban cities in search of work. [1] [2] They generally carry their burdens on their heads.
The term kayayei (singular, kaya yoo) is a compound formed from two languages spoken in Ghana. Kaya means "load, luggage, goods [1] or burden" [3] in the Hausa language, and yei means "women or females" in the Ga language,. [1] People in Kumasi refer to the porters as paa o paa.
Kaya have always been manual labourers. They transport goods to and from markets, particularly agricultural goods. [4] Typically, Kaya carry their loads in a large pan placed on their heads, using a moistened coil of cloth as a buffer, see Head-carrying.

Kaya Yei still toil away in markets in Ghana today, often in poor conditions and with minimal income. Occasionally, Kaya are brought into private homes to perform domestic tasks, where they may earn slightly more. The Kaya are often transient, and often without basic sanitation. Basic hygiene & nutrition conditions are also poor. In larger cities such as Accra & Kumasi, Kaya are often migrants from remote regions who have come to the cities in search for better employment prospects. [1] [2]
In May 2016, the Minister for Gender, Children and Social Protection Nana Oye Lithur ensured that over 1,000 kayayei from Agbogbloshie and Mallam Atta markets in Accra were registered onto the National Health Insurance Scheme, to help provide them access to basic healthcare service. [5] In the 2017 annual budget, the Minister of Finance Ken Ofori-Atta exempted kayayei from paying market tolls to their various assemblies . [6]

The University of Ghana is the oldest and largest of the thirteen Ghanaian national public universities. It was founded in 1948, in the British colony of the Gold Coast, as the University College of the Gold Coast, and was originally an affiliate college of the University of London, which supervised its academic programs and awarded degrees. After independence in 1957, the college was renamed the University College of Ghana. It changed its name again to the University of Ghana in 1961, when it gained full university status. The University of Ghana is situated on the West view of the Accra Legon hills and at the northeast of the centre of Accra, now has various schools, institutions, colleges and departments and has over 40,000 registered students.
Articles related to Ghana include:
Georgina Theodora Wood is a Ghanaian judge and also a former police prosecution officer. She was the Chief Justice of Ghana and the first woman to occupy that position. She retired in 2017 after five decades of service to the state. She is a member of the Council of State.
Pokuase, also spelled Pokoasi, is a suburb of Accra, the capital city of Ghana and spans the area from Pokuase, leading off the Accra-Kumasi motorway on the right coming from Accra central; and leading off the motorway at Pokuase Junction and rising to ‘Okai Kwei Hill’, on the left coming from town. It is a mixture of lively retail shopping areas, with local stores, bars or 'drinking spots', bus/taxi stations, and a market. It also has many hotels, guest houses and rental apartments- such as the eco-chic Legassi Gardens Apartments-, and 'high-end' developing residential estates, such as Ofankor Hills Estates and Franko Estates, amongst many others; as well as the long-established executive gated community of ACP Estates.; and HFS Estates which borders the erstwhile Gua Koo Sacred Grove in Pokuase.

Jane Naana Opoku-Agyemang is a Ghanaian academic and politician who served as Minister for Education from February 2013 to January 2017. She is a full professor of literature. She served as the first female Vice-Chancellor of a state university in Ghana when she took over as Vice-Chancellor of University of Cape Coast. She currently serves as the Chancellor of the Women's University in Africa.

The Ghana Prisons Service is responsible for the safe custody of prisoners in Ghana, as well as their welfare, reformation and rehabilitation. It is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of the Interior.

Ghana gained independence from the British on 6 March 1957. It is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. The country became a republic on July 1, 1960.

The Ministry of Women and Children's Affairs (MWCA) or Ministry of Gender, Children and Social Protection (MGCSP) of Ghana is the government ministry responsible for the formulation of policies that promote the institutionalization and development of women and children issues.
Abofour is a town in the Offinso Municipality in Ashanti Region of Ghana It is the second largest town in the Municipality after the Offinso township. It is in fact one of the most populated townships in the Ashanti REGION of Ghana. Though Offinso is the Municipal capital, Abofour undoubtedly is the ecomic hub of the municipality by the virtue of having one of the largest Markets in the country.
Ghanaian Indians are Ghanaians citizens of Indian origin or descent. Many Ghanaian Indians are descendants from those who migrated from India following India's partition in 1947.

Nana Oye Lithur is a Ghanaian barrister and politician. She was the Minister for Gender, Children and Social Protection in Ghana from 2013 to 2017, appointed by President John Mahama after the Ghanaian general election. She is a member of the National Democratic Congress.

The Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration (GIMPA) is a public co-educational university spread over four campuses and made up of six schools, ten research centers located at Greenhill in Accra, Ghana. The location of GIMPA, Greenhill, was named by Nicholas T. Clerk who served as the Rector of the Institute from 1977 to 1982. The name, "Greenhill", is a reference to the lush greenery and hilly topography of the main campus, as well as its location in Legon which was historically on the periphery of the Ghanaian capital, Accra. Together with 200 state institutions, GIMPA successfully participated in a Public Sector Reform Programme under the auspices of the World Bank and became a self-financing institution as part of the National Institutional Reform Programme in 2001. It was established as a public university by an Act of Parliament in 2004. The institute was established in 1961 by the Government of Ghana with assistance from the United Nations Special Fund Project and was initially called the Institute of Public Administration, intended as a specialist training graduate school for civil servants in Ghana. Today, GIMPA offers bachelor's, master's and executive master's degree programmes in business administration, entrepreneurship, law, public administration, development management, governance, leadership and technology.
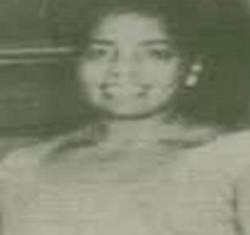
Susan Barbara Gyankorama Ofori-Atta also de Graft-Johnson, was a Ghanaian medical doctor – the first female doctor on the Gold Coast. She was the first Ghanaian woman and fourth West African woman to earn a university degree. Ofori-Atta was also the third West African woman to become a physician after the Nigerians Agnes Yewande Savage (1929) and Elizabeth Abimbola Awoliyi (1938). In 1933, Sierra Leonean political activist and higher education pioneer, Edna Elliot-Horton became the second West African woman university graduate and the first to earn a bachelor's degree in the liberal arts. Eventually Ofori-Atta became a medical officer-in-charge at the Kumasi Hospital, and later, she assumed in charge of the Princess Louise Hospital for Women. Her contemporary was Matilda J. Clerk, the second Ghanaian woman and fourth West African woman to become a physician, who was also educated at Achimota and Edinburgh. Ofori-Atta was made an Honorary Doctor of Science by the University of Ghana for her work on malnutrition in children, and received the Royal Cross from Pope John Paul II when he visited Ghana in 1980, in recognition of her offering of free medical services at her clinic. She helped to establish the Women's Society for Public Affairs and was a Foundation Fellow of the Ghana Academy of Arts and Sciences. Her achievements were a symbol of inspiration to aspiring women physicians in Ghana.
Samuel Attah-Mensah, also known as 'Sammens', is a Ghanaian media personality, business man and lecturer. He is the managing director of award-winning Accra-based English speaking radio station Citi FM. He is also the Vice President of Ghana Independent Broadcasters Association (GIBA). He is a Fellow of the third class of the African Leadership Initiative-West Africa and a member of the Aspen Global Leadership Network.
Mary Grant was a Ghanaian physician and politician. She was Ghana's first Council of State member and also the first Wesley Girls High School alumna to be a medical doctor. Grant was the third Ghanaian woman to qualify in medicine after Susan Ofori-Atta (1947) and Matilda J. Clerk (1949). She was a relation of Paa Grant, who has been called "the father of Gold Coast politics".

Freda Akosua Oheneafrewo Prempeh is a Ghanaian politician, and Member of Parliament in the Seventh Parliament and Eighth Parliament of the fourth republic of Ghana representing Tano North Constituency in the Ahafo Region, Ghana. She's currently the Minister of State, for the Ministry of works and housing, Ghana. She previously served as the Deputy Gender Minister and also Assembly member - "Assembly Woman" from 2002 to 2010 for the Lakoo Electoral Area of the La-Dadekotopo Constituency in the Greater Accra Region.

MatildaJohannaClerk was a medical pioneer and a science educator on the Gold Coast and later in Ghana as well as the second Ghanaian woman to become an orthodox medicine-trained physician. The first woman in Ghana and West Africa to attend graduate school and earn a postgraduate diploma, Clerk was also the first Ghanaian woman in any field to be awarded an academic merit scholarship for university education abroad. M. J. Clerk was the fourth West African woman to become a physician after Nigerians, Agnes Yewande Savage (1929), the first West African woman medical doctor and Elizabeth Abimbola Awoliyi (1938) in addition to Susan de Graft-Johnson, née Ofori-Atta (1947), Ghana's first woman physician. These pioneering physicians were all early advocates of maternal health, paediatric care and public health in the sub-region. For a long time after independence in 1957, Clerk and Ofori-Atta were the only two women doctors in Ghana. By breaking the glass ceiling in medicine and other institutional barriers to healthcare delivery, they were an inspiration to a generation of post-colonial Ghanaian and West African female doctors at a time the field was still a male monopoly and when the vast majority of women worldwide had very limited access to biomedicine and higher education. Pundits in the male-dominated medical community in that era described Matilda J. Clerk as "the beacon of emancipation of Ghanaian womanhood."

The Ridge Church School is an independent and parochial co-educational preparatory day school in Accra, Ghana. Situated between the Gamel Abdul Nasser Avenue and Guinea Bissau Road and opposite the Efua Sutherland Children's Park, it was founded by the Accra Ridge Church in 1957, the year of Ghana's independence from the United Kingdom. The Ridge Church School is located on the premises of the church. It was the first wholly private basic school to be established in modern Ghana. The Accra Ridge Church was the first international solely English-speaking Protestant church in Ghana. The school is inter-denominational Christian, holding ties to the Anglican, Methodist and Presbyterian churches, that assign chaplains to both the church and school. The school runs a ten–year programme from kindergarten to lower primary through upper primary to junior high and culminating in the Basic Education Certificate Examination (BECE) administered by the West African Examinations Council (WAEC). The school largely follows the prescribed curriculum and syllabus of the Ghana Education Service (GES).
Pisces Aviation is a domestic airline of Ghana with its head office in Accra, Ghana, and its main hub at Kotoka International Airport in Accra.

Mohammed Adamu Ramadan is a Ghanaian politician. He is a member of the National Democratic Congress. He is the member of parliament for the Adenta Constituency. He is the son of politician Ahmed Ramadan and the elder brother of Samira Bawumia, the Second Lady of Ghana.