
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Lusophone (Portuguese-speaking) country in both total area and population and is the seventh-largest country in Africa. It is bordered by Namibia to the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Zambia to the east, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Angola has an exclave province, the province of Cabinda, that borders the Republic of the Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The capital and most populous city is Luanda.

The Republic of the Congo is located in the western part of central Africa, on the Equator. Congo has several important ports. The Republic of the Congo covers an area of 342,000 km², of which 341,500 km² is land while 500 km² is water. Congo claims 200 nautical miles (370 km) of territorial sea.
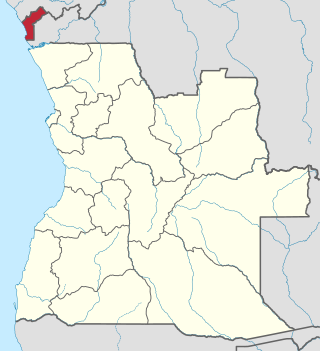
Cabinda is an exclave and province of Angola, a status that has been disputed by several political organizations in the territory. The capital city is also called Cabinda, known locally as Tchiowa, Tsiowa or Kiowa. The province is divided into four municipalities—Belize, Buco-Zau, Cabinda and Cacongo.

Matadi is the chief sea port of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the capital of the Kongo Central province, adjacent to the border with Angola. It had a population of 245,862 (2004). Matadi is situated on the left bank of the Congo River, 148 km (92 mi) from the mouth and 8 km (5.0 mi) below the last navigable point before the rapids that make the river impassable for a long stretch upriver.

Zaire is one of the 18 provinces of Angola. It occupies 40,130 square kilometres (15,490 sq mi) in the north west of the country and had a population of 594,428 inhabitants in 2014. It is bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean, on the north by the Democratic Republic of Congo, on the east by the Uíge Province, and on the south by the Bengo Province.

Kouilou is a department of the Republic of the Congo. Covering the country's coastline, it has an area of 13,650 square kilometres and at the start of 2023 it was home to about 97,362 people. The department borders Niari Department, the commune of Pointe-Noire, and internationally, Gabon and the Cabinda area of Angola.

Niari is a department of the Republic of the Congo in the western part of the country. It borders the departments of Bouenza, Kouilou, and Lékoumou, and internationally, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Cabinda portion of Angola. The regional capital is Dolisie.

The Departments of the Republic of the Congo are divided into 86 districts and 6 communes; which are further subdivided into urban communities and rural communities ; which are further subdivided into quarters or neighborhoods (quartiers) and villages. Note the departments of Brazzaville and Pointe-Noire are made of 1 commune each, then divided in urban districts (arrondissements).

The Republic of Cabinda was an independent protectorate of Portugal that was taken over by Angola after Portugal declared Angola a free country. It is currently an unrecognized state, which Angola considers its Cabinda Province property. The Front for the Liberation of the State of Cabinda-Exército de Cabinda (FLEC) claimed sovereignty just after the Republic of Cabinda was proclaimed as an independent country in 1975 from Portugal and just after Angola invaded. The government of this entity operates in exile, with offices located in Paris, France, and Pointe Noire, Republic of the Congo.
Caianda is a town in eastern Moxico province, which is in the northeastern part of Angola, adjacent to the border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Brazza's martin is a passerine bird in the swallow family, Hirundinidae. It is 12 centimeters (4.7 in) long with grey-brown upperparts, heavily black-streaked white underparts, and a brownish tint to the breast plumage. The sexes are similar, but juvenile birds have more diffuse breast streaking and reddish-brown edges to the feathers of the back and wings. The song consists of a series of short notes of increasing frequency, followed by a complex buzz that is sometimes completed by a number of clicks.

The Angolan fruit bat, Angolan rousette or silky bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of Congo, Democratic Republic of Congo, Kenya, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest, moist savanna, and rocky areas.

Angola is located on the western Atlantic Coast of Southern Africa between Namibia and the Republic of the Congo. It also is bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia to the east. The country consists of a sparsely watered and somewhat sterile coastal plain extending inland for a distance varying from 50 to 160 km. Slightly inland and parallel to the coast is a belt of hills and mountains and behind those a large plateau. The total land size is 1,246,700 km2 (481,400 sq mi). It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 518,433 km2 (200,168 sq mi).

Congo, officially the Republic of the Congo or Congo Republic, also known as Congo-Brazzaville is a country located on the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo River. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to the northwest by Cameroon, to the northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda, and to the southwest by the Atlantic Ocean.

The Chiloango River is a river in western Central Africa. It forms the westernmost part of the border between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of Congo, and then forms approximately half of the border between the DRC and Cabinda, Angola passing just south of the town of Necuto. The river then bisects Cabinda, making it the most important river in the province. It enters the Atlantic Ocean just north of the town of Cacongo.

The Cabinda War is an ongoing separatist insurgency, waged by the Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda (FLEC) against the government of Angola. FLEC aims at the restoration of the self-proclaimed Republic of Cabinda, located within the borders of the Cabinda province of Angola.

Kwango is a province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It's one of the 21 provinces created in the 2015 repartitioning. Kwango, Kwilu, and Mai-Ndombe provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Bandundu province. Kwango was formed from the Kwango district whose town of Kenge was made the provincial capital and thus gained city status.

Mayombe is a geographic area on the western coast of Africa occupied by low mountains extending from the mouth of the Congo River in the south to the Kouilou-Niari River to the north. The area includes parts of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, the Republic of the Congo and Gabon. In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mayombe is part of the north-western province of Kongo Central on the right bank of the River Congo, and contains the cities and towns of Lukula, Seke Banza, Kangu and Tshela.

The Sundi are a Central African people established in three countries, in the Republic of Congo – particularly in the Niari department, in the Bouenza department (Boko-Songho) and in the Pool Department –, in Angola (Cabinda) and in the Democratic Republic of Congo. They are considered to be the largest subgroup of the Kongo people. Early in the nineteenth century there were wars between Sundi and Teke when Teke moved southwest into the Niari valley.


















