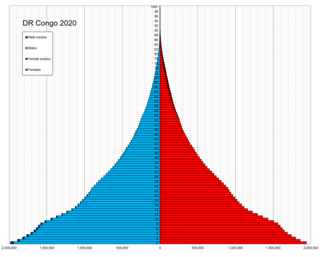
Demographic features of the population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo include ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The Republic of the Congo is located in the western part of central Africa, on the Equator. Congo has several important ports. The Republic of the Congo covers an area of 342,000 km², of which 341,500 km² is land while 500 km² is water. Congo claims 200 nautical miles (370 km) of territorial sea.

The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world by discharge volume, following the Amazon and Ganges rivers. It is the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths of around 220 m (720 ft). The Congo–Lualaba–Luvua–Luapula–Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,900 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,100 mi).

French Equatorial Africa was a federation of French colonial territories in Equatorial Africa which consisted of Gabon, French Congo, Ubangi-Shari, and Chad. It existed from 1910 to 1958 and its administration was based in Brazzaville.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo, also known as the DR Congo, the DRC, or Congo-Kinshasa, is a country in Central Africa. By land area the Congo is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 109 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, the Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean.

The French Congo or Middle Congo was a French colony which at one time comprised the present-day area of the Republic of the Congo and parts of Gabon, and the Central African Republic. In 1910, it was made part of the larger French Equatorial Africa.

Kouilou is a department of the Republic of the Congo. Covering the country's coastline, it has an area of 13,650 square kilometres and at the start of 2023 it was home to about 97,362 people. The department borders Niari Department, the commune of Pointe-Noire, and internationally, Gabon and the Cabinda area of Angola.

Plateaux is a department of the Republic of the Congo in the central part of the country. It borders the departments of Cuvette, Cuvette Ouest, Lékoumou and Pool, and internationally, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the east and Gabon on the west. The regional capital is Djambala. Principal cities and towns include Gamboma and Lekana.

The Congo Basin is the sedimentary basin of the Congo River. The Congo Basin is located in Central Africa, in a region known as west equatorial Africa. The Congo Basin region is sometimes known simply as the Congo. It contains some of the largest tropical rainforests in the world and is an important source of water used in agriculture and energy generation.

Turn It On Again: The Hits is a greatest hits album by British progressive rock/pop-rock band Genesis. The album was originally released as a single album on 25 October 1999 by Virgin Records in the UK and on 26 October 1999 by Atlantic Records in the US.
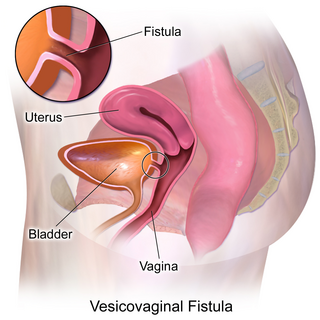
Vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) is a subtype of female urogenital fistula (UGF).

The Senate is the upper house of the Parliament of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The senate was established in 1960, abolished in 1967 and re-established in 2003.

The Parliament of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the legislative branch of the Congolese government. It consists of two chambers:
The National Assembly is the lower house and main legislative political body of the Parliament of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is one of the two legislative bodies along with the Senate. The National Assembly is composed of deputies who are elected by the citizens of the DRC. The deputies serve as the voice of the people and are responsible for enacting legislation, representing their constituents' interests, and overseeing the executive branch of government. The National Assembly is responsible for deliberating and passing laws that impact the nation and its citizens. It was established by the 2006 constitution, which provided for a bicameral parliament consisting of the National Assembly and the Senate. It is located at the People's Palace in Kinshasa.

The People's Republic of the Congo was a Marxist–Leninist socialist state that existed in the Republic of the Congo from 1969 to 1992.

The Republic of the Congo was a sovereign state in Central Africa, created with the independence of the Belgian Congo in 1960. From 1960 to 1966, the country was also known as Congo-Léopoldville to distinguish it from its northwestern neighbor, which is also called the Republic of the Congo, alternatively known as "Congo-Brazzaville". In 1964, the state's official name was changed to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, but the two countries continued to be distinguished by their capitals; with the renaming of Léopoldville as Kinshasa in 1966, it became also known as Congo-Kinshasa. After Joseph Désiré Mobutu, commander-in-chief of the national army, seized control of the government in 1965, the Democratic Republic of the Congo became the Republic of Zaire in 1971. It would again become the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1997. The period between 1960 and 1964 is referred to as the First Congolese Republic.

Congo, officially the Republic of the Congo or Congo Republic, also known as Congo-Brazzaville is a country located on the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo River. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to the northwest by Cameroon, to the northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda, and to the southwest by the Atlantic Ocean.
Kouan-Houlé is a town in the far west of Ivory Coast. It is a sub-prefecture of Danané Department in Tonkpi Region, Montagnes District.
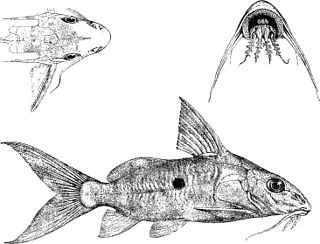
Synodontis nummifer, known as the two spot synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was first described by the Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, based upon a holotype discovered in Léopoldville, Belgian Congo. The specific name "nummifer" comes from the Latin for "to bear a coin", which refers to the large spots on its sides.