
The Republic of Haiti comprises the western three-eighths of the island of Hispaniola, west of the Dominican Republic. Haiti is positioned east of the neighboring island of Cuba, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean. Haiti's geographic coordinates are at a longitude of 72° 25′ west and a latitude of 19° 00′ north.

Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital and largest city, Luxembourg City, is one of the four official capitals of the European Union and the seat of several EU agencies, notably the Court of Justice of the European Union, the highest judicial authority. Luxembourg's culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its French and German neighbors; while Luxembourgish is legally the only national language of the Luxembourgish people, French and German are used in administrative and judicial matters and jointly considered administrative languages of the country.

Luxembourg is a small country located in the Low Countries, part of North-West Europe It borders Belgium for 148 kilometres to the west and north, France (73 km [45 mi]) to the south, and Germany (138 km [86 mi]) to the east. Luxembourg is landlocked, separated from the North Sea by Belgium.

The economy of Luxembourg is largely dependent on the banking, steel, and industrial sectors. Luxembourgers enjoy the highest per capita gross domestic product in the world.

Luxembourg, also known as Luxembourg City, is the capital city of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg and the country's most populous commune. Standing at the confluence of the Alzette and Pétrusse rivers in southern Luxembourg, the city lies at the heart of Western Europe, situated 213 km (132 mi) by road from Brussels, 372 km (231 mi) from Paris, and 209 km (130 mi) from Cologne. The city contains Luxembourg Castle, established by the Franks in the Early Middle Ages, around which a settlement developed.
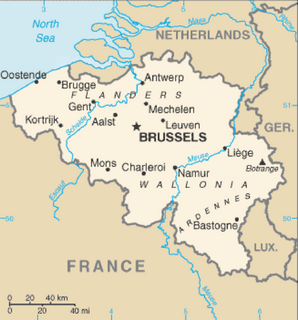
Belgium is a federal state located in Western Europe, bordering the North Sea. Belgium shares borders with France (556 km), Germany (133 km), Luxembourg (130 km) and the Netherlands (478 km). Belgium is divided into three regions: Flanders, Wallonia and Brussels.

The Ardennes, also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, extending into Germany and France. Geologically, the range is a western extension of the Eifel; both were raised during the Givetian age of the Devonian, as were several other named ranges of the same greater range.

The Vosges are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around 8,000 km2 (3,100 sq mi) in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate to the Börrstadt Basin, and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain.

The A75 is an autoroute (motorway) in France.

Buurgplaatz is a hill in the commune of Troisvierges, in northern Luxembourg. The 559-metre-high (1,834 ft) summit lies within the Oesling region at 50.1615°N 6.0281°E.

Jonas Ferdinand Gabriel Lippmann was a Franco-Luxembourgish physicist and inventor, and Nobel laureate in physics for his method of reproducing colours photographically based on the phenomenon of interference. His parents were French Jews.

Troisvierges is a commune and town in northern Luxembourg, in the canton of Clervaux. The two highest hills in Luxembourg, the Kneiff and Buurgplaatz, are located in the commune.

Luxembourg's National Olympic Committee, the Luxembourg Olympic and Sporting Committee, was founded in 1912 and sent its first team to the 1912 Summer Olympics in Stockholm.

Napoléonsgaard is a hill in the commune of Rambrouch, in western Luxembourg. It is 554 metres (1,818 ft) tall, and lies to the north-east of

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Luxembourg enjoy similar rights to non-LGBT people. Partnerships, which grant many of the benefits of marriage, have been recognised since 2004. In June 2014, the Luxembourgish Parliament passed a law enabling same-sex marriage and adoption rights, which took effect on 1 January 2015. Additionally, discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and "change of sex" in employment, healthcare and the provision of goods and services is outlawed, and transgender people are allowed to change their legal gender on the basis of self-determination.

This is a list of the extreme points of Luxembourg, the points that are farther north, south, east or west, higher or lower than any other location in the territory of the state.

Joué-du-Plain is a commune in the Orne department in north-western France. The commune was mentioned in 1216 by the name of "Jeum". There are 201 people living there. It is 1,456 hectares (5.6 sq mi) in size. The highest point in the commune is 170 metres (560 ft). The river Udon flows through the commune. The community festival is 29 June.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Luxembourg:

The Esch-sur-Sûre Dam is an arch dam on the River Sauer just upstream of Esch-sur-Sûre in the Wiltz canton of Luxembourg. The primary purpose of the dam and its reservoir, Upper Sûre Lake, is to provide municipal water supply and hydroelectric power generation. The dam is operated jointly by the Administration of Roads and Bridges and the Syndicate des Eaux du Barrage d'Esch-sur-Sûre (SEBES) while the power station is operated by Société Electrique de l'Our (SEO).
The Council of Luxembourg was the central institution in the government of the Duchy of Luxembourg from 1444 to 1795, in direct descent from the medieval council of the dukes. It was a body that had both administrative and judicial authority. The council was reorganized by Charles V in 1531–1532. Until 1782, legal decisions of the council could be appealed to the Great Council of Mechelen. On 1 August 1782 the council was made "sovereign", that is, the highest court in its jurisdiction.



















