
Hemidactylus is a genus of the common gecko family, Gekkonidae. It has 174 described species, newfound ones being described every few years. These geckos are found in all the tropical regions of the world, extending into the subtropical parts of Africa and Europe. They excel in colonizing oceanic islands by rafting on flotsam, and are for example found across most of Polynesia. In some archipelagoes, cryptic species complexes are found. Geckos like to live in and out of houses. They have been introduced to Australia.

Parvoscincus is a genus of skinks, lizards in the family Scincidae. The genus is endemic to the Philippines.

Acanthodactylus is a genus of lacertid lizards, commonly referred to as fringe-fingered lizards, fringe-toed lizards, and spiny-toed lizards.

Lates is a genus of lates perches belonging to the family Latidae. The generic name is also used as a common name, lates, for many of the species.

George Albert Boulenger was a Belgian-British zoologist who described and gave scientific names to over 2,000 new animal species, chiefly fish, reptiles, and amphibians. Boulenger was also an active botanist during the last 30 years of his life, especially in the study of roses.

The Microhylidae, commonly known as narrow-mouthed frogs, are a geographically widespread family of frogs. The 683 species are in 63 genera and 11 subfamilies, which is the largest number of genera of any frog family.

Tetraodon is a genus in the pufferfish family (Tetraodontidae) found in freshwater in Africa. It is the type genus of the family and historically included numerous other species; several Asian species were only moved to the genera Dichotomyctere, Leiodon and Pao in 2013.

Leptodactylus is a genus of leptodactylid frogs. It includes the species commonly called ditch frogs or white-lipped frogs. It is very similar to Physalaemus, a close relative, and indeed the recently described Leptodactylus lauramiriamae is in some aspects intermediate between them. The name means ‘slender finger’, from leptos (‘thin, delicate’) and the Greek daktylos.

Mantidactylus is a frog genus in the mantellid subfamily Mantellinae. This genus is restricted to Madagascar. The genus is divided into several subgenera that form monophyletic genetic clusters and are ecologically similar.

Philautus is a genus of shrub frogs in the family Rhacophoridae from Asia. Some species in this genus are now considered extinct by IUCN, while others are widespread and abundant. The taxonomy of the group is unclear, with many poorly described species.

Rhacophorus is a genus of frogs in the shrub frog family (Rhacophoridae)and the related Hylidae make up the true tree frogs. They are found in India, Japan, Madagascar, Africa, and Southeast Asia. Over 40 species are currently recognised.
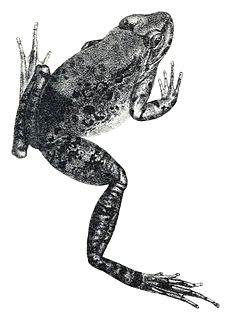
Nanorana is a genus of dicroglossid frogs. They are found in Asia, from the Himalayan region of northern Pakistan and northern India, Nepal, and western China east to montane southern China and southeast to Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, and northern Vietnam. Common names of these frogs reflect the complex taxonomic history of the genus and include Yunnan slow frogs and High Himalaya frogs.

Labeo is a genus of carps in the family Cyprinidae. They are found in freshwater habitats in the tropics and subtropics of Africa and Asia.

Xenotilapia is a genus of cichlids species endemic to Lake Tanganyika in east Africa.

Synodontis is the largest genus of mochokid catfishes. It is the biggest genus within the 10 genera and 190 different species in the family Mochokidae. Synodontis has over 131 different species within the genus. Synodontis are also known as squeakers, due to their ability to make stridulatory sounds through their pectoral fin spines when handled or disturbed. Synodontis make a sound that sounds like squeaking by rubbing their spines together. They do this when they have been frightened or when they become angry. Synodontis may also squeak when they are taken out of the water. These catfish are small- to medium-sized fish with many species exhibiting attractive spotted markings. Some species are also known for naturally swimming belly-up, earning the name upside-down catfish. Some of these species are Synodontis contractus and Synodontis nigriventris. While some of these species are known to swim upside down, another species, Synodontis multipunctatus, is a brood parasitic cuckoo catfish.

Phrynobatrachus is a genus of Sub-Saharan frogs that form the monogeneric family Phrynobatrachidae. Their common name is puddle frogs, dwarf puddle frogs, African puddle frogs, or African river frogs. The common name, puddle frog, refers to the fact that many species breed in temporary waterbodies such as puddles.

The Ceratobatrachidae are a family of frogs found in the Malay Peninsula, Borneo, the Philippines, Palau, Fiji, New Guinea, and the Admiralty, Bismarck, and Solomon Islands.

Labeobarbus is a mid-sized ray-finned fish genus in the family Cyprinidae. Its species are widely distributed throughout eastern Africa and especially southern Africa, but also in Lake Tana in Ethiopia. A common name, in particular for the southern species, is yellowfish. The scientific name refers to the fact that these large barbs remind of the fairly closely related "carps" in the genus Labeo in size and shape. As far as can be told, all Labeobarbus species are hexaploid.
The Myuchelys is a genus of turtles, the Australian saw-shelled turtles, in the family Chelidae and subfamily Chelodininae. They inhabit the headwaters and tributaries of rivers within their range and this led to the name Myuchelys, which is formed from the Aboriginal word myuna meaning clear water and the Greek chelys meaning turtle. They have a short neck and the intergular scute completely separates the gular scutes. They have no alveolar ridge separating them from the snapping turtles of the genus Elseya.

Cladistia is a clade of bony fishes that currently consists of few anguilliform (eel-shaped) remnants of an ancient diversity. Their major synapomorphies are a dorsal fin with independent rays, and a posteriorly elongated parasphenoid.



















