
New Zealand lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights are some of the most extensive in the world. The protection of LGBT rights is advanced, relative to other countries in Oceania, and among the most liberal in the world, with the country being the first in the region to legalise same-sex marriage.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in Australia rank among the highest in the world; having significantly advanced over the latter half of the 20th century and early 21st century. Opinion polls and the Australian Marriage Law Postal Survey indicate widespread popular support for same-sex marriage within the nation. Australia in 2018, in fact was the last of the Five Eyes set of countries - that consisted of namely Canada (2005), New Zealand (2013), United Kingdom (2014) and the United States (2015) to legalize same-sex marriage. A 2013 Pew Research poll found that 79% of Australians agreed that homosexuality should be accepted by society, making it the fifth-most supportive country surveyed in the world. With its long history of LGBTQ activism and annual Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras festival, Sydney has been named one of the most gay-friendly cities in the world.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in Australia since 9 December 2017. Legislation to allow it, the Marriage Amendment Act 2017, passed the Parliament of Australia on 7 December 2017 and received royal assent from Governor-General Peter Cosgrove the following day. The law came into effect on 9 December, immediately recognising overseas same-sex marriages. The first same-sex wedding under Australian law was held on 15 December 2017. The passage of the law followed a voluntary postal survey of all Australians, in which 61.6% of respondents supported legalisation of same-sex marriage.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in Malta rank among the highest in the world. Throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the rights of the LGBTQ community received more awareness and same-sex sexual activity was legalized on 29 January 1973. The prohibition was already dormant by the 1890s.
Tasmania's Relationships Act 2003 provided for registration and recognition of a type of registered partnership in two distinct categories: Significant Relationships and Caring Relationships. The same Act also amended 73 pieces of legislation to provide registered partners with nearly all of the rights offered to married couples within the state. Furthermore, since July 2009, these relationships are recognised at federal level, providing couples with almost all of the federal rights and benefits of marriage. The legislation came into effect on 1 January 2004. In September 2010, the Parliament of Tasmania approved legislation to recognize same-sex unions performed outside Tasmania as significant relationships.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in India face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ people. There are no legal restrictions against gay sex or gay expression within India. Same-sex couples have some limited cohabitation rights, colloquially known as live-in relationships. However, India does not currently provide for common law marriages, same-sex marriage, civil unions, guardianship or issue partnership certificates.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Scotland are generally in line with the rest of the United Kingdom, which have evolved extensively over time and are now regarded as some of the most progressive in Europe. In both 2015 and 2016, Scotland was recognised as the "best country in Europe for LGBTI legal equality".

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in Queensland have advanced significantly from the late 20th century onwards, in line with progress on LGBTQ rights in Australia nationally. 2019 polling on gay rights consistently showed that even in regional areas, Queensland is no more conservative about the subject than any other states.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people in the Australian state of New South Wales have most of the same rights and responsibilities as non-LGBTQ people.
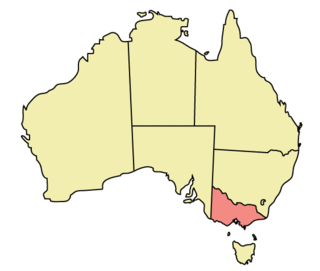
The Australian state of Victoria is regarded as one of the country's most progressive jurisdictions with respect to the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people. Victoria is the only state in Australia, that has implemented a LGBTIQA+ Commissioner.
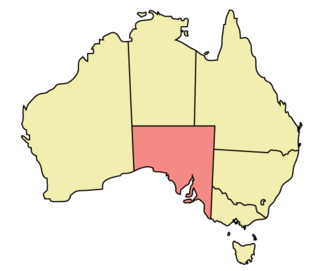
The rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Australian state of South Australia are advanced and well-established. South Australia has had a chequered history with respect to the rights of LGBT people. Initially, the state was a national pioneer of LGBT rights in Australia, being the first in the country to decriminalise homosexuality and to introduce a non-discriminatory age of consent for all sexual activity. Subsequently, the state fell behind other Australian jurisdictions in areas including relationship recognition and parenting, with the most recent law reforms regarding the recognition of same-sex relationships, LGBT adoption and strengthened anti-discrimination laws passing in 2016 and going into effect in 2017.
Australia is one of the most LGBTQ-friendly countries in the world. In a 2013 Pew Research poll, 79% of Australians agreed that homosexuality should be accepted by society, making it the fifth most supportive country in the survey behind Spain (88%), Germany (87%), and Canada and the Czech Republic. With a long history of LGBTQ rights activism and an annual three-week-long Mardi Gras festival, Sydney is considered one of the most gay-friendly cities in the world.

This article details the history of the LGBTQ rights movement in Australia, from the colonial era to the present day.
Law in Australia with regard to children is often based on what is considered to be in the best interest of the child. The traditional and often used assumption is that children need both a mother and a father, which plays an important role in divorce and custodial proceedings, and has carried over into adoption and fertility procedures. As of April 2018 all Australian states and territories allow adoption by same-sex couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Australian state of Tasmania have the same legal rights as non-LGBTQ people. Tasmania has a transformative history with respect to the rights of LGBTQ people. Initially dubbed "Bigots' Island" by international media due to intense social and political hostility to LGBTQ rights up until the late 1990s, the state has subsequently been recognised for LGBTQ law reforms that have been described by activists such as Rodney Croome as among the most extensive and noteworthy in the world. Tasmania's criminal penalties for homosexual activity were the harshest in the Western world when they were repealed in 1997. It was the last Australian jurisdiction to decriminalise homosexuality after a United Nations Human Rights Committee ruling, the passage of federal sexual privacy legislation and a High Court challenge to the state's anti-homosexuality laws. Following decriminalisation, social and political attitudes in the state rapidly shifted in favour of LGBTQ rights ahead of national trends with strong anti-LGBTQ discrimination laws passed in 1999, and the first state relationship registration scheme to include same-sex couples introduced in 2003. In 2019, Tasmania passed and implemented the world's most progressive gender-optional birth certificate laws. In July 2023, the Tasmanian government officially included and also added "asexual or asexuality".
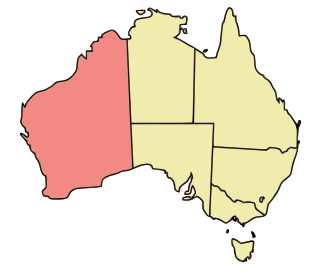
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBTQ) rights in Western Australia have seen significant progress since the beginning of the 21st century, with male sex acts legal since 1990 and the state parliament passing comprehensive law reforms in 2002. The state decriminalised male homosexual acts in 1990 and was the first to grant full adoption rights to LGBT couples in 2002.
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT) is one of Australia's leading jurisdictions with respect to the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people. The ACT has made a number of reforms to territory law designed to prevent discrimination of LGBTQ people; it was the only state or territory jurisdiction in Australia to pass a law for same-sex marriage, which was later overturned by the High Court of Australia. The Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, Queensland and both South Australia and New South Wales representing a population of 85% on Australia – explicitly ban conversion therapy practices within their jurisdictions by recent legislation enacted. The ACT's laws also apply to the smaller Jervis Bay Territory.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) rights in the British Crown dependency of Jersey have evolved significantly since the early 1990s. Same-sex sexual activity was decriminalised in 1990. Since then, LGBTQ people have been given many more rights equal to that of heterosexuals, such as an equal age of consent (2006), the right to change legal gender for transgender people (2010), the right to enter into civil partnerships (2012), the right to adopt children (2012) and very broad anti-discrimination and legal protections on the basis of "sexual orientation, gender reassignment and intersex status" (2015). Jersey is the only British territory that explicitly includes "intersex status" within anti-discrimination laws. Same-sex marriage has been legal in Jersey since 1 July 2018.
This is a list of notable events in LGBT rights that took place in the 2010s.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 2020.














