
Escherichia coli ( ESH-ə-RIK-ee-ə KOH-lye) is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes such as EPEC, and ETEC are pathogenic and can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut and are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of E. coli benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between E. coli and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship — where both the humans and the E. coli are benefitting each other. E. coli is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh fecal matter under aerobic conditions for three days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.

Bacteriocins are proteinaceous or peptidic toxins produced by bacteria to inhibit the growth of similar or closely related bacterial strain(s). They are similar to yeast and paramecium killing factors, and are structurally, functionally, and ecologically diverse. Applications of bacteriocins are being tested to assess their application as narrow-spectrum antibiotics.

Lactobacillus is a genus of gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus Lactobacillus comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera.

Lactobacillus acidophilus is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive, homofermentative, anaerobic microbe first isolated from infant feces in the year 1900. The species is commonly found in humans, specifically the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity as well as some speciality fermented foods such as fermented milk or yogurt, though it is not the most common species for this. The species most readily grows at low pH levels, and has an optimum growth temperature of 37 °C. Certain strains of L. acidophilus show strong probiotic effects, and are commercially used in dairy production. The genome of L. acidophilus has been sequenced.
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum is a widespread member of the genus Lactiplantibacillus and commonly found in many fermented food products as well as anaerobic plant matter. L. plantarum was first isolated from saliva. Based on its ability to temporarily persist in plants, the insect intestine and in the intestinal tract of vertebrate animals, it was designated as a nomadic organism. L. plantarum is Gram positive, bacilli shaped bacterium. L. plantarum cells are rods with rounded ends, straight, generally 0.9–1.2 μm wide and 3–8 μm long, occurring singly, in pairs or in short chains. L. plantarum has one of the largest genomes known among the lactic acid bacteria and is a very flexible and versatile species. It is estimated to grow between pH 3.4 and 8.8. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum can grow in the temperature range 12 °C to 40 °C. The viable counts of the "L. plantarum" stored at refrigerated condition (4 °C) remained high, while a considerable reduction in the counts was observed stored at room temperature.
Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis is a heterofermentative species of lactic acid bacteria which, through the production mainly of lactic and acetic acids, helps give sourdough bread its characteristic taste. It is named after San Francisco, where sourdough was found to contain the variety, though it is dominant in Type I sourdoughs globally. In fact, F. sanfranciscensis has been used in sourdough breads for thousands of years, and is used in 3 million tons of sourdough goods yearly. For commercial use, specific strains of F sanfranciscensis are grown on defined media, freeze-dried, and shipped to bakeries worldwide.

Lacticaseibacillus casei is an organism that belongs to the largest genus in the family Lactobacillaceae, a lactic acid bacteria (LAB), that was previously classified as Lactobacillus casei. This bacteria has been identified as facultatively anaerobic or microaerophilic, acid-tolerant, non-spore-forming bacteria.

Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus is a bacterium that originally was considered to be a subspecies of L. casei, but genetic research found it to be a separate species in the L. casei clade, which also includes L. paracasei and L. zeae. It is a short Gram-positive homofermentative facultative anaerobic non-spore-forming rod that often appears in chains. Some strains of L. rhamnosus bacteria are being used as probiotics, and are particularly useful in treating infections of the female urogenital tract, most particularly very difficult to treat cases of bacterial vaginosis. The species Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and Limosilactobacillus reuteri are commonly found in the healthy female genito-urinary tract and are helpful to regain control of dysbiotic bacterial overgrowth during an active infection. L. rhamnosus sometimes is used in dairy products such as fermented milk and as non-starter-lactic acid bacterium (NSLAB) in long-ripened cheese. While frequently considered a beneficial organism, L. rhamnosus may not be as beneficial to certain subsets of the population; in rare circumstances, especially those primarily involving weakened immune system or infants, it may cause endocarditis. Despite the rare infections caused by L. rhamnosus, the species is included in the list of bacterial species with qualified presumed safety (QPS) status of the European Food Safety Agency.

Vaginal flora, vaginal microbiota or vaginal microbiome are the microorganisms that colonize the vagina. They were discovered by the German gynecologist Albert Döderlein in 1892 and are part of the overall human flora. The amount and type of bacteria present have significant implications for an individual's overall health. The primary colonizing bacteria of a healthy individual are of the genus Lactobacillus, such as L. crispatus, and the lactic acid they produce is thought to protect against infection by pathogenic species.

Latilactobacillus sakei is the type species of the genus Latilactobacillus that was previously classified in the genus Lactobacillus. It is homofermentative; hexoses are metabolized via glycolysis to lactic acid as main metabolite; pentoses are fermented via the Phosphoketolase pathway to lactic and acetic acids.
Lactobacillus gasseri is a species in the genus Lactobacillus identified in 1980 by François Gasser and his associates.
Limosilactobacillus mucosae is a rod shaped species of lactic acid bacteria first isolated from pig intestines. It has mucus-binding activity. The species is an obligate anaerobe, catalase-negative, doesn't form spores and is non-motile. Its type strain is S32T, and has been found to be most closely related to Limosilactobacillus reuteri.
Lactobacillus gallinarum is a species in the genus Lactobacillus. Its type strain is ATCC 33199.
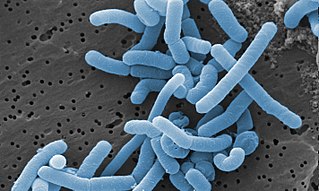
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei (commonly abbreviated as Lc. paracasei) is a gram-positive, homofermentative species of lactic acid bacteria that are commonly used in dairy product fermentation and as probiotic cultures. Lc. paracasei is a bacterium that operates by commensalism. It is commonly found in many human habitats such as human intestinal tracts and mouths as well as sewages, silages, and previously mentioned dairy products. The name includes morphology, a rod-shaped bacterium with a width of 2.0 to 4.0μm and length of 0.8 to 1.0μm.
Lactobacillus crispatus is a common, rod-shaped species of genus Lactobacillus and is a lactic acid producing bacterial species located in both the vagina, through vaginal discharge, and the vertebrate gastrointestinal tract. This species commonly found in vaginal microbiome and is thought to be beneficial to health.

Lactocillin is a thiopeptide antibiotic which is encoded for and produced by biosynthetic genes clusters in the bacteria Lactobacillus gasseri. Lactocillin was discovered and purified in 2014. Lactobacillus gasseri is one of the four Lactobacillus bacteria found to be most common in the human vaginal microbiome. Due to increasing levels of pathogenic resistance to known antibiotics, novel antibiotics are increasingly valuable. Lactocillin could function as a new antibiotic that could help people fight off infections that are resistant to many other antibiotics.
Lactobacillus jensenii is a lactic acid bacteria species in the genus Lactobacillus.

Lactobacillus vaccines are used in the therapy and prophylaxis of non-specific bacterial vaginitis and trichomoniasis. The vaccines consist of specific inactivated strains of Lactobacilli, called "aberrant" strains in the relevant literature dating from the 1980s. These strains were isolated from the vaginal secretions of patients with acute colpitis. The lactobacilli in question are polymorphic, often shortened or coccoid in shape and do not produce an acidic, anti-pathogenic vaginal environment. A colonization with aberrant lactobacilli has been associated with an increased susceptibility to vaginal infections and a high rate of relapse following antimicrobial treatment. Intramuscular administration of inactivated aberrant lactobacilli provokes a humoral immune response. The production of specific antibodies both in serum and in the vaginal secretion has been demonstrated. As a result of the immune stimulation, the abnormal lactobacilli are inhibited, the population of normal, rod-shaped lactobacilli can grow and exert its defense functions against pathogenic microorganisms.
Limosilactobacillus vaginalis is a lactic acid bacterium that is a normal, but infrequent part of the vaginal microbiome.
LACTIN-V, also known as CTV-05 or as Lactobacillus crispatus CTV-05, is a live biopharmaceutical medication containing a strain of Lactobacillus crispatus (L. crispatus) which is under development for the treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and bacterial vaginosis (BV). It is administered intravaginally and is described as the first vaginal microbiome (VMB)-based live biotherapeutic product (LBP). Depletion of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-producing Lactobacillus strains such as Lactobacillus crispatus in the vagina has been strongly associated with BV and UTIs. Most commercially available probiotic Lactobacillus strains are not vaginal strains and do not appear to improve vaginal or urinary health outcomes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)'s Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines (2021) noted that intravaginal LACTIN-V produced a considerably lower recurrence of BV following initial antibiotic treatment with metronidazole in a randomized controlled trial. However, the guidelines also noted that LACTIN-V is not yet Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved or commercially available. As of December 2021, LACTIN-V is in phase 2/3 clinical trials for the treatment of UTIs and is in phase 2 trials for the treatment of BV. It was originated by GyneLogix and is under development by Osel Inc., the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and other organizations.









