In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands. Plains are one of the major landforms on earth, being present on all continents and covering more than one-third of the world's land area. Plains in many areas are important for agriculture. There are various types of plains and biomes on them.

Russia is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,125,191 km2 (6,612,073 sq mi), and encompassing more than one-eighth of Earth's inhabited land area. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations.
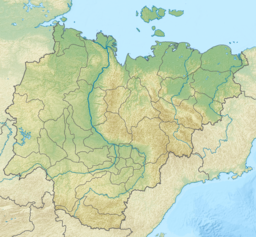
Siberia is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the centuries-long conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in the late 16th century and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over 13.1 million square kilometres (5,100,000 sq mi), but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area.

Lake Baikal is the deepest rift lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Republic of Buryatia to the southeast.

The Yenisey is the fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean.

The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over 9,289 kilometers, it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the east.

Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siberia and the third-most populous city in Russia after Moscow and Saint Petersburg. It is also the most populous city in the Asian part of Russia. Novosibirsk is located in southwestern Siberia, on the banks of the Ob River.

The Russian Far East is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast.

The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east.

The Siberian tiger or Amur tiger is a population of the tiger subspecies Panthera tigris tigris native to the Russian Far East, Northeast China and possibly North Korea. It once ranged throughout the Korean Peninsula, but currently inhabits mainly the Sikhote-Alin mountain region in southwest Primorye Province in the Russian Far East. In 2005, there were 331–393 adult and subadult Siberian tigers in this region, with a breeding adult population of about 250 individuals. The population had been stable for more than a decade because of intensive conservation efforts, but partial surveys conducted after 2005 indicate that the Russian tiger population was declining. An initial census held in 2015 indicated that the Siberian tiger population had increased to 480–540 individuals in the Russian Far East, including 100 cubs. This was followed up by a more detailed census which revealed there was a total population of 562 wild Siberian tigers in Russia. As of 2014, about 35 individuals were estimated to range in the international border area between Russia and China.

The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east. This sea borders on the Laptev Sea to the west and the Chukchi Sea to the east.
The Siberian High is a massive collection of cold dry air that accumulates in the northeastern part of Eurasia from September until April. It is usually centered on Lake Baikal. It reaches its greatest size and strength in the winter when the air temperature near the center of the high-pressure area is often lower than −40 °C (−40 °F). The atmospheric pressure is often above 1,040 millibars (31 inHg). The Siberian High is the strongest semi-permanent high in the northern hemisphere and is responsible for both the lowest temperature in the Northern Hemisphere outside Greenland, of −67.8 °C (−90.0 °F) on 15 January 1885 at Verkhoyansk, and the highest pressure, 1083.8 mbar at Agata, Krasnoyarsk Krai, on 31 December 1968, ever recorded. The Siberian High is responsible both for severe winter cold and attendant dry conditions with little snow and few or no glaciers across Asian part of Russia, Mongolia, and China. During the summer, the Siberian High is largely replaced by the Asiatic low.

The Siberian musk deer is a musk deer found in the mountain forests of Northeast Asia. It is most common in the taiga of southern Siberia, but is also found in parts of Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Manchuria and the Korean peninsula.
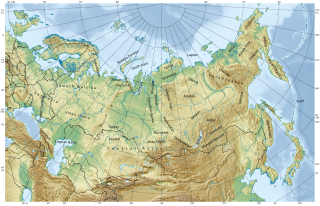
The geology of Russia, the world's largest country, which extends over much of northern Eurasia, consists of several stable cratons and sedimentary platforms bounded by orogenic (mountain) belts.

City of Kollam or Quilon is known as Prince of Arabian Sea, situated on the banks of Arabian Sea and Ashtamudi Lake. A major portion of Kollam Municipal Corporation area is occupied by Ashtamudi Lake. It is the most visited backwater and lake of Kerala, with a unique wetland ecosystem, a palm-shaped large water body, next only to the Vembanad estuary ecosystem of the state. Ashtamudi means 'eight coned'(Ashta = 'eight'; mudi = 'coned') in the local language of Malayalam. This name is indicative of the lake's topography: a lake with multiple branches. The lake is also called the gateway to the backwaters of Kerala. This lake is extremely famous for House Boat and Backwater Resorts.

The Siberian Tiger Introduction Project involves reestablishing populations of the Siberian tiger, also known as the Amur tiger, in their former range and also expanding their range by introducing them as replacements of their genetically similar relative, the extinct Caspian tiger, which inhabited Central and Western Asia. Currently, the Siberian tiger inhabits the cold mountains of the Russian Far East and northern China.

Pribaikalsky National Park covers the southwest coast of Lake Baikal in southeastern Siberia. The coastal strip includes the lake-facing slopes of the Primorsky Range to the west, as well as offshore islands such as Olkhon Island to the east. It is about 50 km southeast of the city of Irkutsk, Irkutsk Oblast. The park is managed with three other nature reserves, and is a major component of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Lake Baikal". The Angara River, which is the outflow of Lake Baikal west into the Yenisei River basin, runs through the park. The park has very high levels of biodiversity and endemic species.

Taymyr Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' located in the northern lowlands of Siberia, on the Taimyr Peninsula, and on the coast of the Laptev Sea of the Arctic Ocean. The reserve includes the most northern forest of Dahurian larch in the world, and also the most northern mainland mountain range in the world. The protected area was established to protect the breeding grounds of the Red-breasted goose as well as the summer residences of wild reindeer and the biodiversity of the Lake Taymyr. The reserve is situated about 120 km east of the town of Norilsk, and 3,000 km northeast of Moscow, in the Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District of Krasnoyarsk Krai. In 1995, the site was designated a UNESCO MAB Reserve. The reserve was formally established in 1979, and covers an area of 1,781,928 ha (6,880.06 sq mi).
The 8th Siberian Rifle Division was an infantry unit of the Imperial Russian Army. The division was formed in 1904 from a brigade, fighting in the Russo-Japanese War and World War I.