
Synodontis granulosus is a species of upside-down catfish endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, Zambia, and Tanzania, where it is only known from Lake Tanganyika. It was first described by Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1900, from specimens collected at multiple points along the shore of Lake Tanganyika. The species name comes from the Latin word "granulum", meaning of grain, and refers to the granular papillae present on the skin of the fish's body.

Synodontis budgetti, known as Budgett's synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish native to Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Côte d'Ivoire, Mali, Niger, and Nigeria where it occurs in Lake Nokoue and the Niger. It was first described by Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1911, from specimens collected in Lokoja, Nigeria. The species name budgetti comes from name of the collector of the original specimen, J.S. Budgett.

Synodontis caudalis, known as the filament tailed synodontis, or the whiptail synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was first described by Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, from specimens collected in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The species name caudalis comes from the Latin word cauda, meaning tail, and refers to the elongated filaments in the caudal fin of the species.

Synodontis caudovittatus, known as the white-finned synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Nile basin of Ethiopia, South Sudan, and Sudan. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1901, from specimens collected in the White Nile, at the mouth of Lake No in South Sudan. The species name caudovittatus comes from the Latin word cauda, meaning "tail", and the Latin word vitta, meaning "stripe" and refers to the coloration of the tailfin.

Synodontis clarias, known as the red tailed synodontis, or the mandi, is a species of upside-down catfish that occurs widely in the waters of northern Africa. It was first described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 as Silurus clarias. The original specimens were obtained in Egypt, near Cairo. The meaning of the species name clarias is not certain, but may possibly have been used to mean "bright" or "clear".

Synodontis filamentosus, known as the longfin synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the basins of the Nile, Volta and Niger Rivers as well as the Chad Basin. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1901, from specimens obtained near the mouth of Lake No, on the White Nile in Sudan. The species name filamentosus comes from the elongated rays of the dorsal and caudal fins.

Synodontis frontosus, known as the Sudan squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is widely distributed throughout northern and central Africa. It has been reported in Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, Sudan, and Uganda. It was first described by French zoologist Léon Vaillant in 1895, from specimens collected in the White Nile in Sudan. The species name frontosus is Latin, and means "broad head".

Synodontis geledensis, known as the Geledi squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia where it can be found in the Lorian Swamp, the Shebelle and Ewaso Ng'iro rivers. It was first described by German zoologist Albert Günther in 1896, from specimens obtained near Geledi, on the Shebeli River in east Africa. The species name geledensis comes from Geledi, Somalia, the location where the first specimens were first found.

Synodontis longirostris, known as the eyespot synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it occurs in the Congo Basin. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1902, from specimens obtained in the Ubangi River at Banzyville. The species name longirostris comes from the Latin word longus, meaning "long", and the Latin word rostrum, meaning snout, referring to the long snout on this species.

Synodontis nigromaculatus, known as the spotted squeaker, the blackspotted squeaker, or the speckled squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is found widely in southern Africa. It has been identified in Angola, Botswana, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1905, from specimens collected in Lake Bangweulu in Zambia.

Synodontis obesus, known as the Coas synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the coastal drainages of Cameroon, Ghana, Nigeria and Togo. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1898. The species name obesus is derived from the Latin word obesus, meaning "fat".
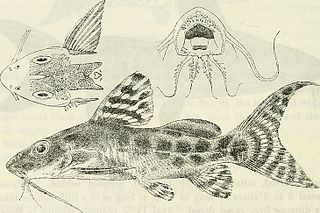
Synodontis ornatipinnis, known as the barfin synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Congo Basin of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, from specimens collected in Mbandaka, on the Congo River in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The species name ornatipinnis means "ornate fins".

Synodontis resupinatus is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Niger basin and the Bénoué River of Cameroon, Mali, and Nigeria. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1904, from specimens obtained near Lokoja, Nigeria.

Synodontis robbianus, known as the russet synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to Nigeria where it is found in the Cross and lower Niger Rivers. It was first described by John Alexander Smith in 1875, from specimens collected in the Calabar River, Nigeria. The species name robbianus is named after Rev. Alexander Robb, a Scottish missionary, who collected the original species samples.

Synodontis serratus, known as the shield-head squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Nile basin of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia and Sudan. It was first described by German naturalist and explorer Eduard Rüppell in 1829, from specimens obtained near Cairo, Egypt. The species name serratus comes from the Latin word serra, meaning "saw", which refers to the serrated pectoral spines of the species.

Synodontis smiti, known as the longtail Synodontis, or Smit's Synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it is found in the middle and upper Congo Basin. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1902, from specimens obtained in the Ubangi River at Banzyville. The species name smiti is named for Pierre Jacques Smit, who illustrated the plates in Boulenger's works.

Synodontis soloni, known as the scissortail synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it is found in the Ubangi River and the rapids just below Stanley Pool. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, from the Congo River in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The species name soloni is a patronym and in memory of Alexandre Solon, who assisted with the collection of fish.

Synodontis sorex is a species of upside-down catfish that is widely distributed in the rivers of northern Africa. It was first described by German zoologist Albert Günther in 1864, from specimens obtained in the upper Nile River, near Khartoum, Sudan. The species name sorex comes from the Latin word for shrew or shrew-mouse, the allusion was not explained. It possibly describes the pointed snout or the long, slender teeth.
Synodontis tanganyicae is a species of upside-down catfish endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, and Tanzania, where it is only known from Lake Tanganyika. It was first described by Russian-American ichthyologist Nikolai Andreyevich Borodin in 1936, from specimens collected at Kasaga, in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The species name tanganyicae comes from the habitat of the species, Lake Tanganyika.

Synodontis melanostictus is a species of upside-down catfish endemic to Lake Tanganyika and its tributaries. It has been found in Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Burundi. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1906, based upon a specimen from the Lofubu River. The species name "melanostictus" is derived from a combination of the Greek melano, meaning black, and the Greek stiktos, meaning punctured or spotted. This refers to the black spotted pattern that occurs on the body of this species.




















