Related Research Articles

The Republic of China Armed Forces are the armed forces of the Republic of China (ROC), which once ruled Mainland China and is now currently restricted to its territorial jurisdictions of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu Islands. They consist of the Army, Navy, Air Force and Military Police Force. The military is under the civilian control of the Ministry of National Defense, a cabinet-level agency overseen by the Legislative Yuan.
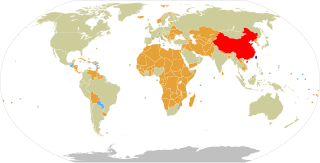
Foreign relations of the Republic of China (ROC), more commonly known as Taiwan, are accomplished by efforts of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China, a cabinet-level ministry of the Government of the Republic of China. As of January 2024, the ROC has formal diplomatic relations with 11 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs the Vatican City State. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories (Guam, Hong Kong, and Macau), and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates. In 2021, the Government of the Republic of China had the 33rd largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.

The Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO), also known as Taipei Economic and Cultural Office (TECO), Taipei Representative Office (TRO) or Taipei Mission, is an alternative diplomatic institution serving as a de facto embassy or a consulate of the Republic of China to exercise the foreign affairs and consular services in specific countries which have established formal diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China. The PRC denies the legitimacy of the ROC as a sovereign state and claims the ROC-controlled territories as an integral part of its territory. An exclusive mandate, namely One-China policy, requires that any country wishing to establish a diplomatic relationship with the PRC must first sever any formal relationship with the ROC. According to The Fletcher Forum of World Affairs, "non-recognition of the Taiwanese government is a prerequisite for conducting formal diplomatic relations with the PRC—in effect forcing other governments to choose between Beijing and Taipei." As a result, these countries only allow the ROC to establish representative offices instead of a fully-fledged embassy or consulate for the purpose of conducting practical bilateral relations without granting full diplomatic recognition.

Joseph Wu Jaushieh is a Taiwanese politician currently serving as the Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Taiwan (ROC) under former President Tsai Ing-wen and current President William Lai since February 26, 2018. He was formerly the Secretary-General to the President of Taiwan and the Secretary-General of the National Security Council of Taiwan. From 2007 to 2008, he was Chief Representative of Taiwan to the United States as the head of the Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in Washington, D.C., having been appointed to that position by President Chen Shui-bian to succeed his predecessor, David Lee. On February 26, 2018, he succeeded Lee as the Minister of Foreign Affairs.

The Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA) is an agency within the United States Department of Defense (DoD) which provides financial and technical assistance, transfer of defense materiel, training and services to allies, and promotes military-to-military contacts.

The Republic of China Army (ROCA), also known as the ROC Army or Chinese Army and unofficially as the Taiwanese Army, is the largest branch of the Republic of China Armed Forces. An estimated 80% of the ROC Army is located on Taiwan, while the remainder are stationed on the Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu, Dongsha and Taiping Islands.

The Republic of China Air Force is the military aviation branch of the Republic of China Armed Forces, based in Taiwan since 1947. The ROCAF was founded in 1920 by the Kuomintang. While its historical name is sometimes used especially in domestic circles, it is not used as often internationally due to the current ambiguous political status of Taiwan and to avoid confusion with the People's Liberation Army Air Force of the People's Republic of China (PRC).

The Foreign Assistance Act is a United States law governing foreign aid policy. It outlined the political and ideological principles of U.S. foreign aid, significantly overhauled and reorganized the structure of U.S. foreign assistance programs, legally distinguished military from nonmilitary aid, and created a new agency, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) to administer nonmilitary economic assistance programs. Following its enactment by Congress on September 4, 1961, President John F. Kennedy signed the Act into law on November 3, 1961, issuing Executive Order 10973 detailing the reorganization.

After the United States established diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1979 and recognized Beijing as the only legal government of China, Taiwan–United States relations became unofficial and informal following terms of the Taiwan Relations Act (TRA), which allows the United States to have relations with the Taiwanese people and their government, whose name is not specified. U.S.–Taiwan relations were further informally grounded in the Six Assurances in response to the third communiqué on the establishment of US–PRC relations. The Taiwan Travel Act, passed by the U.S. Congress on March 16, 2018, allows high-level U.S. officials to visit Taiwan and vice versa. Both sides have since signed a consular agreement formalizing their existent consular relations on September 13, 2019. The US government removed self-imposed restrictions on executive branch contacts with Taiwan on January 9, 2021.
The United StatesForeign Military Financing (FMF) program provides grants and loans to friendly foreign governments to fund the purchase of American weapons, defense equipment, services and training. The program was established through the 1976 Arms Export Control Act and is overseen by the Office of Security Assistance within the Bureau of Political-Military Affairs of the United States Department of State and executed by the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA) of the United States Department of Defense. The program's stated aims are to promote U.S. interests by "ensuring coalition partners and friendly partner governments are equipped and trained to pursue common security objectives by contributing to regional and global stability, strengthening military support for democratically-elected governments, fighting the War on Terror, and containing other transnational threats including trafficking in narcotics, weapons and persons."
Offsets are compensatory trade agreements, reciprocal trade agreements, between an exporting foreign company, or possibly a government acting as intermediary, and an importing entity. Offset agreements often involve trade in military goods and services and are alternatively called: industrial compensations, industrial cooperation, offsets, industrial and regional benefits, balances, juste retour or equilibrium, to define mechanisms more complex than counter-trade. Counter-trade can also be considered one of the many forms of defense offset, to compensate a purchasing country. The incentive for the exporter results from the conditioning of the core transaction to the acceptance of the offset obligation.
Foreign Military Sales (FMS) is a security assistance program of the United States government to facilitate the purchase of U.S. arms, defense equipment, design and construction services, and military training to foreign governments. FMS is a government-to-government program where the United States Department of Defense through the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA) acquires defense articles on behalf of the foreign governments, protecting them from contract risks in negotiating with the arms industry and providing the contract benefits and protections that apply to U.S. military acquisitions. The FMS program was established through the 1976 Arms Export Control Act (AECA) and is overseen by the United States Department of State and the United States Congress through the annual Foreign Operations Appropriations Acts and National Defense Authorization Acts.

The GBU-39/B Small Diameter Bomb (SDB) is a 250-pound (110 kg) precision-guided glide bomb that is intended to allow aircraft to carry a greater number of smaller, more accurate bombs. Most US Air Force aircraft will be able to carry a pack of four SDBs in place of a single 2,000-pound (910 kg) Mark 84 bomb. It first entered service in 2006. The Ground Launched Small Diameter Bomb (GLSDB) was later developed to enable the SDB to be launched from a variety of ground launchers and configurations.

The Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States represents the interests of Taiwan in the United States in the absence of formal diplomatic relations, functioning as a de facto embassy. Its counterpart in Taiwan is the office of the American Institute in Taiwan (AIT) in Taipei.

Stanley Kao is a Taiwanese diplomat. He was Taiwan's representative to the United States from 2016 to 2020.

Charles Wayne Hooper is a retired lieutenant general in the United States Army who held the position of director of the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA) from 2017 to 2020. DSCA administers security cooperation programs that support U.S. policy interests and objectives identified by the White House, Department of Defense, and Department of State. These objectives include developing specific partner capabilities, building alliances and partnerships, and facilitating U.S. access. DSCA integrates security cooperation activities in support of a whole-of-government approach; provides execution guidance to DoD entities that implement security cooperation programs; exercises financial and program management for the Foreign Military Sales system and many other security cooperation programs; and educates and provides for the long-term development of the security cooperation workforces.
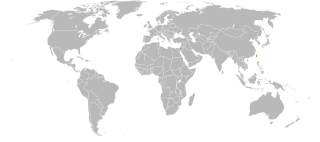
Israel–Taiwan relations describe the relations between the State of Israel and the Republic of China (Taiwan), which are not official in light of Taiwan's international status, although the two countries have economic and commercial relations, and Israel has an Economic and Cultural Office in Taipei since 1993. The unofficial relations between the two countries are mainly expressed in the fields of science, trade and industry.

The Representative Office in Taipei for the Moscow-Taipei Coordination Commission on Economic and Cultural Cooperation is the representative office of Russia in Taiwan, functioning as a de facto embassy in the absence of diplomatic relations. Its counterpart is the Representative Office in Moscow for the Taipei-Moscow Economic and Cultural Coordination Commission in Moscow.
References
- ↑ Wong, Edward (2020-09-17). "U.S. Pushes Large Arms Sale to Taiwan, Including Jet Missiles That Can Hit China". The New York Times . Retrieved 2020-10-15.
- 1 2 3 Kan, Shirley (2014-09-29). "Taiwan: Major U.S. Arms Sales Since 1990" (PDF). Congressional Research Service . Retrieved 2020-10-15.
- ↑ http://www.nvr.navy.mil/SHIPDETAILS/SHIPSDETAIL_MSO_455.HTML
- ↑ http://www.nvr.navy.mil/SHIPDETAILS/SHIPSDETAIL_MSO_488.HTML
- ↑ http://www.nvr.navy.mil/SHIPDETAILS/SHIPSDETAIL_MSO_489.HTML
- ↑ http://www.nvr.navy.mil/SHIPDETAILS/SHIPSDETAIL_MSO_492.HTML
- ↑ "61 FR 48895 pgs. 48895-48898 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 17 September 1996. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "62 FR 8932 pgs. 8932-8933 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 27 February 1997. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "62 FR 32084 pgs. 32084-32088 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 27 February 1997. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "62 FR 42516 pgs. 42516-42520 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 7 August 1997. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "62 FR 48231 pgs. 48231-48234 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 15 September 1997. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "62 FR 63104 pgs. 63104-63107 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 15 September 1997. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "62 FR 63129 pgs. 63129-63132 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 26 November 1997. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "63 FR 6537 pgs. 6537-6541 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 9 February 1998. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "63 FR 33356 pgs. 33356-33359 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 18 June 1998. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "63 FR 48705 pgs. 48705-48708 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 18 June 1998. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "63 FR 48709 pgs. 48709-48713 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 11 September 1998. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "63 FR 56915 pgs. 56915-56920 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 23 October 1998. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "64 FR 31828 pgs. 31828-31832 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 14 June 1999. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "64 FR 31833 pgs. 31833-31837 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 14 June 1999. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "64 FR 43993 pgs. 43993-43997 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 August 1999. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "64 FR 43998 pgs. 43998-44001 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 August 1999. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "65 FR 14246 pgs. 14246-14249 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. March 16, 2000. Archived from the original on October 23, 2015. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "65 FR 14250 pgs. 14250-14254 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 16 March 2000. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "65 FR 38251 pgs. 38251-38254 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 20 June 2000. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "65 FR 38255 pgs. 38255-38258 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 20 June 2000. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "65 FR 60622 pgs. 60622-60625 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 October 2000. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "65 FR 60625 pgs. 60625-60628 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 October 2000. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "65 FR 60628 pgs. 60628-60632 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 October 2000. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "65 FR 60633 pgs. 60633-60636 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 October 2000. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States – AH-64D APACHE Helicopters and Related Weapons" (PDF). Defense Security Cooperation Agency. October 3, 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 27, 2009. Retrieved December 17, 2023.
- ↑ "75 FR 5971 pgs. 5971-5994 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 5 February 2010. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "75 FR 5971 pgs. 5971-5994 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 5 February 2010. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "75 FR 5971 pgs. 5971-5994 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 5 February 2010. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "75 FR 5971 pgs. 5971-5994 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 5 February 2010. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "75 FR 5971 pgs. 5971-5994 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 5 February 2010. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "76 FR 60459 pgs. 60459-60461 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 29 September 2011. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "76 FR 60463 pgs. 60463-60467 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 29 September 2011. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "76 FR 60467 pgs. 60467-60469 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 29 September 2011. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "81 FR 7522 pgs. 7522-7524 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "81 FR 7528 pgs. 7528-7530 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "81 FR 7524 pgs. 7524-7526 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "81 FR 7513 pgs. 7513-7516 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "81 FR 7518 pgs. 7518-7520 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "81 FR 7516 pgs. 7516-7518 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "81 FR 7526 pgs. 7526-7528 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "81 FR 7520 pgs. 7520-7522 - 36(b)(1) Arms Sales to Taiwan Notification". Federal Register. 12 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "UPDATED: U.S. Plans Modest $1.83B Taiwan Arms Deal; Little Offensive Power in Proposed Package". U.S. Naval Institute. 16 December 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 16-67)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. June 29, 2017. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 16-68)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. June 29, 2017. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 16-69)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. June 29, 2017. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 16-70)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. June 29, 2017. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 16-73)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. June 29, 2017. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 16-74)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. June 29, 2017. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 16-75)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. June 29, 2017. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 18-09)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. September 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2019.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 19-11)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. April 15, 2019. Retrieved August 24, 2019.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 19-21)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. July 8, 2019. Retrieved August 24, 2019.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 19-22)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. July 8, 2019. Retrieved August 24, 2019.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 19-50)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. August 20, 2019. Retrieved August 24, 2019.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 20-07)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. May 20, 2020. Retrieved September 24, 2020.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 20-24)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. July 9, 2020. Retrieved September 24, 2020.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 20-75)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. October 22, 2020. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 20-69)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. October 22, 2020. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 20-77)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. October 22, 2020. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 20-68)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. October 26, 2020. Retrieved October 26, 2020.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 20-74)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. November 3, 2020. Retrieved November 3, 2020.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 20-87)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. December 7, 2020. Retrieved December 7, 2020.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 21-44)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. August 4, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ↑ "Taiwan to buy 18 more HIMARS from US amid Ukrainian wins". Taiwan News . August 31, 202. Retrieved January 7, 2024.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 21-66)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. February 7, 2022. Retrieved February 7, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-16)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. April 5, 2022. Retrieved April 5, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-22)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. June 8, 2022. Retrieved June 8, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-31)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. July 15, 2022. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-44)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. September 2, 2022. Retrieved September 2, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-45)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. September 2, 2022. Retrieved September 2, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-46)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. September 2, 2022. Retrieved September 2, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-55)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. December 6, 2022. Retrieved December 6, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-56)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. December 6, 2022. Retrieved December 6, 2022.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the United States (Transmittal No: 22-70)". Defense Security Cooperation Agency. December 28, 2022. Retrieved December 28, 2022.
- ↑ "TAIPEI ECONOMIC AND CULTURAL REPRESENTATIVE OFFICE IN THE UNITED STATES – F-16 MUNITIONS" . Retrieved 2023-03-01.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States (TECRO) – Blanket Order Cooperative Logistics Supply Support Arrangement (CLSSA) Foreign Military Sales Order II (FMSO II) | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2023-09-27.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States (TECRO) – 30 mm Ammunition | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2023-09-27.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States (TECRO) – F-16 Infrared Search and Track (IRST) systems | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2023-09-27.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States (TECRO) – Command, Control, Communications, and Computers (C4) Life Cycle Support | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-01-01.
- ↑ "TAIPEI ECONOMIC AND CULTURAL REPRESENTATIVE OFFICE IN THE UNITED STATES (TECRO) – TAIWAN ADVANCED TACTICAL DATA LINK SYSTEM UPGRADE PLANNING | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-06-18.
- ↑ "TAIPEI ECONOMIC AND CULTURAL REPRESENTATIVE OFFICE IN THE UNITED STATES – F-16 NON-STANDARD SPARE AND REPAIR PARTS | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-01-01.
- ↑ "TAIPEI ECONOMIC AND CULTURAL REPRESENTATIVE OFFICE IN THE UNITED STATES – F-16 STANDARD SPARE AND REPAIR PARTS | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-06-18.
- ↑ "TAIPEI ECONOMIC AND CULTURAL REPRESENTATIVE OFFICE IN THE UNITED STATES – SWITCHBLADE 300 ANTI-PERSONNEL AND ANTI-ARMOR LOITERING MISSILE SYSTEM | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-06-18.
- ↑ "TAIPEI ECONOMIC AND CULTURAL REPRESENTATIVE OFFICE IN THE UNITED STATES – ALTIUS 600M-V UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLES | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-06-18.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States – Return, Repair, and Reshipment of Spare Parts | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-09-16.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States – National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-10-25.
- ↑ "Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States – AN/TPS-77 and AN/TPS-78 Radar Turnkey Systems | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 2024-10-25.