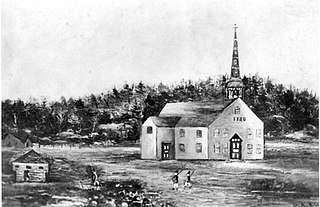Scouting in Maine dates back to the creation of the Katahdin Area Council in 1920 and has continued prominently to the present day.

Interstate 95 (I-95) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs north–south from Miami, Florida to Houlton, Maine. The highway enters Maine from the New Hampshire state line in Kittery and runs for 303 miles (488 km) to the Canada–United States border at Houlton. It is the only primary Interstate Highway in Maine. In 2004, the highway's route between Portland and Gardiner was changed so that it encompasses the entire Maine Turnpike, a toll road running from Kittery to Augusta. As an Interstate Highway, all of I-95 in Maine is included in the National Highway System, a network of roads important to the country's economy, defense, and mobility.

John Calvin Stevens was an American architect who worked in the Shingle Style, in which he was a major innovator, and the Colonial Revival style. He designed more than 1,000 buildings in the state of Maine.

The railroad history of Portland, Maine, began in 1842 with the arrival of the Portland, Saco & Portsmouth Railway (PS&P). Most of the rail activity in Portland revolved around agricultural goods bound for export and import freight from Europe. Yet Maine's largest city also enjoyed 125 years of continuous passenger rail service, from 1842 until 1967, and Amtrak began serving the city in 2001. For most of Portland's history, passenger train schedules were designed with intercity travel rather than daily commuting in mind; passenger activities were mostly confined to intercity travel from Portland to Boston, Montreal, Nova Scotia, and points west.

The First Parish Congregational Church is a historic church at 116 Main Street in Yarmouth, Maine. The congregation was established in 1730, as the ninth church founded in what is now Maine. The current Italianate meeting house was constructed in 1867–68, and is an important surviving design of Portland architect George M. Harding. The building was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1995. The present congregation is affiliated with the United Church of Christ.

The North Yarmouth and Freeport Baptist Meetinghouse, also known as the Old Baptist Meeting House, is an historic church on Hillside Street in Yarmouth, Maine. Built in 1796 and twice altered in the 19th century, it is believed to be the oldest surviving church built for a Baptist congregation in the state of Maine. It is now owned by the town and maintained by a local non-profit organization.

Harry S. Coombs (1878-1939) was an American architect practicing in Lewiston, Maine. He was the son of and successor to architect George M. Coombs.

Benjamin S. Deane (1790–1867) was an American master builder and architect in practice in Bangor, Maine, from c. 1832 to 1867.

Yarmouth is a town in Cumberland County, Maine, United States, twelve miles north of the state's largest city, Portland. When originally settled in 1636, as North Yarmouth, it was part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, and remained part of its subsequent incarnations for 213 years. In 1849, twenty-nine years after Maine's admittance to the Union as the twenty-third state, it was incorporated as the Town of Yarmouth.

The Maine Central Railroad Company main line extended from Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–US border with New Brunswick at the Saint Croix-Vanceboro Railway Bridge. It is the transportation artery linking Maine cities to the national railway network. Sections of the main line had been built by predecessor railroads consolidated as the Maine Central in 1862 and extended to the Canada–US border in 1882. Through the early 20th century, the main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a lower road through Brunswick and Augusta and a back road through Lewiston which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Westbound trains typically used the lower road with lighter grades, while eastbound trains of empty cars used the back road. This historical description does not include changes following purchase of the Maine Central Railroad by Guilford Transportation Industries in 1981 and subsequent operation as part of Pan Am Railways.

Miller & Mayo, later Miller, Mayo & Beal, was a prominent architectural firm from Portland, Maine, established in Lewiston in 1907.
Miller & Beal, Inc., was a prominent architectural firm based in Portland, Maine, established in 1929. It was the successor to Miller, Mayo & Beal. Architect Lester I. Beal led the office.
The historical buildings and structures of Yarmouth, Maine, represent a variety of building styles and usages, largely based on its past as home to almost sixty mills over a period of roughly 250 years. These mills include that of grain, lumber, pulp and cotton. Additionally, almost three hundred vessels were launched by Yarmouth's shipyards in the century between 1790 and 1890, and the homes of master shipwrights and ship captains can still be found throughout the town.

Old Baptist Cemetery is a historic cemetery in Yarmouth, Maine, United States. Dating to the late 17th century, it stands on Hillside Street, adjoining the North Yarmouth and Freeport Baptist Meetinghouse, a National Register of Historic Places property, on its southern side. It is the only burial site in the town attached to an extant church building.

Ledge Cemetery, also known as the Cemetery under the Ledge, is a historic cemetery in Yarmouth, Maine, United States. Dating to 1770, it stands on Gilman Road, around 450 feet (140 m) southwest of the older and smaller Pioneer Cemetery. Some headstones bear dates earlier than 1770, for many burials — such as that of Revd. Nicholas Loring — were removed from the older cemetery
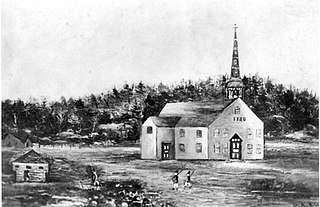
The Meetinghouse under the Ledge, also known as the Old Ledge Meetinghouse, was a church that stood in present-day Yarmouth, Maine, between 1729 and 1836.
For references related to individual interments, see articles for the particular individuals.